What Is AFib?
AFIB, or atrial fibrillation, is a condition in which an irregular heartbeat interrupts blood flow. This can lead to thrombosis and even strokes. It is a type of heart arrhythmias and the most common at that. To understand what happens in AFIB, the heart is composed of four chambers: two at the top and two at the bottom. The upper chambers are called right and left atria and the bottom chambers are called right and left ventricles.
Normally, blood moves from the atria to the ventricles. However, atrial fibrillation disrupts this flow of blood. When this happens, the flow of blood is subsequently disrupted in the whole body. The condition can be permanent or temporary and is more common among people aged more than 60 years. If the condition is left untreated, it can be fatal.

1. Symptoms of AFIB
Atrial fibrillation can be asymptomatic, which means you might not have any prior symptoms. This, however, is not always the case. The most common symptoms include palpitations of the heart, which is the sensation of your heartbeat being too fast or too strong.
Other symptoms include chronic fatigue, dyspnea, chest pain, general weakness, confusion, dizziness, and inability to perform any physical activity. In general, the symptoms last for minutes to hours depending on the severity of the condition. If the symptoms persist for more than one day, the condition is called chronic atrial fibrillation.
2. Causes of Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation occurs when the four heart chambers fail to work normally. This can happen because the electrical signals of the heart are faulty. Normally, the atria and ventricles are supposed to beat together in harmony. However, in AFIB, the atria beat at an irregular and quick pace.
There are many possible causes of atrial fibrillation. Most of these causes are cardiovascular and include hypertension, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, heart valves diseases, cardiac surgeries, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital cardiac defects, hyperthyroidism, pericarditis, and intake of certain medications.
It is essential to have the cause of the problem determined by qualified medical personnel.
3. Atrial Fibrillation Complications
If you experience symptoms that suggest you may have AFIB, go for a check-up without delay.
You should also go for regular follow-ups if you are diagnosed with the condition. This will help prevent any complications. Taking your medications, changing your lifestyle, and following some healthy habits can prevent complications in most patients.

4. Stroke and Heart Failure
The most common complications of AFIB include strokes and heart failure. Strokes occur when a blood clot gets into the brain, preventing oxygenated blood from reaching the affected part.
Such blood clots can cause serious damage or even be fatal. Heart failure happens when the cardiac muscle cannot function properly. Heart failure does not occur suddenly as does heart attacks and strokes. It develops over time.
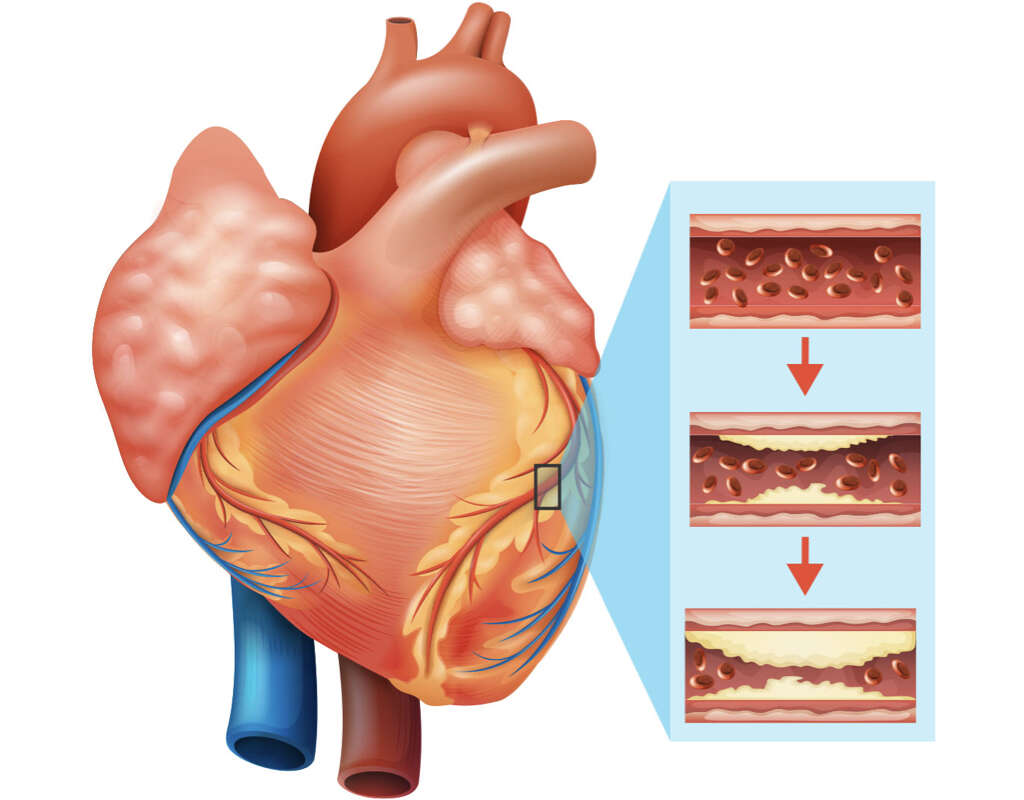
5. Atrial Fibrillation Diagnosis
If you visit your doctor with AFIB symptoms, the doctor will ask for tests to confirm your diagnosis and determine your overall heart function. This includes a physical examination in order to check your pulse, heart rate, blood pressure, and pulmonary functions. But it is the electrocardiogram (EKG) that will help trace your heart impulses.
If, however, the atrial fibrillation does not occur while you undergo EKG, your doctor will order for other tests such as a Holter monitor, which can monitor your heart for up to two days, and an echocardiogram (ECG), which produces a moving image of your heart. Blood tests and chest x-rays may also be done as part of the diagnosis process.

