What Causes an Enlarged Spleen?
The spleen is one of the most important organs in the body located in the upper-left part of the abdomen where it is protected by the ribcage. Its functions include storage of red blood cells, production and storage of lymphocytes, filtration of blood, and destruction of old and abnormal red blood cells. Certain dysfunctions and illnesses can lead to an enlarged spleen; a potentially serious, but treatable condition.
A typical healthy spleen is 1 inch thick, 3 inches wide, 5 inches long, and weighs about 7 ounces. These measurements keep changing as a consequence of the workings of the spleen. An enlarged spleen, on the other hand, weighs more than 35 ounces and is longer than 8 inches. In most cases, an enlarged spleen is diagnosed during a medical examination when the doctor notices a palpable spleen. However, palpability of the spleen is usually only possible in a slim person, and is therefore not a good basis to reach a diagnosis of an enlarged spleen.
1. Symptoms of an Enlarged Spleen
People with splenomegaly usually do not experience any kind of symptoms. In most cases, the condition is discovered during a physical examination. In a slim person, the spleen is palpable. The most common symptom of splenomegaly is a pain in the upper-left quadrant of the abdomen. In addition, the feeling of abdominal fullness is also common, especially after eating a small amount of food. This symptom indicates that the spleen is large enough to create pressure on the stomach. Decreased immunity may also signify splenomegaly, in which case, the body is unable to fight infections.

2. Causes of an Enlarged Spleen
Many diseases and conditions can lead to splenomegaly. The most common cause of enlarged spleen is a viral infection called mononucleosis. Liver problems such as liver cirrhosis, cystic fibrosis, and chronic liver failure can also lead to an enlarged spleen.
In addition, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is associated with many organ problems including enlarged spleen, since it leads to inflammation of the lymph system, which includes the spleen.
3. Other Causes
Other causes of an enlarged spleen include liver problems such as liver cirrhosis, cystic fibrosis, and chronic liver failure. In addition, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis is associated with many organ problems including an enlarged spleen, since it leads to inflammation of the lymph system, which also includes the spleen.
Damage to the spleen due to health issues in other organs of the body, especially the liver and the immune system, can also cause an enlarged spleen.
4. Diseases Associated with an Enlarged Spleen
There many diseases and conditions associated with an enlarged spleen. These include malaria, Hodgkin’s disease, leukemia, heart failure, splenic tumors, or any other tumors that may spread to the spleen.
Additionally, viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections, inflammatory diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, and sickle cell disease are all possible causes of an enlarged spleen.
5. Complications of an Enlarged Spleen
Complications of an enlarged spleen will depend upon the cause of the enlarged spleen. A Common complications include low blood cell count, pressure on other organs, obstruction of blood, and compromised immunity all of which can lead to other health problems.
Additionally, if the condition remains untreated, an enlarged spleen can end up rupturing, leading to internal bleeding. This is an emergency condition that can be fatal if not attended to without delay.

