10 Symptoms Of Eye Cancer
Eye cancer is rare. It may affect the outer areas of the eye, which consist of muscles, nerves, and skin. If the cancer originates in the eyeball, it’s known as intraocular cancer.
Melanoma and lymphoma are the most common types of intraocular cancer in adults. In children, the most common cancer of the eye is retinoblastoma, which begins in the retina cells. Cancer from other areas of the body can also reach the eye.
Eye cancer patients may experience the following signs or symptoms. Sometimes they don’t show any of the symptoms below, or the symptoms might be due to a medical problem that’s not cancer.

Symptom #1: Blurred Vision
If your eyesight is not sharp enough, you may have blurred vision. As such, objects will appear hazy and out of focus. Refractive errors, such as farsightedness, nearsightedness, and presbyopia (astigmatism) are the main causes of blurry vision. However, blurry vision can also indicate more serious issues, such as a potentially vision-threatening eye condition like eye cancer or a neurological disorder.
The initial blurring of eyesight can often be overlooked or attributed to refractory errors, necessitating the use of eye glasses. This seemingly harmless symptom must be examined by an ophthalmologist to rule out eye cancer, especially in people with eye cancer risk factors.

Symptom #2: Full/Partial Loss of Vision
Loss of vision is normal with aging. The primary causes of vision loss in people over the age of 40 include macular degeneration, cataracts, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy. Other common causes include infections, injury, and vision changes caused by certain illnesses, including eye cancer.
You may have partial or full loss of vision if you have difficulty going about your routine activities, including reading mail, reading a book, signing your name, paying bills, watching TV, or using the stairs. You may also have difficulty recognizing people. You might notice you squint so much in order to clearly see things.
Symptom #3: Peripheral Vision Loss
Peripheral vision issues mean you lack the normal, wide-angle vision field, although your central vision might be okay. Moderate and severe peripheral vision loss causes the feeling of seeing through something like a tunnel, a condition commonly known as tunnel vision.
One common cause of peripheral vision loss is optic nerve damage due to glaucoma. Occlusions (“eye “strokes”) that block the normal flow of blood to the internal structures of the eye, like the optic nerve, may also cause peripheral vision loss, and so can cancer of the eye. If you are experiencing this symptom, you should make an appointment to get it checked out.

Symptom #4: Eye Floaters
Eye floaters, characterized by spots or flashes in visual fields, are normal with aging. In fact, conditions like vitreous detachment, which lead to more floaters, more commonly occur after the age of 60. Everyone can have eye floaters at any time, though most people overlook them. Many can only notice them upon looking at a bright, blank surface or area, like the sky.
With eye floaters, patients may notice floating points, black spots, or wiggly lines in their vision. This problem is common with many eye disorders, including cataract and eye cancer. It requires thorough examinations to rule out eye cancer, especially in people at risk.

Symptom #5: Pain
Also called ophthalmalgia, eye pain can occur around the eye, on the eye’s surface, or inside the eye. The pain may be felt on the right eye, left eye, or both eyes. No eye is affected more frequently than the other. Eye pain is quite common, but it rarely indicates a serious problem. Most often, the symptom resolves without treatment or medication.
Eye pain due to eye cancer results from the pressure applied by the tumor of the eye. It happens when eye cancer affects nerves, adnexal structures, or moves to other parts. Most types of eye cancer rarely cause pain.

