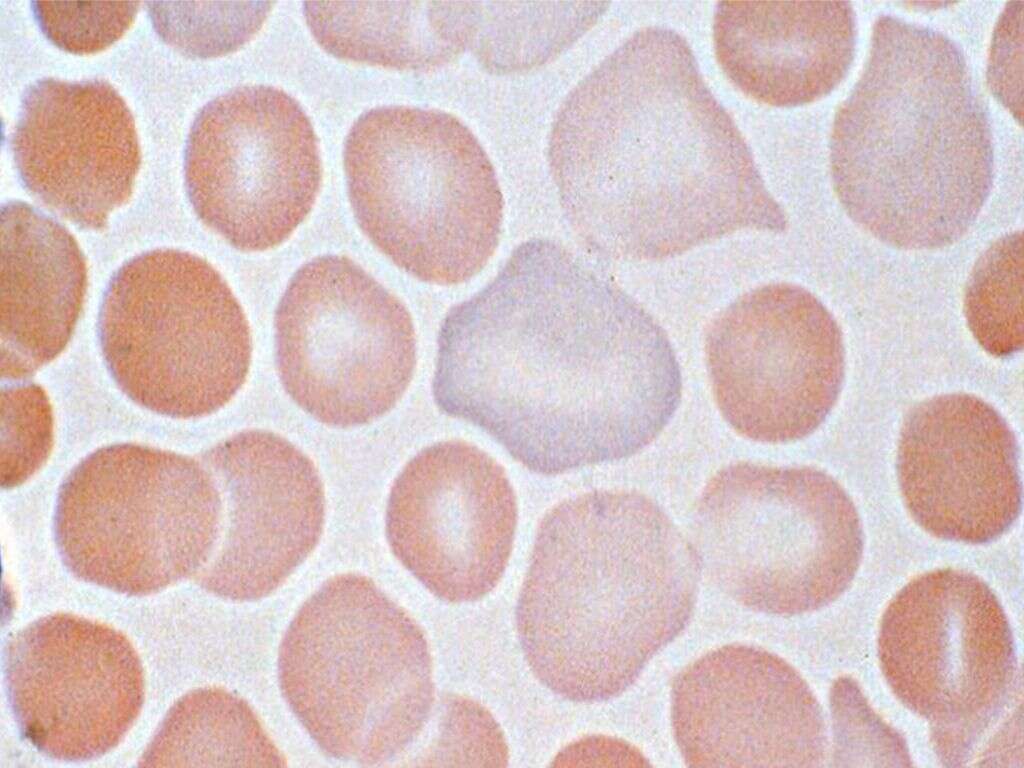
What Is Anemia?
Our blood is extremely important to us because it helps ensure that oxygen is carried to where it is needed in the body. It does this with the help of a substance known as hemoglobin, which is found in our red blood cells. Hemoglobin contains a high quantity of iron, and oxygen has a high affinity to iron, which means it will be attracted to, and will attach to it.
When we breathe in, oxygen is absorbed into our blood with help from the hemoglobin. This freshly oxygenated blood will then travel on to our hearts, where it can then be forced around the rest of the body. Anemia is a condition where the patient does not have enough red blood cells, and there are different types of the disease.
1. Iron Deficiency Anemia
Of all the different varieties of anemia, iron deficiency anemia is the most common. As the name suggests, it means the body does not have enough iron with which to make hemoglobin. There are several reasons this can occur, one of which is that the patient simply does not have enough iron in their diet.
Other potential causes include excessive blood loss, and some women will suffer from anemia during their period. Cancer, ulcers, and inflammation of the digestive system are other potential causes of anemia through loss of blood. Pregnant women are also prone, and iron supplements can help anybody to restore the number of red blood cells in their body.

