What Is ALS Disease?
Our bodies are controlled with help from our brain. The brain processes all information coming into it from signals sent by nerve cells. Once the information is processed, messages can then be sent the other way to make our muscles move, and to ensure the rest of the body is functioning as it should be.
If something was to go wrong with these nerve cells, however, then the patient’s body will begin to lose its functionality. The patient can lose the ability to control their muscles, and it can even result in the patient’s organs losing their functionality. ALS is a disease that can cause this, and it is fatal to anybody who develops it.

1. ALS
ALS is the commonly used acronym for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. It is also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease. It is a condition that affects the cells in the spinal cord and in the brains. The result of this is a gradual loss of control over their muscles. The condition tends to begin with twitching of the muscles, and overall weakness.
Patients will also often develop slurred speech early on in the condition. As the disease progresses, so the patient loses more control over their body. There is no known cure for the disease, and it will be fatal for anybody that develops it.

2. Causes
ALS is caused by the deterioration of motor neurons in the central nervous system. These are specialized cells that help to pass messages around the body in the form of electrical impulses. As these cells gradually deteriorate, so the body will become less able to send messages to muscles to tell them to move.
Of the people that have ALS, the condition was inherited in between 5% to 10% of cases. It is not known what causes the condition in the remaining cases. It is suspected that the condition might be the result of certain environmental factors combining with genetic factors.
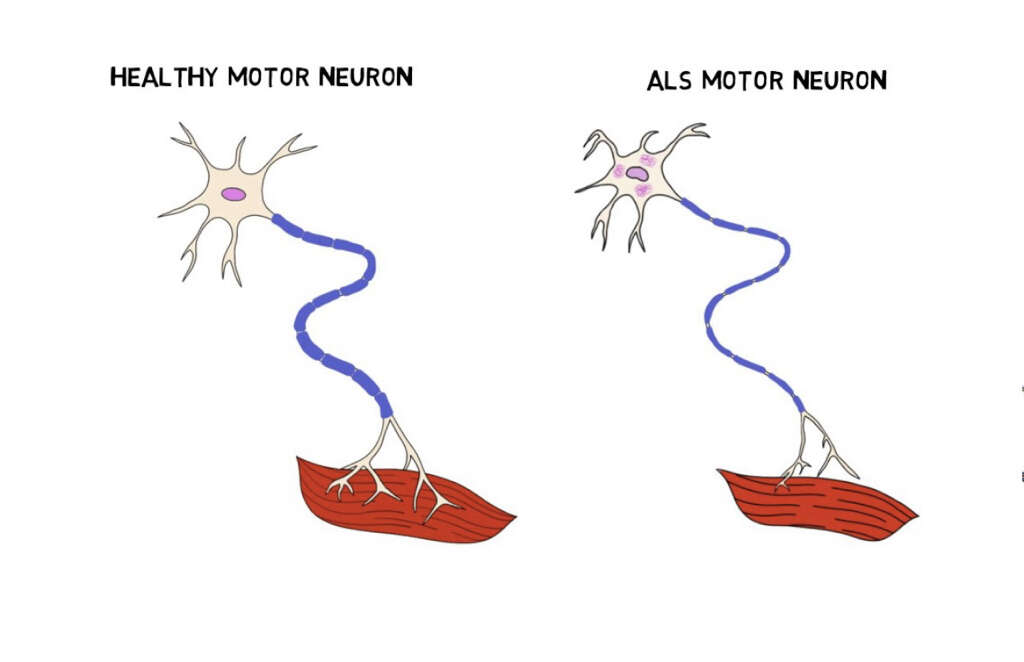
3. Symptoms
As mentioned, the main symptoms of ALS disease typically include the loss of control over muscles. This can result in various mobility and strength issues, and even walking will become difficult. The patient is also likely to trip and fall more easily than usual.
Muscle cramps will become increasingly regular, mostly in the arms, the shoulders, and even the tongue. The patient’s grip can also become weaker and they will eventually find it difficult to perform even simple tasks. They can also develop difficulty swallowing and their speech can become slurred. Changes in behavior and cognitive ability can also develop, and the patient may laugh or cry for no apparent reason.

4. Speaking Problems
As mentioned, the condition will cause the patient to slur their speech. This happens as they begin to lose control of the muscles that are responsible for speech. While the symptoms will start off as a slight slurring, they are going to get a whole lot worse.
The condition will progress to the point where the patient finds it so difficult to talk that other people are not able to understand them. This will often be associated with an inability to write, making it harder still for the patient to communicate. Technologies are available that will allow people with these symptoms to communicate.

5. Eating Problems
We don’t usually think about it, but the eating process involves a lot of coordination from different muscle groups. We need to move our mouths in a certain way that allows us to chew, and the muscles of our esophagus need to contract in waves to help push food down.
While most of us are able to take these abilities for granted, the same cannot be said for people with ALS disease. Even chewing and swallowing can become all but impossible for them, and they will eventually need to be put on a feeding tube. The loss of control over these muscles can also sometimes cause aspiration pneumonia.

6. Breathing Problems
We also take breathing for granted, and taking a breath is one of the first things that every person will do in their lives. As the muscles that allow us to breathe begin to fail, however, so we will begin to lose our ability to breath. As the condition progresses, the patient will become increasingly reliant on technology to help them breathe.
Various devices are available that can help the patient to breathe, including continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). As the condition worsens, the patient will eventually need to be put on a respirator to ensure their bodies get oxygen. Respiratory failure is the most common cause of death in people that have ALS.

7. Dementia
It is not uncommon for people to begin to lose their mental faculties as they grow older. However, it will be a lot worse for some people than for others. Some medical conditions can make it worse, and many people that have ALS will develop dementia as the condition reaches its advanced stages.
Dementia will cause the patient to develop difficulties making conditions, and their memory can also be affected. The patient’s memory can be affected to such a degree that they even forget their immediate family. Dementia can be devastating to the patient’s closest loved ones, in addition to the patient.

8. Environmental Factors
Although it is not understood what causes ALS in most cases, there are still certain factors that are associated with the condition. For example, people who smoke are more likely to develop the condition than those that don’t. Post-menopausal women who smoke are most at risk.
There is also a link between the condition and people that have served with the military, although it is not known why this is the case. It is also thought that exposure to certain toxins might be a contributing factor. No toxin has yet been identified as a cause of the condition, however.

9. Risk Factors
In addition to environmental factors, there are other factors that are associated with ALS. As mentioned, up to around 10% of cases will have been inherited from the patient’s parents. There is a 50/50 chance of somebody with familial ALS passing it onto their children.
Studies have also suggested that genetics may be a factor in people that did not inherit the condition. Sex is another potential factor, and women below the age of 65 are more likely to develop the condition. The patient’s age can also be a factor, and people between the ages of 40 and 60 are most likely to develop the condition.

10. Treatment
The damage caused by ALS disease cannot be reversed. However, treatment can help to slow down the development of the disease. Treatment is also available that can help to reduce the severity of the patient’s symptoms. As mentioned, the patient may also be provided with equipment that will make it easier for them to breathe.
Therapy is also available that can help to slow down the progress of the condition. This includes occupational therapy that can help the patient to maintain their ability to look after themselves for as long as possible. There is also speech therapy that can help the patient to be able to communicate for longer.