10 Symptoms Of Middle Ear Infections
Middle ear infection, also known as otitis media, is an infection that affects the part of the ear behind the eardrum. These infections are usually caused by bacteria or viruses. In most cases, middle ear infection occurs during or soon after another infection in the upper respiratory tract like a cold or flu. It may also arise as a result of an allergic reaction.
Otitis media is more common in infants and children. This can be attributed to the underdeveloped Eustachian tubes in these children and exposure to more pathogens once the children start feeding on other foods beside breast milk or formula. However, middle ear infections also affect older children and adults. If otitis media does not clear soon, and it is not treated in time, it can lead to complications like long-term loss of hearing. Following are 10 middle ear infection symptoms.
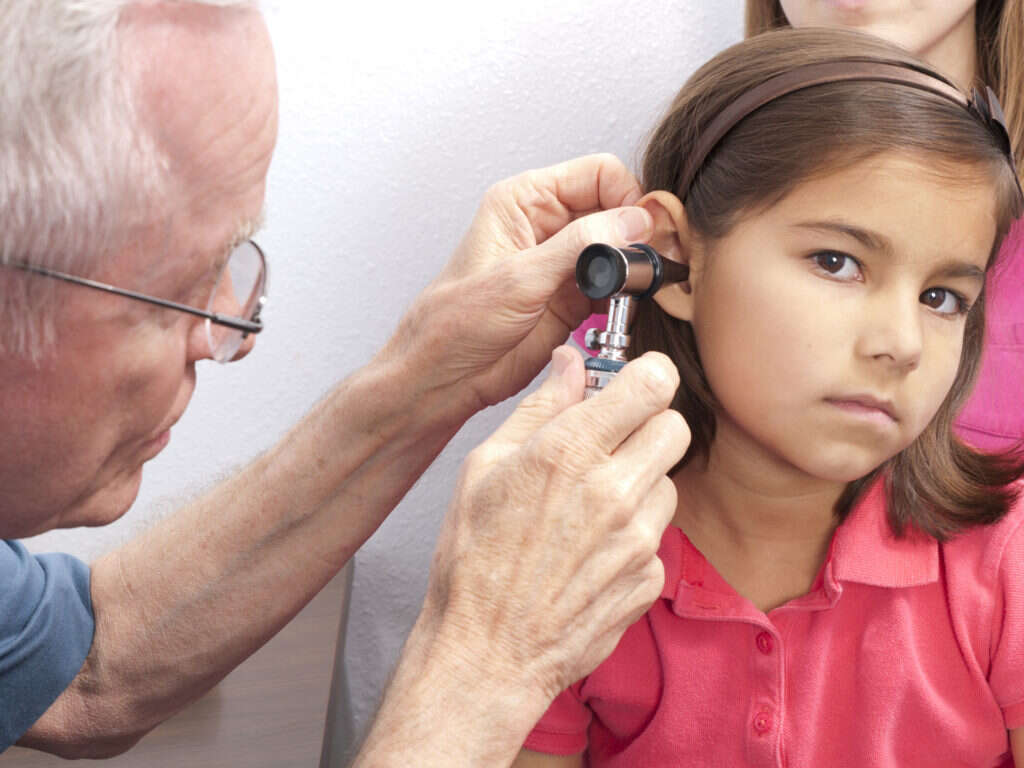

Symptom #1: Ear Pain
Ear pain is a common middle ear infection symptom. The pain is caused by the inflammation within the middle ear, including the Eustachian tube. Infection or inflammation may be caused by bacteria, viruses or an allergy. This can lead to swelling and collection of fluid within the middle ear. When the inflammation affects the Eustachian tube, it causes a blockage in it.
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the atmosphere in order to balance the pressure in the middle ear with the atmospheric pressure. Blockage of the Eustachian tube means that fluid will collect in the middle ear. This causes pressure build up within the middle ear which may cause discomfort or ear pain.

