What Is an Autoimmune Disease?
If it was not for our immune system then we would likely fall ill often. Indeed, it would probably not be long before a pathogen is able to kill us outright. Thankfully, however, we do have an immune system that helps to keep us safe, but it will also sometimes causes problems for us.
Autoimmune diseases are conditions where the patient’s body is being attacked by their immune system. This happens because, for unknown reasons, the immune system recognizes the body’s cells as unwelcome intruders. There are more than 80 different type of autoimmune disease, and the symptoms will vary from type to type.

1. Causes
Autoimmune diseases are not at all well understood. However, there are some groups of people who are more likely to have an autoimmune disease, giving some insight as to what the causes might be. For example, women are more likely to develop autoimmune disease than men, as are people from certain ethnic groups.
People are also more likely to develop certain autoimmune conditions if there is a history of them in their family. It is also thought that modern medicine might contribute by making the immune system more reactive to certain stimuli. Another potential factor is how the patient takes care of themselves in general, including what they eat.

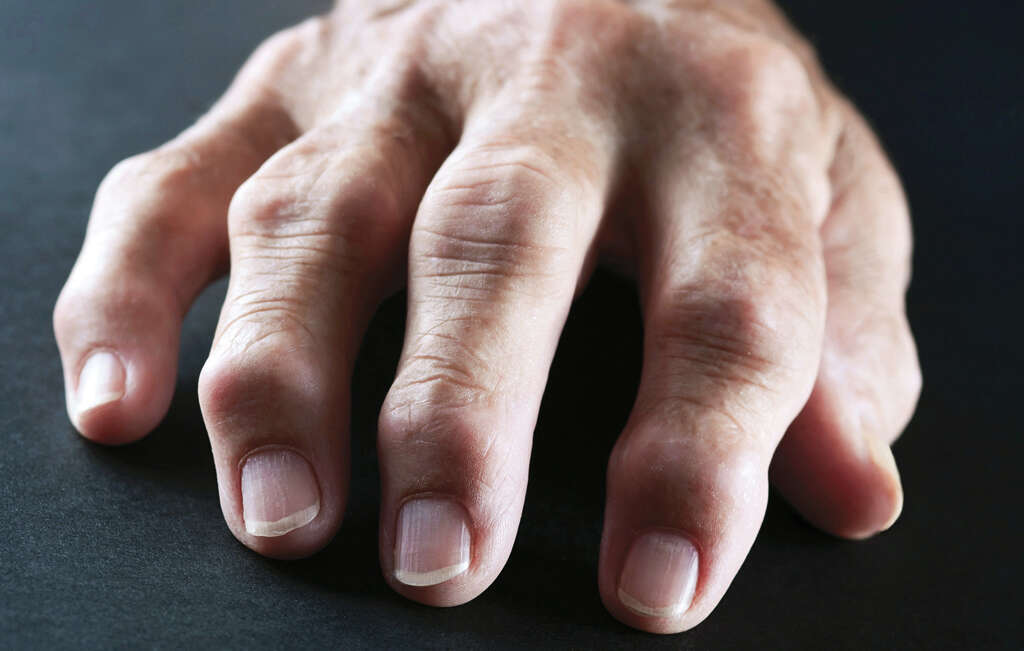
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Arthritis is a fairly common condition that tends to affect people when they get older. There are different types of condition and perhaps the most common is osteoarthritis. This happens when the patient’s joints become worn down over time. Another type of arthritis is rheumatoid arthritis, and this is a type of autoimmune condition.
Rheumatoid arthritis happens when the immune system attacks the patient’s joints. This results in symptoms like inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the joints. Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is not dependent on the joint being worn over time. For this reason, it is more likely to affect younger people as well as older people.
3. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
In type 1 diabetes mellitus, the immune system is attacking the cells in the pancreas that are responsible for producing insulin. Without sufficient insulin, the patient will not be able to regulate their blood sugar levels, thus resulting in diabetes. The patient will need to manage their condition carefully for the rest of their lives.
Another type of autoimmune disease that can affect the blood is pernicious anemia. This causes a lack of a substance known as intrinsic factor, and this means the patient is unable to absorb vitamin B12. This, in turn, means the patient’s blood vessels develop abnormally.

4. Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is a potentially devastating disease that can affect peoples’ ability to care for themselves. It attacks a protective coating known as the myelin sheath, which usually helps protect our nerve cells. If this sheath is damaged then messages would not be able to pass through the nerves as well as they otherwise would do.
This, in turn, means that the patient will experience difficulties controlling their muscles. Symptoms that occur include a loss of balance, weakness, numbness, and difficulty walking. The disease is not usually fatal, but it can mean that the patient becomes completely dependent on other people.
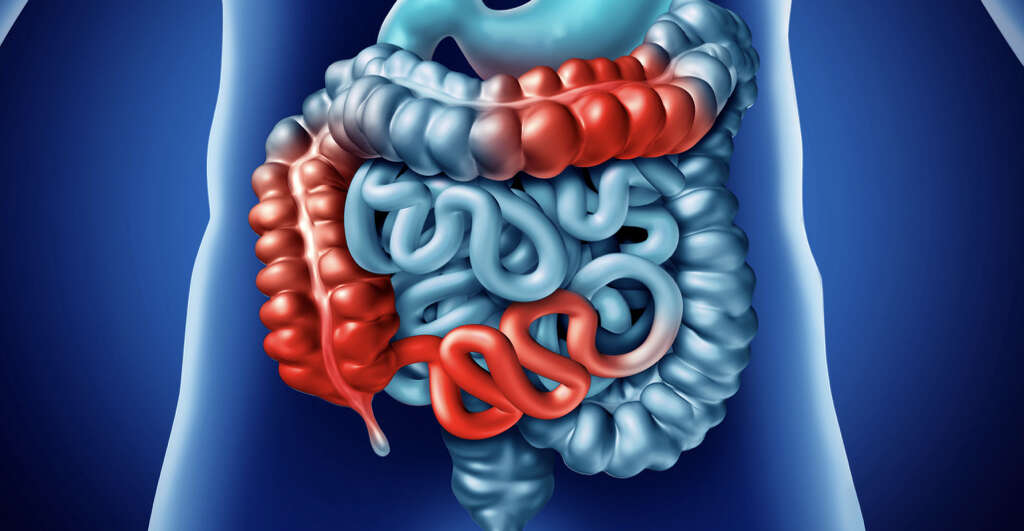
5. Crohn’s Disease
It is common to get an upset stomach after eating the wrong type of food. For people with Crohn’s disease, however, there is a much wider range of foods that can cause them discomfort. Chron’s disease is another type of autoimmune disease, and it attacks the digestive system causing some very unwelcome symptoms for the patient.
Another immune condition that affects the digestive system is celiac disease. Celiac disease is triggered by a type of protein known as gluten. When the patient ingests gluten, which is found in some types of grain, it causes the immune system to attack the digestive system.
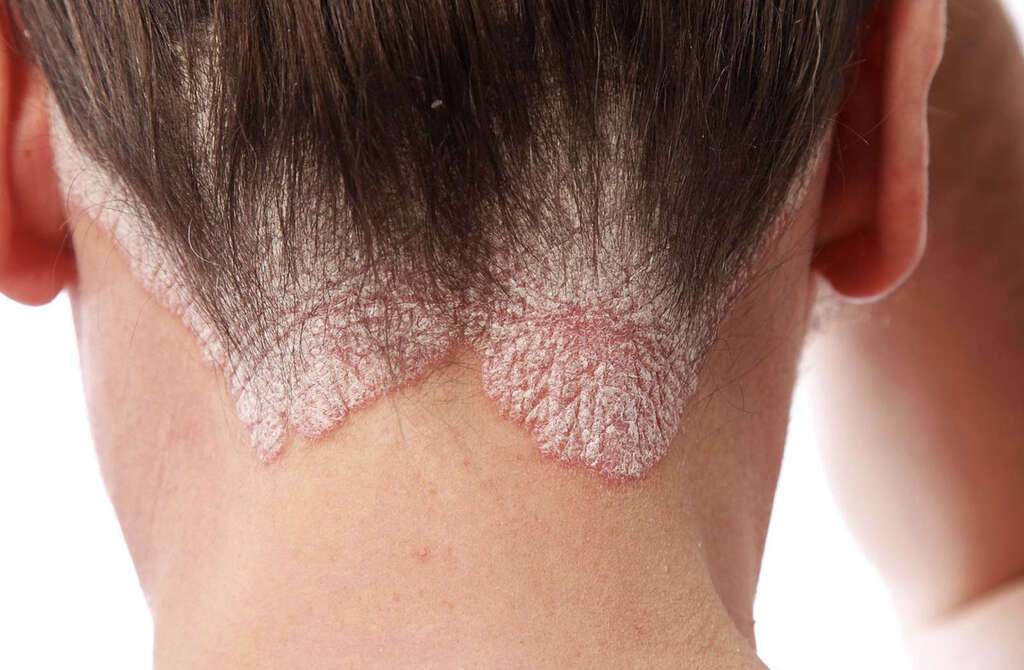
6. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that causes the patient to develop skin problems. Skin cells are naturally shed when they expire, making way for new cells to emerge from below. In cases of psoriasis new skin cells are developing too quickly, resulting in skin cells accumulating in patches of the skin.
