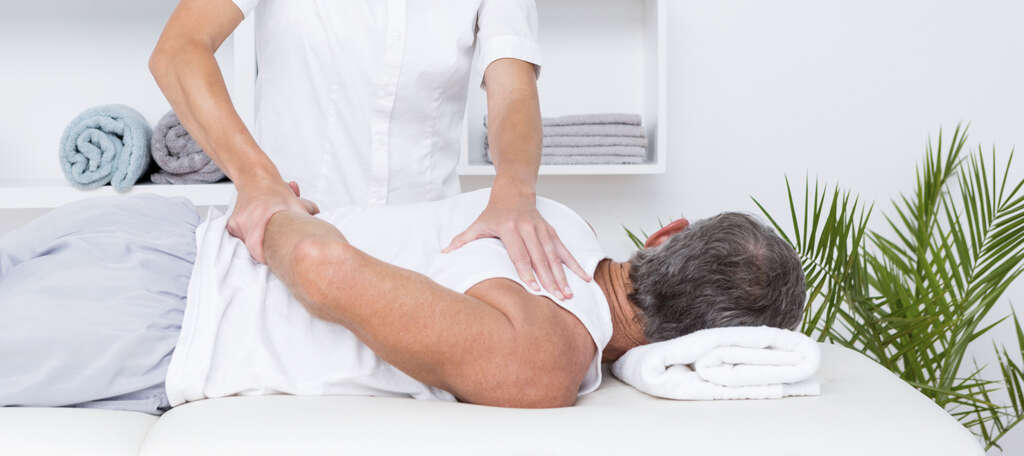
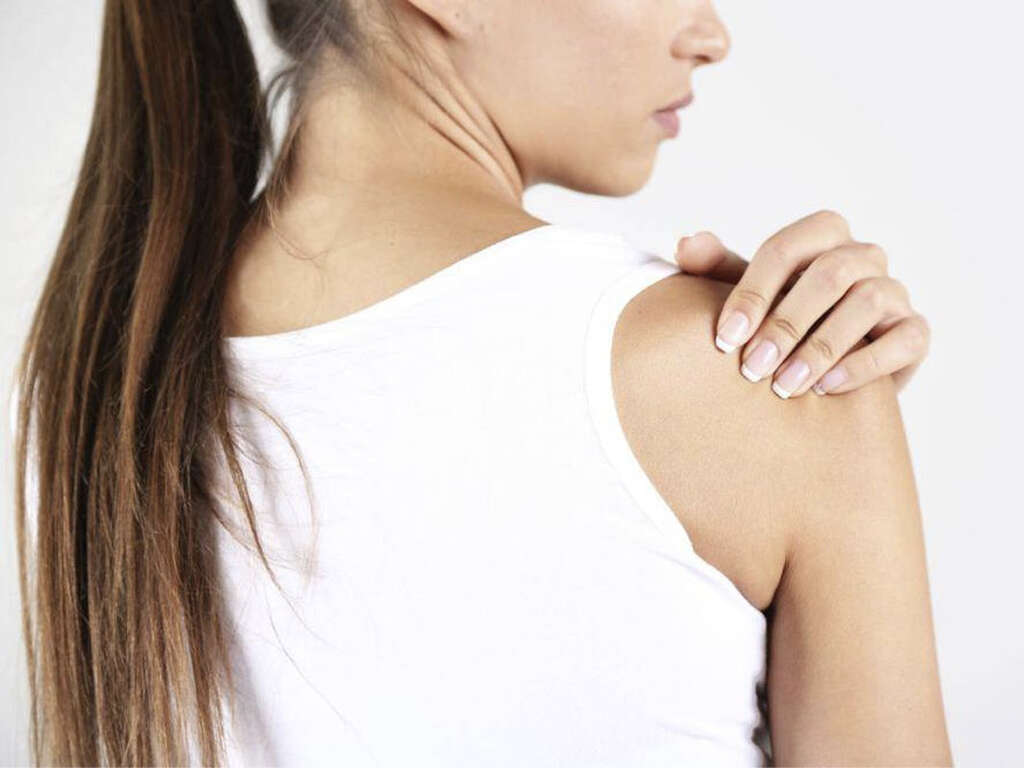
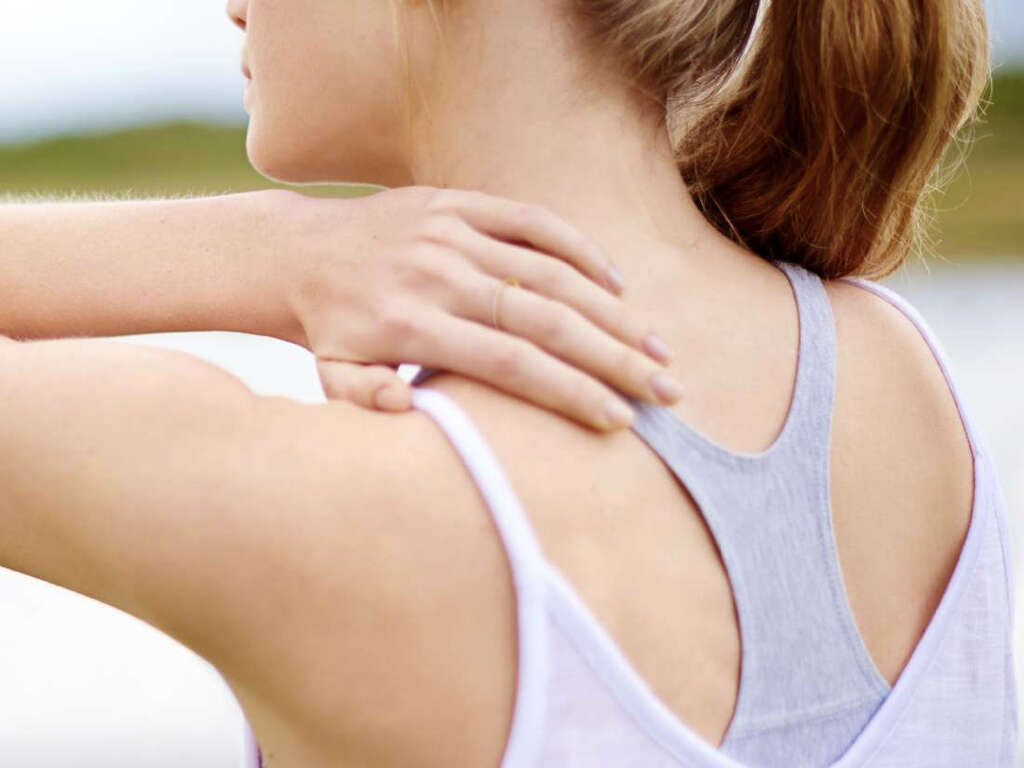
What Is a Frozen Shoulder?
5. Diagnosis
Since frozen shoulder is mostly a clinical diagnosis, laboratory studies are rarely required. However, if a predisposing condition is suspected to contribute to frozen shoulder, some tests may be beneficial. This includes a complete blood count (CBC), C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, hemoglobin A1c, blood glucose, free thyroxine, thyroid stimulating hormone, and more.
Imaging studies are not generally indicated. However, routine radiographs can help rule out any pathological process. The use of ultrasonography is controversial but has been shown to be able to measure the thickness of the acromiohumeral ligament, presence of fibrovascular inflammatory tissue, and increased vascularity in the rotator interval. Arthrography can also be helpful. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help rule out other pathology if the patient does not improve after 6 weeks.
Advertisement