What Causes White Spots On Skin?
Finding white spots on the skin can be an alarming discovery. In general, however, they are not a cause for concern. If you have any, though, it is a good idea to see a dermatologist to determine the cause and possible treatment options.
There are numerous conditions that can cause different types of white spots. They are frequently due to an accumulation of excess dead cells or skin protein that gets trapped beneath the skin’s surface. Depigmentation is another possible reason for white spots or patches.

1. What Is Eczema?
Eczema is a common skin condition that causes an itchy rash. It may appear in a number of places on the body, including the hands, feet, scalp, face, elbows, wrists and back of the knees. The rash is often red with bumps, and some of these bumps can be white in color. There may also be white patches in the rash. The rash may be particularly itchy at night.
This skin condition often begins in childhood, though it is found in adults as well. Those who have allergies are more at risk for eczema. Flareups are interspersed with dormant periods that can last for varying lengths of time, sometimes for years. Often the cause of the flareup is unknown.
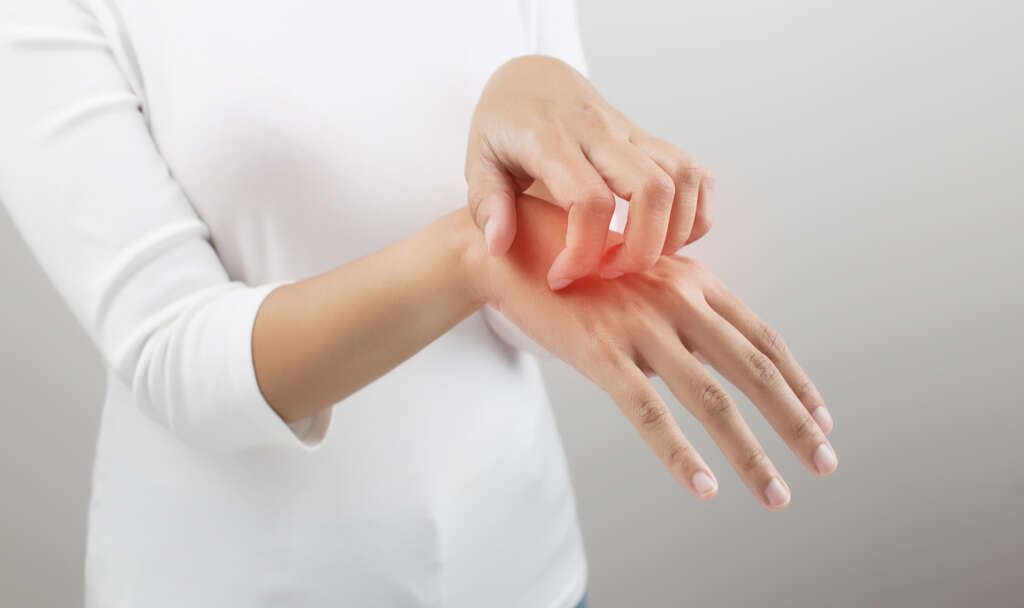
2. How Is Eczema Treated?
Keeping the skin in a healthy condition can help reduce flareups. Moisture and humidity can aggravate the symptoms, so wearing breathable clothing and minimizing the length of hot showers or baths can be helpful. It may also be beneficial to use natural products, as some people react to the harsh chemicals in some cleaning and bath products.
Environmental allergens and air pollution may also exacerbate the condition, so avoid these when possible. During an outbreak, taking an antihistamine may alleviate some of the symptoms and anti-itch creams can reduce the discomfort.

3. What Is Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis?
Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis is more commonly known as sunspots. These white patches occur in areas where skin pigmentation has been lost. Generally, the spots first appear on the legs, but they often then spread to other parts of the body, including the back, arms and face.
Sunspots often run in families, but the reason for the lack of pigmentation is unclear. People over the age of 40 are more likely to develop the condition. The presence of sunspots is not associated with skin cancer, and the condition is medically benign.

4. How Is Idiopathic Guttate Hypomelanosis Treated?
There is no cure for the condition. The only symptom is discoloration; thus, treatment is generally for cosmetic purposes and to protect the lighter-colored skin from the sun. Wearing a good sunscreen prevents sun damage that can lead to skin cancer. It is an important preventative for anyone spending a lot of time outdoors, but lighter skin is even more at risk.
Once sunspots appear, there is little that can be done to diminish them. Skin abrasion and topical retinoid creams remove the outer layer of skin, but these do not necessarily reduce the size or appearance of the spots.