2. Pernicious Anemia
While we need iron in our diets, we also need vitamin B-12 and folate in order to make enough red blood cells. This is not usually a problem because, for most people, these vitamins are plentiful in our diet. Pernicious anemia is a condition where the patient is unable to absorb vitamin B-12, thus resulting in a lack of red blood cells.
Pernicious anemia is so called because it used to be deadly. It is now easy to treat, however, with supplements. A similar condition is vitamin deficiency anemia which means the patient does not have enough Vitamin B-12 and folate because there are not enough of the vitamins in their diet.
3. Sickle Cell Anemia
This variety if anemia is one of the most dangerous. It is caused when the red blood cells take on an abnormal sickle shape, instead of their usual doughnut-like shape. This happens when there is an abnormal type of hemoglobin, which causes the red blood cells to form abnormally.
Sickle cell anemia is a type of hemolytic anemia. This means that the red blood cells will die sooner than they usually would, thus resulting in a lack of red blood cells overall. There is no known cure for sickle cell anemia, and patients can expect to live with unwelcome symptoms. Most will have a shorter than usual life-span.
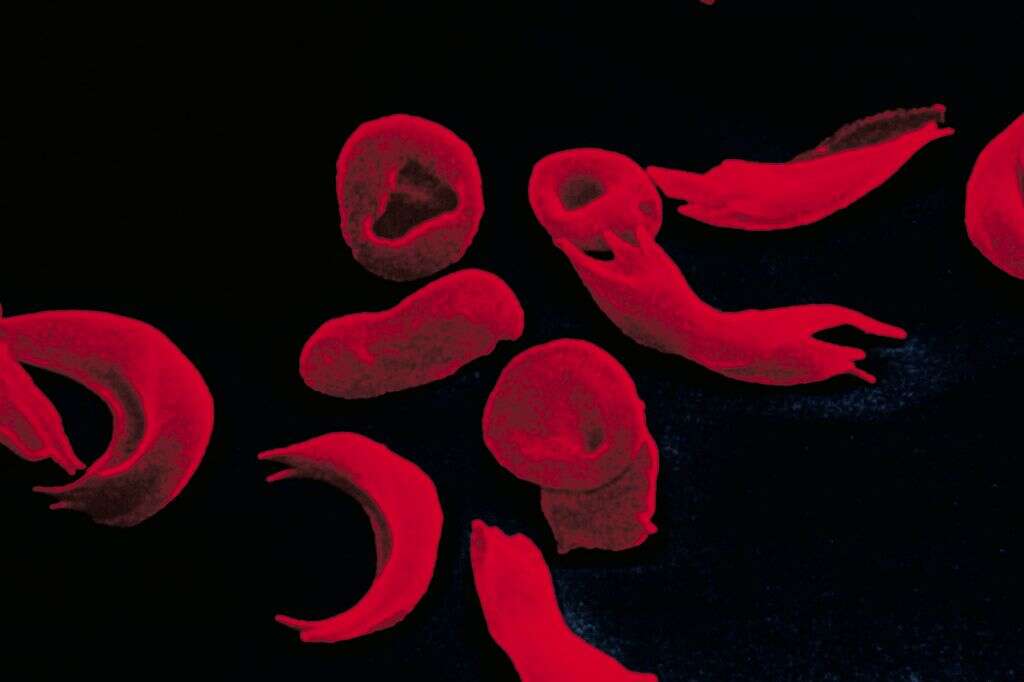
4. Hemolytic Anemia
As mentioned, sickle cell anemia is a type of hemolytic anemia. There are also other types of hemolytic anemia. The process of breaking down expired blood cells is normal and it happens in everybody. Problems only arise when the blood cells are being broken down faster than they can be produced.
Whether or not hemolytic anemia can be treated depends on the underlying cause of the condition. In many cases, the condition can be treated so the patient experiences few, if any, symptoms. Hemolytic anemia will sometimes develop at some point during the patient’s life, while it will sometimes be inherited.