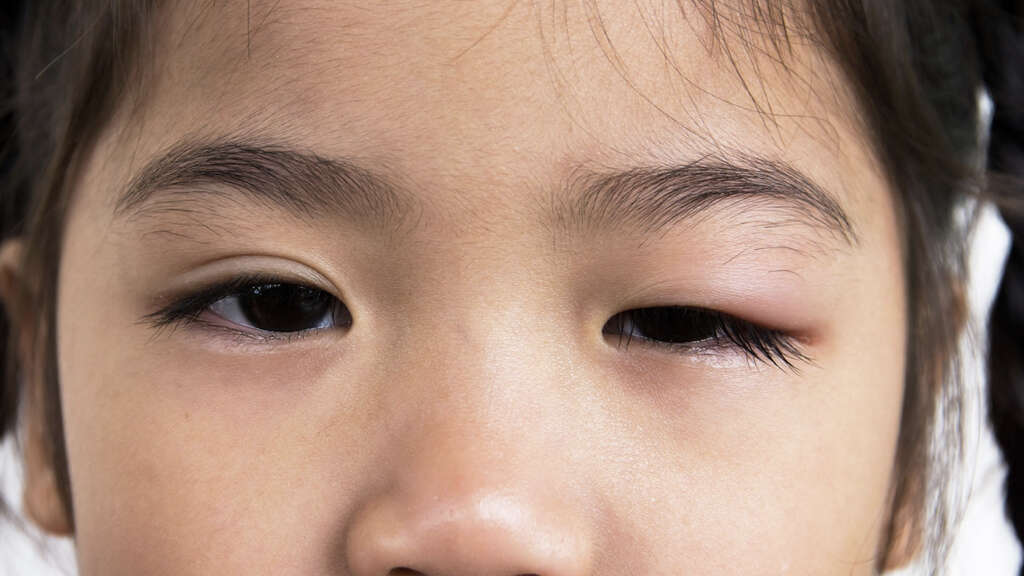
Symptom #6: Bulging of One Eye
Bulging of the eye(s) is known as exophthalmos. It might be seen kids with retinoblastoma, a form of eye cancer. It’s not similar to prominent eyes, though. Other possible causes of a bulging eye include leukemia, neuroblastoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, hemangioma, sarcoidosis, and rhabdomyosarcoma.
In people with a bulging eye, some characteristics and symptoms are a cause for alarm and should be attended to. They include double vision, decrease or loss of vision, eye redness or pain, headache, fever, and pulsation of the bulging eye. Bulging eyes are not a good sign, so you should see a medical professional to find out what the cause is.
Symptom #7: Crossed Eyes
If you have crossed eyes, it means your eyes gaze in different directions, with each eye focusing on a different item. The condition more commonly affects kids, but it may also develop in adulthood. In older kids, a range of underlying medical issues can cause crossed eyes, including stroke, cerebral palsy, and eye cancer.
If your eyes are crossed, they might point outward or inward or focus in different directions. You also might have double vision, impaired vision, decreased perception of depth, and headache or eyestrain. Your symptoms might be frequent or only appear when you’re not feeling well or are tired.
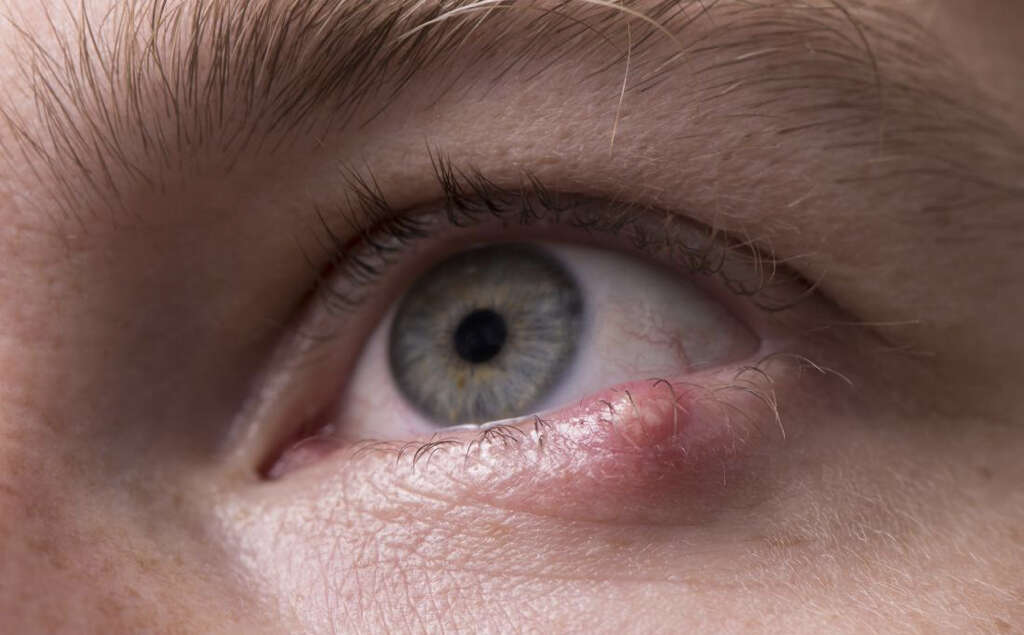
Symptom #8: Lump around the Eye or on the Eyelids
Issues on eyelids are quite common and seldom serious. There are several potential causes, so it’d be best to consult your doctor for a solid diagnosis. You should immediately seek medical attention if you experience loss of sight or pain in/around the eye.