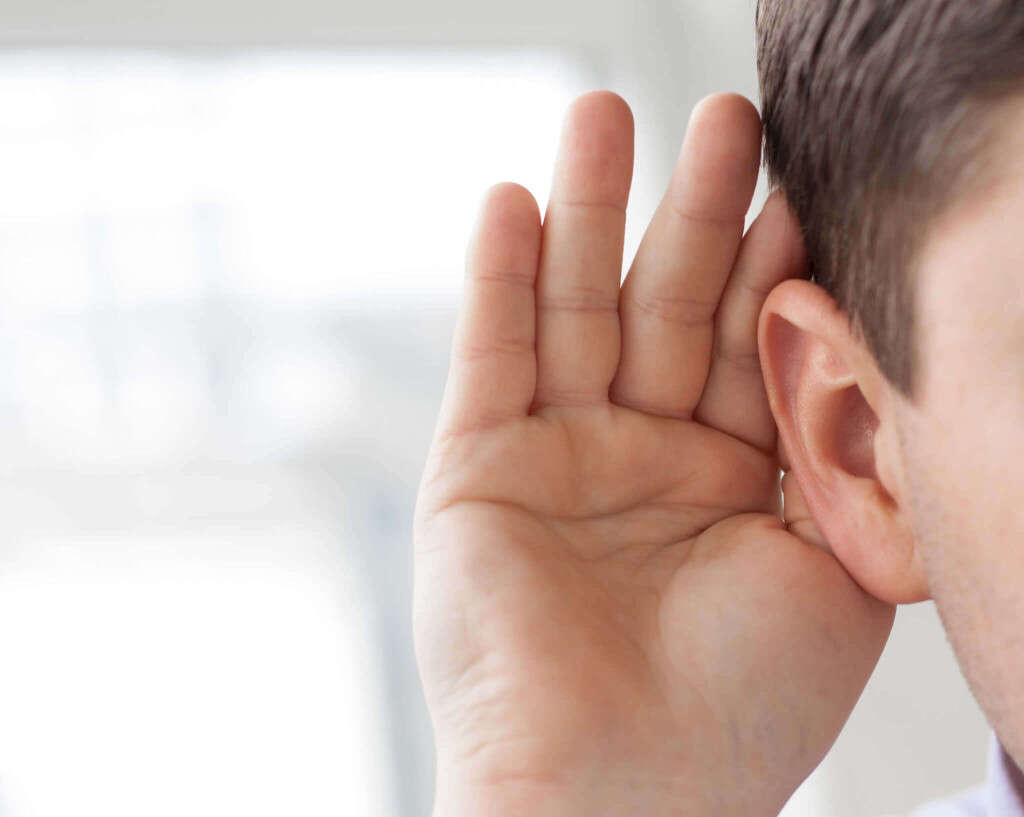
Symptom #2: Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a very common symptom associated with Otitis Media. The middle ear connects the external ear canal and the inner ear, therefore, when it becomes inflamed it creates an obstacle for the whole hearing system.
This symptom is usually unilateral (only on the affected ear) and resolves easily after the proper medication is administered by a healthcare specialist.

Symptom #3: Irritability
This symptom is very important especially in younger children as it might be the only thing that signals the presence of an ear infection.
Children are especially prone to ear infections; this is because they have an immature immune system. Irritability can be seen as excessive crying, unusual behavior and/or an apprehensive response towards caregivers.

Symptom #4: Ear Discharge
Ordinarily, ear discharge is made up of wax. However, ear discharge that is whitish, yellowish or bloody colored is a strong indicator of a middle ear infection.
As the middle ear becomes inflamed, pus can start to build-up and leak through the external ear canal. If the discharge becomes red, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible as this symptom may signal serious damage to the eardrum or perhaps something more serious than that.

Symptom #5: Fever
Fever is a sign of many types of infections. It is also a possible symptom of middle ear infection. As in other infections, middle ear infection causes the body’s defense mechanism to kick in to attempt to destroy the infection-causing pathogens. One way for the body to deal with pathogens is by raising body temperature.
Disease-causing organisms multiply and grow best at their victim’s normal body temperature. By raising the body temperature, the defense system aims to make conditions unfavorable for the pathogens thereby causing their death.

Symptom #6: Dizziness
If you or your child is experiencing dizziness, this could be a symptom of a middle ear infection. When a middle ear infection occurs, the space behind the eardrum becomes inflamed and may be filled with fluid.
It is worth noting that the middle ear also houses the small bones that connect the eardrum to the oval window and effectively to the inner ear. The inner ear houses the semicircular bones responsible for maintaining balance. Collection of fluid in the middle ear and the corresponding increase in pressure interferes with the workings of the semicircular bones. This leads to dizziness or loss of balance associated with middle ear infections.

Symptom #7: Difficulty Sleeping
A middle ear infection can cause difficulty sleeping. This is more noticeable in babies and young children. The discomfort that comes with middle ear infection, ear pain and fever are reasons why a child may find it hard to sleep. These symptoms may also disrupt a child’s sleep. Pain due to middle ear infections can worsen at night when the body is in a horizontal position.
While the pain may still be present during the day, it is not as noticeable as it is at night. This is because when in a vertical position, the Eustachian tubes may help in the flow of fluid from the middle ear. However, when in a horizontal position, the Eustachian tubes are less able to drain and may get totally blocked. This causes increased pressure in the middle ear which may worsen the pain and make it impossible to sleep.

Symptom #8: Nausea
Nausea is a non-specific symptom associated with many infectious conditions. In the case of a middle ear infection, this symptom can be linked to the dizziness caused by the inflamed middle ear.
It usually resolves quickly after proper medications are prescribed and it rarely ends in vomit. If you are suffering from this symptom, you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.

Symptom #9: Poor Appetite
Middle ear infections can lead to poor appetite, especially in babies and young children. As with many other health conditions, middle ear infections present with symptoms like ear pain, headache, dizziness, fever, nausea, and vomiting. These symptoms can cause a patient to lose their appetite as well.
For some patients, ear pain may be worse during chewing. Causing them to refrain from eating to avoid more pain. Once the inflammation and the infection are treated, this symptom should disappear as well.

Symptom #10: Tinnitus
Tinnitus is described as a temporary ringing noise that can become quite uncomfortable. This high pitched noise usually goes away on its own and it is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions.
Because younger children are unable to express their symptoms very well, this symptom is more associated with older children and adults. If you are suffering from this symptom you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.