6. Treatment
Atrial fibrillation medications include beta blockers, which can decrease the heart rate, calcium channel blockers, which relax muscles within the blood vessels and slow down the heart rate, sodium or potassium channel blockers, which are responsible for controlling the electric impulses of the heart, and digitalis, which strengthens the heart muscle.
Some doctors also use blood thinners like rivaroxaban and apixaban to prevent the formation of blood clots. Treatment is usually not required for those without symptoms if they do not suffer from any other cardiac problems, and those for who the condition resolves spontaneously.
7. Surgical Intervention
Chronic and severe AFIB may require surgical intervention. Surgeries differ according to the condition, but the aim in each case is to help the heart pump more efficiently and prevent damage to the heart. The most common surgery is electrical cardioversion, which can normalize the electric impulses.
Catheter ablation is another option in which the surgeon removes any tissues that may be causing the abnormality of the heart rhythm. Atrioventricular node ablation prevents the signals coming out of the atria to reach the ventricles. The final surgery is the maze surgery, which is only used if the medicine and other surgeries fail.
8. Diet for AFIB
There is no specific diet for atrial fibrillation. However, healthy food is essential for your heart and overall health. The best diet for a heart condition should be high in plant-based foods such as oats, fruits, and vegetables. Fish is also recommended because it is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids and protein, which are great for the health of your heart.
Additionally, there are certain foods that you should avoid. These include alcohol, caffeine, gluten, salt, and saturated fats. Each of these forbidden foods may cause problems for cardiac patients. An AFIB diet is similar to the one that you should follow if you have high cholesterol levels or other cardiac problems.

9. Can You Prevent Atrial Fibrillation?
While it is not possible to prevent AFIB in totality, you should do whatever you can to reduce the risk of its recurrence. There are certain ways to go about this, which include following a healthy diet and lifestyle.
Cut out saturated foods, incorporate regular exercise in your routine in the form of walking, running, or lifting weights. Also, shed excess weight and keep it off and quit smoking and alcohol drinking for better results.

10. Long-Term Outlook
It is important that you are aware of your AFIB condition because it is potentially fatal.
The good news is that if AFIB is discovered and treated early, you can lead a normal life. And although the condition can recur and get worse over time, following a healthy lifestyle and taking your medications as directed can prevent any complications. AFIB patients who follow these tips live a normal, full life with some even forgetting that they have a heart condition.











