10 Symptoms of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer or hepatic cancer, as the name suggests, is cancer that originates from the liver. Like all cancers, liver cancer may spread to other parts of the body. This is known as metastasis. The main cause of liver cancer is cirrhosis due to prolonged excessive alcohol consumption, hepatitis B infection, and hepatitis C infection. Other causes that can lead to liver cancer are non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, aflatoxin, and liver flukes. 80 percent of liver cancer are hepatocellular carcinoma. The diagnosis of liver cancer can be achieved through blood tests, tissue biopsy, and medical imaging. Some of the preventative efforts of liver cancer involves immunization against hepatitis B infection and providing treatment to those with hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection.
Treatment options available are radiation therapy, surgery, targeted therapy, embolization therapy, ablation therapy, and liver transplantation. Liver cancer is the fifth commonest cancer and the third leading cause of death from cancer worldwide. Liver cancer is more common in men and it is usually diagnosed in person’s aged between 55 to 75 years old.
Symptom #1: Abdominal Mass
This is usually due to the enlarged liver or also known as hepatomegaly. They may also feel a lump under the ribs on the left side which refers to an enlarged spleen or splenomegaly.
As the disease progresses, the liver enlargement may cause pain or tenderness in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen but this is not a common finding.

Symptom #2: Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain or stomach ache is a common symptom that is seen in both serious and non-serious conditions. The abdomen can be divided into nine regions: right hypochondrium, epigastric, left hypochondrium, left lumbar, umbilical, right lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric, and left iliac regions.
Causes of abdominal pain include abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, gastroenteritis, irritable bowel syndrome, ectopic pregnancy, and more. In liver cancer, the pain is primarily felt in the upper right region of the abdomen, but this is not always present.

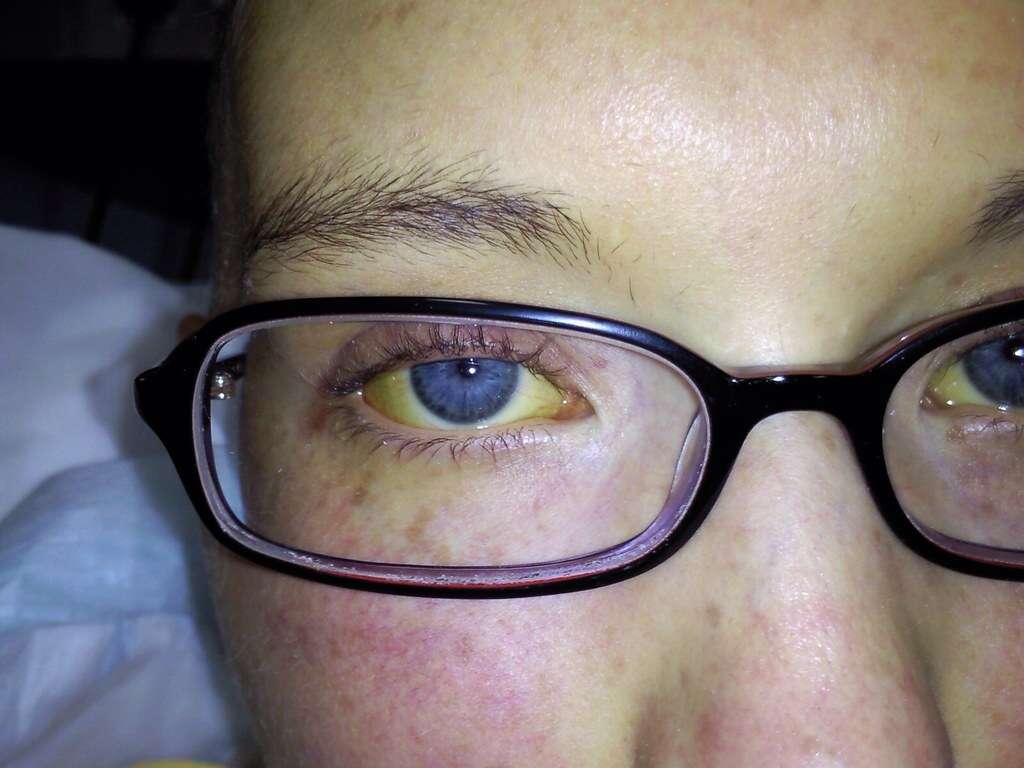
Symptom #3: Jaundice
Jaundice or icterus describes the yellowish pigmentation of the skin and eyes due to high bilirubin levels. One of the associated symptoms of jaundice is itchiness.
When a patient has jaundice, he or she may also experience pale feces and dark urine. Causes of jaundice range from serious to non-serious such as cirrhosis, infections, bile duct blockage, side effect of medications, leptospirosis, malaria, schistosomiasis, cancer, pancreatitis, gallstones, and many more.