In eyelid cancer, lumps can show up on or around your eyelids. The most common type of eyelid cancer is basal cell carcinoma—which occurs on the lower lid and results from staying in the sun for far too long. People with pale or fair skin are at higher risk. Eyelid cancer is often treated successfully if it’s detected early.
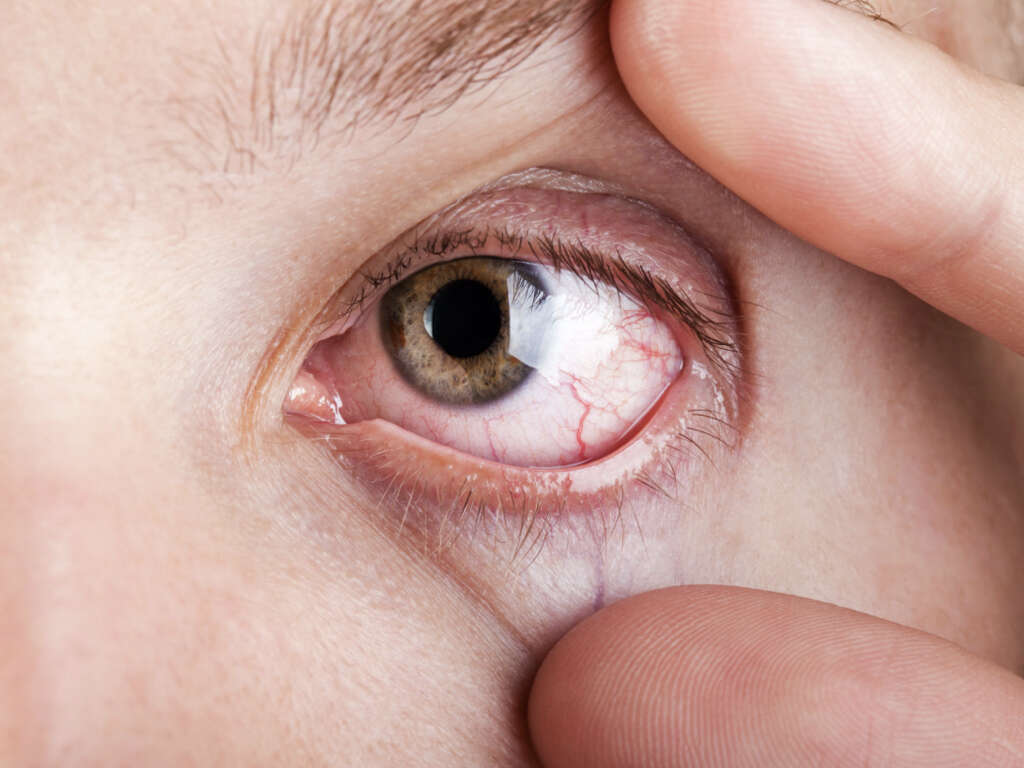
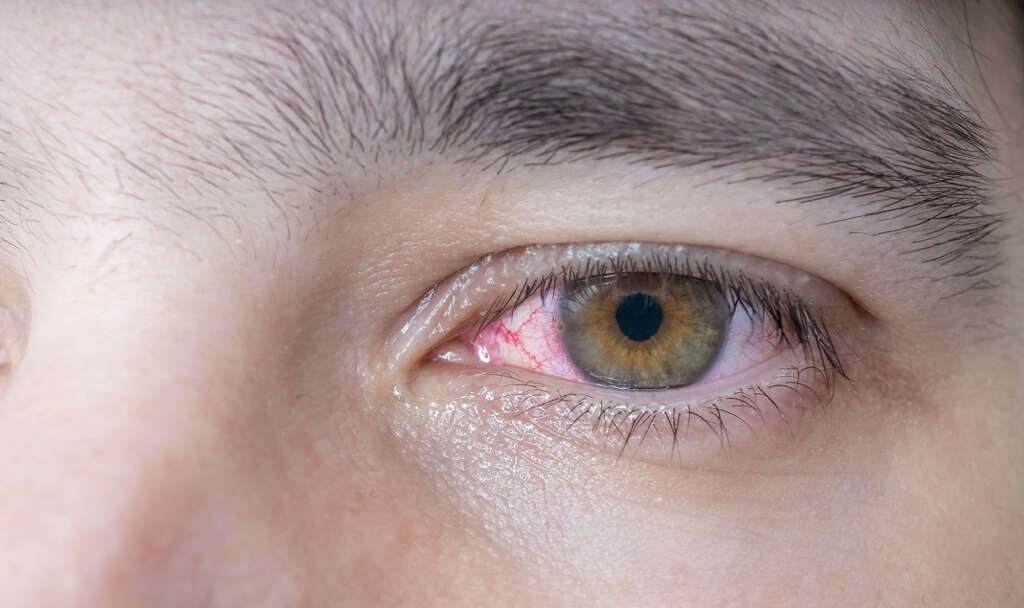
Symptom #9: Red Eyes
Red eyes occur when the whites of eyes get reddened or “bloodshot.” The look of red eyes may vary widely. It may appear that there are many squiggly red or pink lines on the whites of eyes or the whole whites of eyes may look diffusely red or pink. Red eyes may affect one eye or both.
