What Is Arrhythmia?
Our hearts have 4 chambers. The left and right atria fill first and, once full, their muscles contract. This forces the blood into the next set of chambers, which are known as the ventricles. These chambers then contract, forcing the blood out of the heart and around the body.
This means that the heart beats twice, once for each pair of chambers. How quickly the following set of beats tends to come according to whether the patient is relaxing or exercising. These beats will sometimes come too quickly or too slowly, however, in a condition known as arrhythmia. There are numerous potential causes of the condition.
1. Arrhythmia
Our hearts have a natural pacemaker. These pacemakers produce electrical signals that travel through the heart, causing the muscles of the organ to contract. These contractions cause the heart to force blood out of its chambers, which is how the organ pumps blood around our body.
These contractions usually occur at a steady pace, although they will often become faster or slower. These changes usually happen according to whether we are at rest or active, but not always. Arrhythmias are a medical condition that causes the heart to pump irregularly, too quickly, or too slowly, regardless of factors like exercise.

2. Causes
There are numerous potential causes of arrhythmias. These include stress, drug abuse, and alcohol abuse. Smokers are also more likely to develop the condition, and some medications can also cause it. Issues with the thyroid gland can also result in arrhythmias.
In some people, their arrhythmia is down to genetic causes. A high blood pressure is another potential cause, as is coronary heart disease. Diabetes will be the cause in some cases, and sleep apnea is another potential factor. The condition is also sometimes caused by scarring from previous heart attacks, while it can also be caused by current heart attacks.

3. Tachycardia
Tachycardia is a variety of arrhythmia that causes the heart to pump too quickly. The condition can occur in the atria or in the ventricles. Among the most common variety are atrial or ventricular fibrillations. These conditions typically make the heart less effective at pumping blood around the body.
The severity of the symptoms of tachycardia will vary from cases to case, and according to which type of tachycardia the patient has. In some cases, the patient will barely notice any symptoms at all. In others, the condition can have a serious negative impact on the patient’s quality of life. Arrhythmias can also be very dangerous.

4. Bradycardia
Another variety of arrhythmia is bradycardia, which means that the heart is pumping more slowly than usual. In many cases, bradycardia is simply down to the patient being particularly fit, meaning their heart will be very efficient. Another potential cause is that the electrical impulses in the heart can be blocked.
Depending on the cause, bradycardia will mean that the blood is not being pumped around the body as well as it should be. This can, in turn, mean that the body is not getting the supply of oxygen and nutrients that it needs. The symptoms of bradycardia can vary, and the condition will be dangerous in some cases.
5. Skipped Beats
It is not uncommon for us to experience what feels like a skipped beat of the heart. It happens to some people when they are surprised, stressed, or excited about something. It will also sometimes be down to medical conditions, while it can also be down to other things such as taking cocaine or drinking caffeine.
What feels like skipped beats, or a premature beat, is really an extra beat. While we can often feel these extra beats, it is not usually a serious condition. Skipped beats will sometimes trigger a longer arrhythmia, however, and they can also weaken the heart in the long term.

6. Symptoms
Many people with an arrhythmia will not have any symptoms at all. Indeed, many cases are only discovered by chance during check-ups. When symptoms do arise, they will typically include the sensation that your heart is beating slowly or quickly, or what is often described as a fluttering sensation.
Other symptoms of arrhythmia include shortness of breath and pain in the chest. Some patients will feel dizzy, and some can feel fatigued throughout the day. Anxiety is another potential symptom of the condition, and it can also cause excessive sweating. It will also cause the patient to faint in some cases.

7. Complications
In addition to the symptoms already mentioned, arrhythmia will also cause some potentially serious complications in some cases. This includes heart failure, which means that your heart becomes less effective at its job. This can often be managed, however. Another, potentially even more serious complication is a stroke.
People that have arrhythmia are also more likely to develop blood clots. These blood clots can become dislodged and then travel through the body where they can potentially become stuck and block the flow of blood to the brain. A stroke is a very serious condition and the patient should be found medical assistance straight away.
8. Risk Factors
People with certain heart conditions are more likely to develop an arrhythmia, as are people with a high blood pressure. Those with diabetes are also at a higher risk, as are people with thyroid problems. People using certain medications are also at a higher risk.
In many cases, the root underlying cause of arrhythmia is the patient’s lifestyle choices. This typically means people that do not eat a healthy diet, and those that do not get sufficient exercise. People that regularly abuse drugs and alcohol are more likely to develop the condition. Living a healthy lifestyle will reduce the chances that a person will develop an arrhythmia.

9. Diagnosis
Your doctor will probably want to perform a brief exam, and also ask you about your symptoms. They may also ask about your medical history, and about any relevant medical conditions that run in your family. A number of methods can also be used to help clarify the cause of your symptoms.
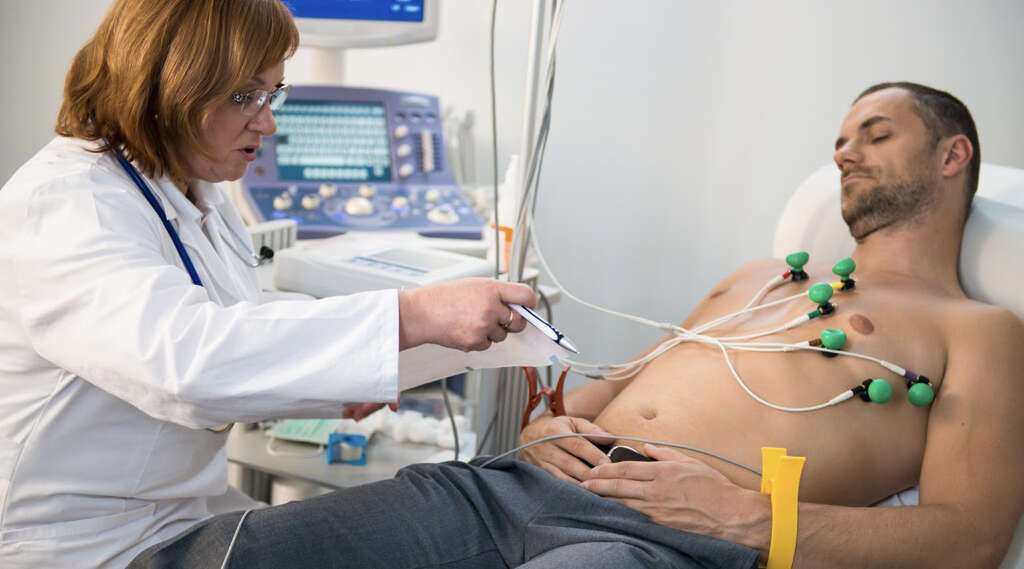
An ECG may be used to help measure the electrical activity in your heart. Different types of ECG can be used to get different readings that will help detect arrhythmias. A stress test may be used to see how your heart performs under demand, and other tests are available that will help measure the structure and the performance of your heart.
10. Treatment
Treatment for arrhythmia is often not considered to be necessary, depending on the nature and severity of the patient’s symptoms. When treatment is considered to be necessary, it will be according to the exact nature of the case. Medication is used to help manage the condition in many cases.
Cardioversion is another potential treatment, and it involves using electric shocks to help restore a natural rhythm. Some patients will also be fitted with a pacemaker, which is a device that helps to deliver a steady electrical impulse to your heart. Performing certain maneuvers may also be able to help treat arrhythmia.