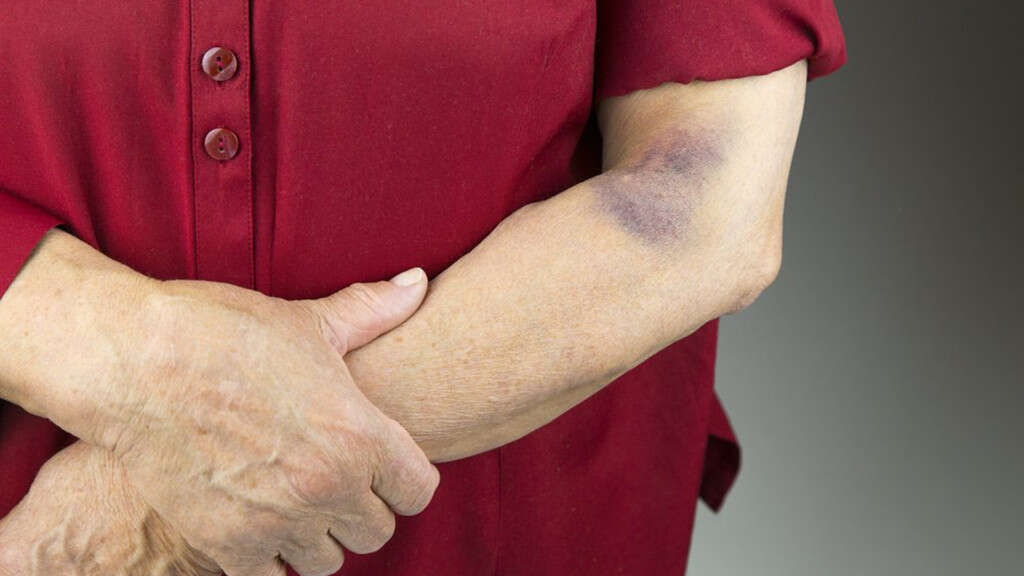
Symptom #4: Easy Bruising
Bruising refers to a hematoma of the tissue where trauma causes damage to capillaries and venules resulting in the blood to seep or extravasate into the surrounding areas. Since most bruises are superficial, the bleeding causes the discoloration of the skin and will be visible until it is cleared by the immune system.
Bruising is usually caused by internal bleeding into the surrounding tissues without a break in the skin. It is easily recognized due to their characteristic purplish or bluish appearance following an injury. In liver cancer, bruises occur more commonly and frequently because of the low platelet levels.
Symptom #5: Weight Loss
Weight loss refers to the total reduction of body mass where there may be loss of adipose tissue, fluids, bone mineral deposits, muscle, or other connective tissue. Weight loss can be categorized into intentional and unintentional. Unintentional weight loss occurs when there is malnourishment, dehydration, diarrhea, gastroenteritis, cancer, and more.
There are four mechanisms of weight loss: impaired intake of food, impaired absorption or digestion, altered metabolic requirements, and excess loss of nutrients.

Symptom #6: Weakness
Weakness or asthenia is a common symptom seen in many conditions. It can be divided into true and perceived weakness. True weakness is a symptom that is seen in conditions that affect skeletal muscles such as myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophy, and inflammatory myopathy.
Perceived weakness occurs when an individual feels that there is more effort required than normal to exert an amount of force despite having normal muscle strength. In liver cancer, weakness can be seen in the early stages of the disease, even before diagnosis.

Symptom #7: Emesis
Emesis is a medical term for vomiting which can be defined as an involuntary expulsion of stomach contents through the nose and mouth. Emesis is a common and non-specific symptom seen in conditions such as gastritis, poisoning, brain tumors, cancer, chemotherapy, side effect of medications, and more.
It has been estimated that 20 to 60 percent of patients with advanced cancer may suffer from nausea and vomiting at some point in the disease.

Symptom #8: Ascites
Ascites is defined as fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity. As the liver functions become affected, many symptoms associated with cirrhosis may appear and this is one of the most common ones.
The fluid will accumulate in the peritoneal cavity and eventually if left untreated it can put pressure into other surrounding structures. It may even cause shortness of breath as the diaphragm struggles to push against the fluid in the abdomen.
Symptom #9: Confusion
Confusion is defined as a sudden or insidious change in an individual’s mental status. Depending on the cause, it can be transitory or progress into a more altered state of consciousness.
As the liver cancer progresses, it may cause a condition known as hepatic encephalopathy to appear. This condition is characterized by sudden changes in mental acuity, memory, mood and it can even result in a coma.

Symptom #10: Itching
Itching is also known as pruritus, the urge or sensation that causes the reflex or desire to scratch. Causes of itching can be categorized to infections, allergies, environmental, skin disorders, medical disorders, medication, pregnancy-related, and more. In liver cancer, the itching is attributed to jaundice.
This is known as cholestatic pruritus, which is itching due to any liver disease. Patients with cholestatic pruritus that have been given bile salt chelating agents report some relief.