This results in symptoms like red patches of skin that are also inflamed. In some cases, psoriasis will also affect the joints in a condition that is known as psoriatic arthritis. This condition will cause symptoms similar to other types of arthritis, including pain in the joints, stiffness, and swelling.
7. Lupus
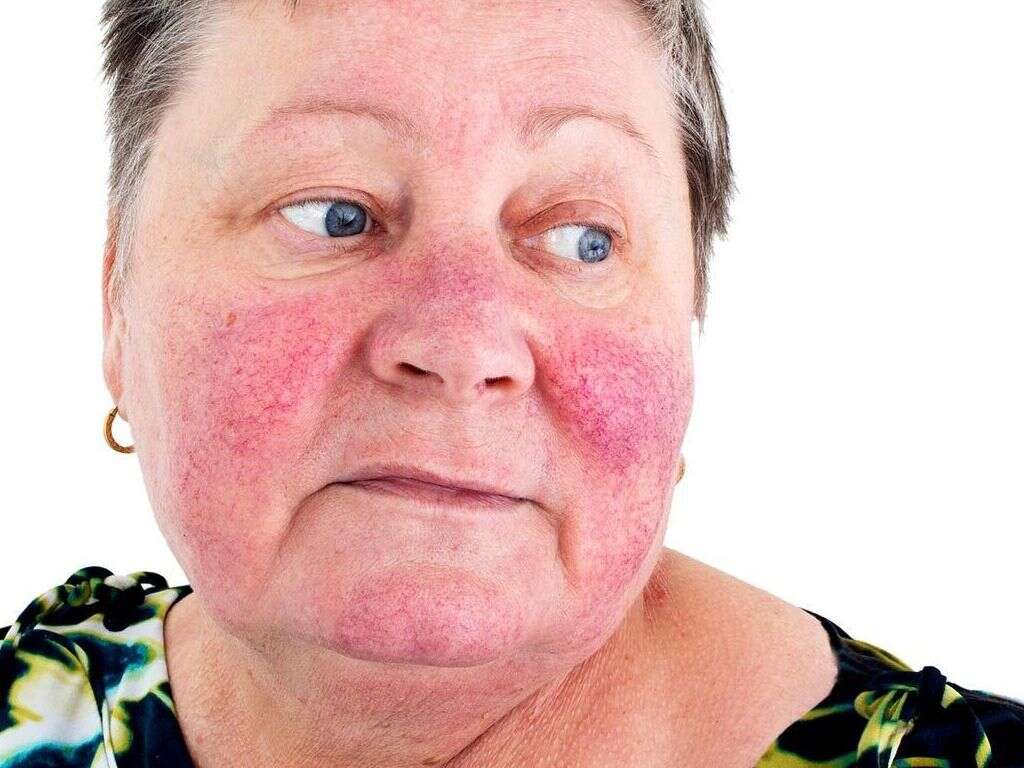
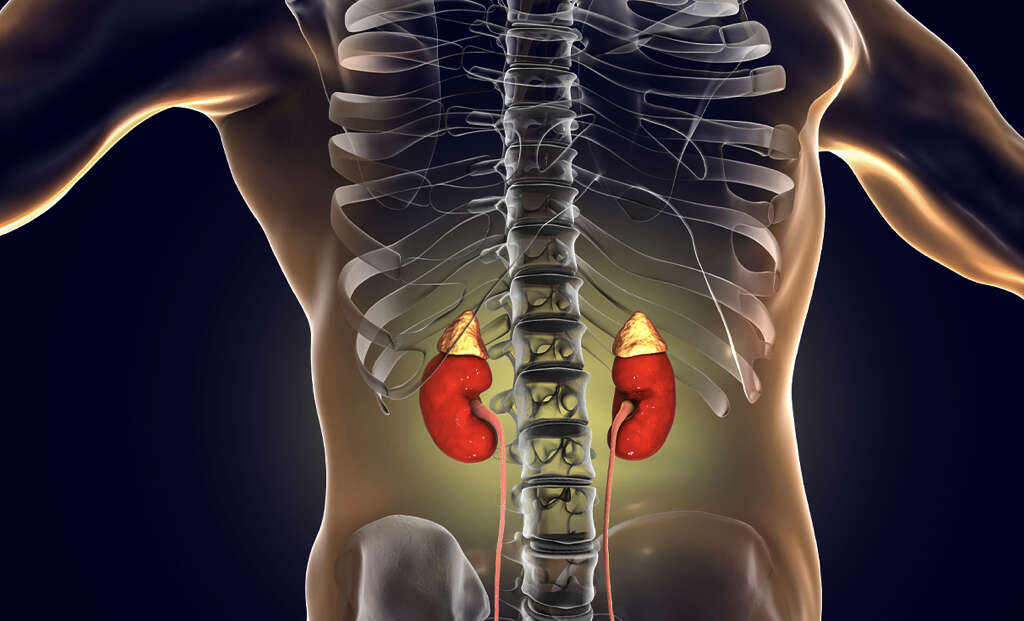
Lupus is an autoimmune condition that can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms are often so similar to other diseases. It can affect many different parts of the body, including the organs, so it is potentially dangerous. One of the leading causes of death in people with lupus is kidney damage.
Symptoms of lupus typically include a rash, and it used to be considered a skin condition. It will often cause a distinctive butterfly shaped rash on the skin. Other symptoms include fatigue, fever, chest pain, being short of breath, headaches, confusion, memory loss, and joint pain and stiffness.

8. Addison’s Disease
Addison’s disease is an autoimmune disease that affects the adrenal glands. These glands are responsible for producing aldosterone, cortisol, and androgen, which are all types of hormone. Deficiencies of these hormones will result in a number of symptoms. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis also affects hormone production by affecting the thyroid gland, which is responsible for making thyroxine.
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis will cause hypothyroidism, which means that too few hormones are being produced by the thyroid gland. Graves’ disease is another autoimmune disease that affects the thyroid gland. However, this disease causes hyperthyroidism, which means that too many hormones are being produced by the hormone.
9. Symptoms
The symptoms of autoimmune conditions will vary according to the specific type of autoimmune disease that the patient has. However, many types will share the same symptoms, one of which is fatigue. Redness and swelling are other common symptoms, and many patients will also experience aches and pains in their muscles.
Skin rashes are also fairly common, and some autoimmune disease will also cause the patient to lose their hair. Fevers are also quite common, as is tingling sensation or numbness in the hands and feet. Autoimmune conditions will also go on to cause potentially dangerous complications in some cases.

10. Treatment
As things stand, there is no known cure for autoimmune diseases. That we know so little about them also means it will likely be a long time yet before we can cure them. In the meantime, however, we can at least treat autoimmune diseases with medication.
Medication that suppresses the immune system can help, although this can make the patient more prone to infections and other ailments. Anti-inflammatories are also available that will help make the patient more comfortable, as well as helping to prevent damage. Living a healthy lifestyle can help, as can avoiding triggers that cause symptoms in some cases.