5. Aplastic Anemia
Aplastic anemia is one of the more serious types of anemia, and it is also thankfully one of the least common. It happens when the body stops producing enough blood cells, so the patient’s blood cell count will begin to plummet. There are a handful of reasons why this can occur.
In some cases, autoimmune conditions are the cause, which means the patient’s own immune system is attacking red blood cell production. Some medication can also be the underlying cause, and some infections will also result in the condition. Being exposed to certain chemicals is another potential cause of aplastic anemia.
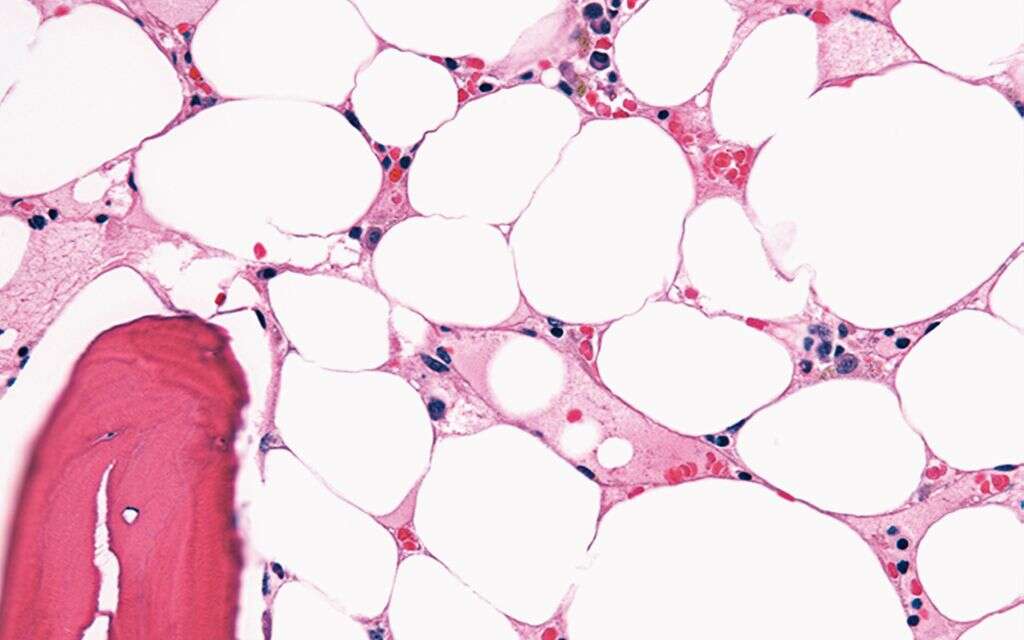
6. Anemia Of Inflammation
Other underlying health conditions will also sometimes cause anemia, in particular those that tend to cause inflammation in the body. This includes disease like Chron’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, and kidney disease.
These conditions, and some others, can cause anemia by affecting the patient’s ability to produce new red blood cells.
Some diseases of the bone marrow, including mylefibrosis and leukemia, can also cause anemia. This is because the bone marrow is responsible for the production of red blood cells. The severity of these conditions can vary, ranging from being only mild in many cases, to being potentially deadly.

7. Symptoms
The lack of oxygenated blood flowing through the body can mean that the patient’s body will have difficulty producing enough energy. This will likely cause them to feel weak and fatigued much of the time. Anemia will also likely cause the patient’s skin to become yellow and paler in color.
A lack of oxygen in the blood will also likely mean the patient is short of breath, and they will sometimes feel lightheaded. Headaches are also a potential symptom, as is a pain in the chest, and an irregular heartbeat. Anemia will also sometimes cause the patient to sometimes have cold hands and feet.

8. Complications
Anemia doesn’t always cause serious symptoms and many patients will live relatively normal lives. Some patients will develop severe complications from the condition, however. One of these is that the patient can develop severe fatigue to the point where they find it difficult to work and perform other important tasks.
Anemia will also sometimes lead to heart failure, or an enlarged heart, both of which have the potential to be serious. Women who are pregnant need to be careful because anemia had the potential to cause severe complications with the pregnancy. In the more severe cases, anemia can even be fatal.

9. Risk Factors
Anemia is a relatively common condition, and nobody is completely safe from it. However, there are some people that are more likely to develop it than others are. Perhaps the most at risk group are people that don’t have a balanced diet, along with people that have digestive system disorders that can prevent them from absorbing the nutrients they need.
Pregnant women are also at risk, as are women that have not yet been through the menopause. Some infections will make people more prone, as will some long term inflammatory diseases. Also at risk are people that have lost a lot of blood. People over the age of 65 are also in a higher risk category.

10. Treatment
In many cases, anemia can be treated simply by having the patient consume enough iron. This can mean changes in their diet, while it will also sometimes mean giving them dietary iron supplements. Anemia that is caused by vitamin deficiencies can also usually be treated in the same way.
For others, treatment of underlying causes may help to cure anemia. In the more severe cases, blood transfusions may be considered to help save the patient’s life. Blood marrow transplants will also sometimes be performed. The patient will also sometimes be provided with medication that will help them to feel comfortable.