5. What Is Tinea Versicolor?
Tinea versicolor is caused by a microscopic yeast. This presence of this yeast on the skin is normal for everyone. For some, however, its growth gets out of control. When this happens, spots appear on the skin. These can be white, or they can be shades of brown, red or pink. The spots may be more apparent on tanned skin. They are often itchy, dry, and scaly.
The reasons for the overgrowth of yeast are unclear, but it is associated with a few factors. People living in a more humid environment are more likely to experience it, as are those with oily skin. Excessive sweating is also a potential contributor. Those with weakened immune systems are more prone to the condition.
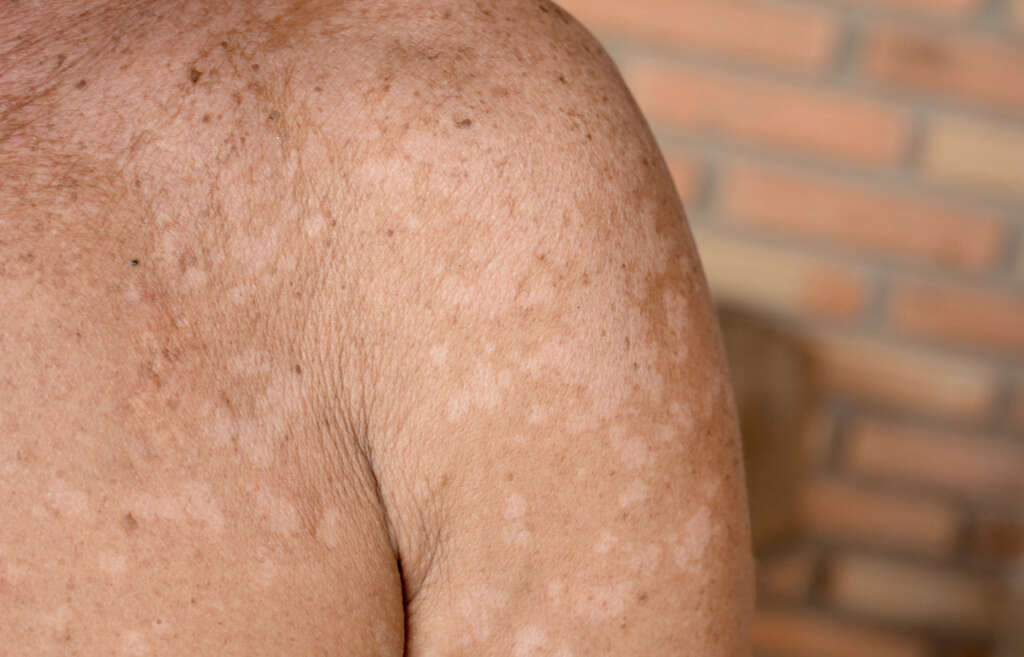
6. How Is Tinea Versicolor Treated?
This disorder often flares in hot and humid conditions, which means that it frequently goes away on its own when the temperatures drop. Often, the spots reappear in warmer weather. Treatment with anti-fungal creams can help get rid of the spots, particularly if it begins early. Milder symptoms may be lessened with over-the-counter ointments.
For more severe symptoms, it may be necessary to treat the condition over a longer period of time. It can take several weeks, sometimes months, before the skin returns to normal. If OTC anti-fungal creams do not work, it may be necessary to contact a dermatologist for a stronger treatment approach using oral or topical medication.

