What Is a Stent?
4. Coronary Stents
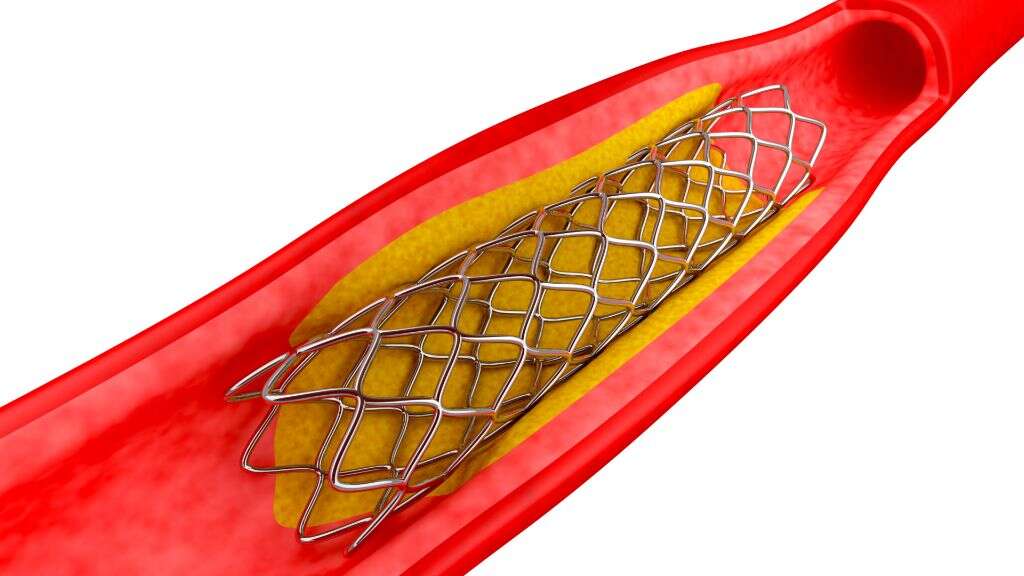
A coronary stent is a small wire mesh tube that is placed in the coronary arteries (vessels that supply the heart) to keep obstructed arteries open and decrease their chance of narrowing again. Coronary stents are often used in percutaneous coronary intervention (coronary angioplasty) to help reduce symptoms such as angina (chest pain) or in the event of myocardial infarction (if applicable). It has been shown to improve survival and reduce complications (i.e. heart attack).
Two of the main complications of coronary stenting are re-occlusion due to proliferation of scar tissue, and restenosis. Restenosis occurs when a thick smooth muscle tissue develops inside the lumen. While the development is variable, it can cause restenosis in some cases.
Advertisement