Bloodshot or red eyes are quite common and are often a sign of other problems that can vary from benign to serious, including eye cancer. If you suddenly get red eyes, be sure to see your doctor to figure out the cause and the right way to treat it.
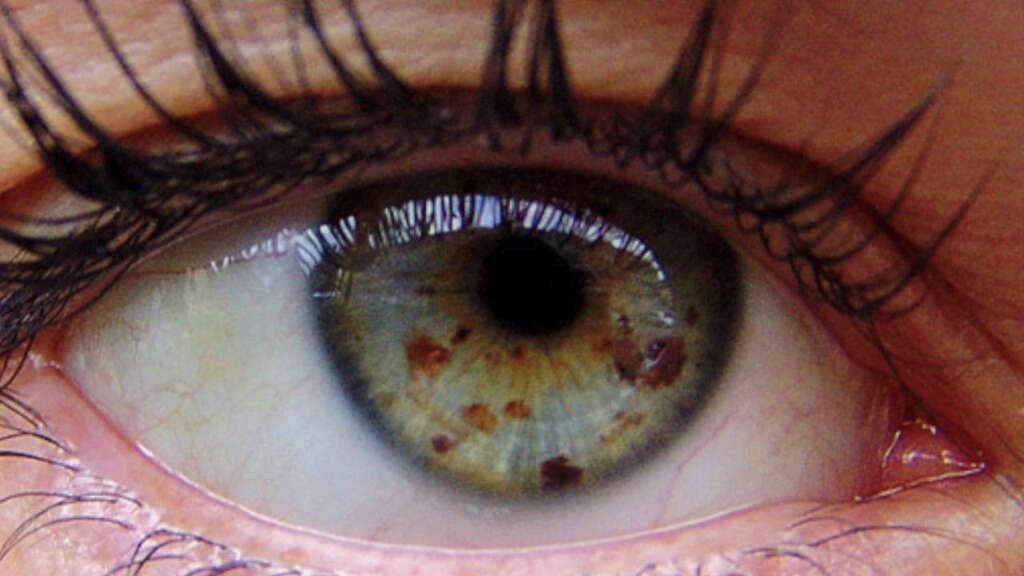
Symptom #10: Eye Freckles
You probably know all about skin freckles already, but are you aware that you can also develop dark spots on your eyes? Also called eye freckles, dark spots can develop on various areas of the eye, including the iris.
While most dark spots on the eyes are benign, it’s vital to have an ophthalmologist monitor them frequently, usually every 6–12 months, to record the shape, size, and any changes of freckle color. There’s a slight chance they can turn into eye cancer. The earlier the problem is detected, the sooner it may be resolved before it potentially becomes something more serious.