6. Disease Process
There are four classification types of splenomegaly according to the causes. The first type is the congestive stage caused by portal hypertension in which there is pooling of blood. The second type is the infiltrative stage in which there is an invasion of the spleen by foreign cells such as metastases of tumors, myeloid neoplasms, and fat cells.
The third one is the immune type caused by a significant increase in immunologic activity. This type is characterized by the subsequent hyperplasia and it is usually associated with conditions such as endocarditis, sarcoidosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. The last type is the neoplastic splenomegaly resulting from immune cells causing a tumor such as lymphomas.
7. Can Diet or Lifestyle Changes Benefit an Enlarged Spleen?
There is a list of precautions you should follow if your spleen is enlarged. First, you should avoid any contact sports such as hockey, soccer, football, and wrestling. You should also discuss with your doctor any other necessary changes in order to avoid a ruptured spleen. Wearing a seat belt reduces your chance of injury in the event of a car accident.
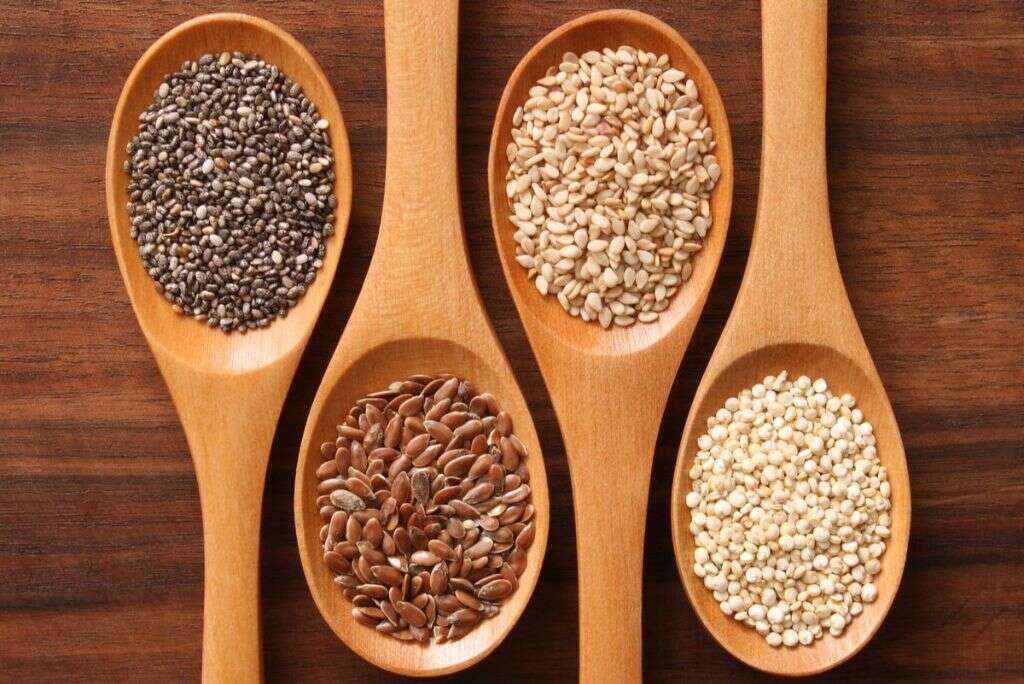
According to some studies, eating nutrient-dense foods including omega-3 items such as salmon, nuts, and seeds such as flax, chia, and pumpkin seeds, and herbs like ginger can help improve the health of the spleen, which may aid in healing from enlargement. Person’s with an enlarged spleen should also avoid alcohol, refined foods, and sugary foods.

8. Diagnosis
An enlarged spleen is discovered during physical examination. Slim people usually have palpable spleens, for which reason an enlarged spleen can be noticed. This is not usually the case in obese persons. Other tests are done to confirm the diagnosis including blood tests such as complete blood count or CBC to check the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
An ultrasound, CT scan, and or MRI can be used to determine the size of the spleen, the effect of the spleen on other organs, and blood flow to the spleen.
9. Treatment
Sustainable treatment for splenomegaly must involve treatment of the main cause of an enlarged spleen. Many times a dysfunction of other organs, such as the liver, are the cause for splenomegaly. If this is the case, the dysfunctional organ will need to be treated in order to stop the problem. If the main cause is a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics.
If the problem is viral or parasitic, the treatment plan will differ accordingly. Medications for the underlying cause is the first line of treatment. However, in some cases, the enlarged spleen may persist, and surgery may be needed to remove it. The operation is called a splenectomy. After removal of the spleen, the patient can live a normal life.
10. Long-Term Outlook
The condition can be serious, but with proper treatment, a patient with an enlarged spleen can recover and lead a normal, healthy life. The condition should be treated at the earliest to prevent serious damage. Besides, an enlarged spleen may rupture, causing internal bleeding or even death.
If you have an untreated enlarged spleen, avoid any contact sports such as football and hockey. Also, wear a seatbelt when driving to protect your spleen.