7. What Is Vitiligo?
Vitiligo is another condition that is due to depigmentation. When the skin cells called melanocytes cease their production of melanin, the skin loses its color. The white patches that result can occur anywhere on the body. They normally appear bilaterally, though on occasion a person may get them on only one side of the body.
The cause of the condition is not known. There does seem to be a genetic factor, as it often runs in families. Vitiligo may also be caused by an autoimmune deficiency or disease. It is most likely to develop in people in their 20s; however, it is found in all age groups.
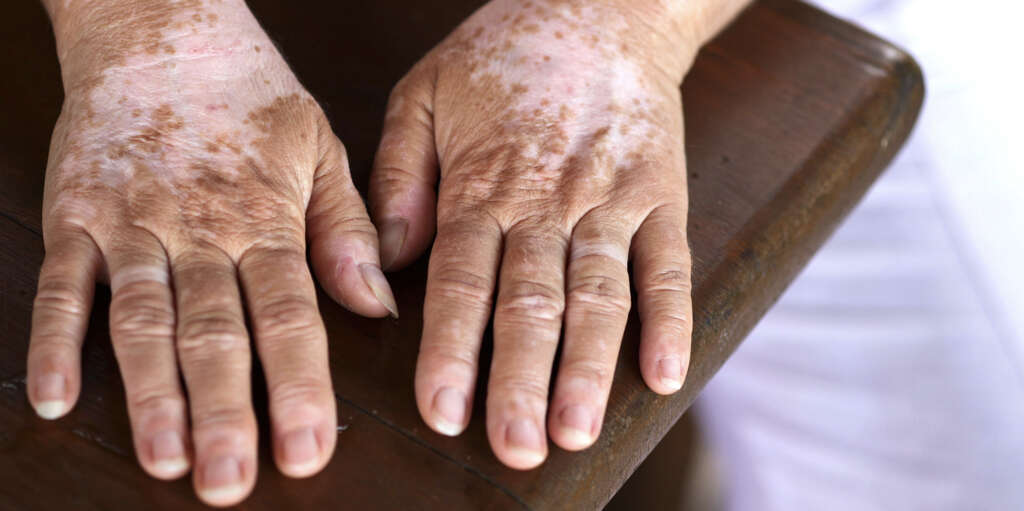
8. How Is Vitiligo Treated?
As with sunspots, treatment for vitiligo is generally cosmetic. The condition does not cause discomfort or pain. Staying out of the sun or wearing sunscreen can reduce the contrast between the vitiligo spots and normal skin.
There are a few treatment options that may help those with more severe cases. Light therapy paired with topical medication can help reduce the appearance of the spots. Topical steroids remove the outer layer of skin and may be beneficial for some.

9. What Is Pityriasis Alba?
Pityriasis alba is a skin condition that begins with red, itchy and scaly patches and leaves behind white patches of skin upon healing. These patches typically appear on the chin and cheeks, but they can occur elsewhere on the body as well. A related, but rare, condition called pigmenting pityriasis alba causes scaly patches that are bluish-white, surrounded by lighter colored skin.
The cause of the condition is uncertain, but it is potentially a milder form of eczema. Pityriasis alba often develops in those who are between the ages of three and 16, but it can occur in individuals of any age.
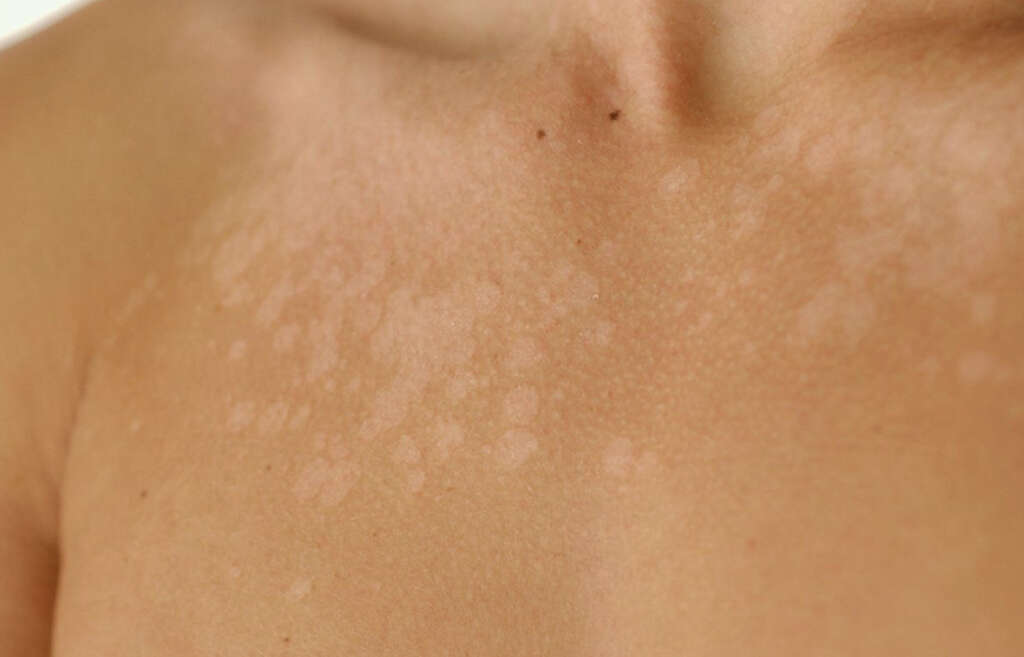
10. How Is Pityriasis Alba Treated?
This skin condition generally resolves on its own. For many, the symptoms are mild enough that no treatment is necessary; however, some seek relief from the itchiness. Those with more severe cases may want to treat the inflammation and dryness that can also occur with this condition.
OTC anti-itch creams may alleviate some of the discomfort and moisturizers can help with dryness. Using natural products is beneficial for those who are sensitive to the chemical ingredients in some skincare creams. Topical steroids may also be useful.












