10 Stomach Flu Symptoms
The stomach flu, also known as gastroenteritis, is a very common condition. It is marked by an inflammation of the gastric or intestinal linings, and two of the main symptoms are diarrhea and vomiting.
The stomach flu can be caused by a number of pathogens, like bacteria, virus, or parasites. However, the most common cause of acute gastroenteritis are viruses (cause 50-70% of gastroenteritis). The main causes of acute viral gastroenteritis in children are rotavirus (group A), calicivirus (i.e. norovirus), astrovirus, and adenovirus. In adults and children, epidemic viral gastroenteritis is most commonly caused by caliciviruses (i.e. Norovirus). Few studies have examined the most common causes of sporadic viral gastroenteritis in adults. The most common species that cause bacterial gastroenteritis worldwide include, Salmonella, Shigella, Escherichia coli, and Campylobacter.
The stomach flu is very contagious, and it’s important that you avoid being in close situations with others if you don’t want to spread it. Make sure to follow through with basic hygienic practices like washing your hands to prevent the spread of disease.

Symptom #1: Diarrhea
One of the most common symptoms of the stomach flu is diarrhea. The World Health Organization defines diarrheas as 3 or more loose stools per day. Diarrhea can be entirely liquid or semi-liquid, and it tends to occur at a much higher frequency than regular bowel movements. The presence of bloody stools can indicate a more serious condition and the patient affected should seek immediate medical care.
Diarrhea is a sign that food is not being digested before being passed through the body, in this case because there is an inflammatory or disruptive infectious process in the gut. There can be bits of undigested food in the stool. Diarrhea is also a sign that your body is not absorbing the nutrients that it needs, so its important to take measures to ensure that you repair any nutritional imbalances that arise during your flu. Most importantly, excessive diarrhea can lead to dehydration. It is important for the patient to remain hydrated, by drinking plenty of fluids. Signs of dehydration include dry mouth, excessive thirst, concentrated or deep yellow urine, little or no urine output, severe weakness, dizziness or lightheadedness.
Symptom #2: Abdominal Cramping
One of the main reasons that the stomach flu can cause cramping is because it causes an inflammation of the gastrointestinal lining. This alone can cause discomfort and cramping, but it can also impede digestion and make it difficult to digest food.
This can cause things like bloating and excessive gas, both of which contribute to abdominal cramping. Oftentimes, people can reduce their abdominal cramping by going to the bathroom, but since the flu can cause diarrhea frequently, it might not subside for long.

Symptom #3: Nausea and vomiting
Other common symptoms of the stomach flu are nausea and vomiting. Nausea is the feeling of stomach upset that you get when you have eaten some bad food, when you are hungover, and, yes, when you are sick with the stomach flu.
There are many mechanisms involved in the generation of nausea sensation and vomiting in gastrointestinal infections. The important thing is to avoid dehydration by increasing the intake of oral fluids.
Adults with acute gastroenteritis should consult their doctor when symptoms increase in severity or last more than 5 days. Reasons to seek medical attention include dehydration, the presence of blood in your vomit, if severe vomit is present for more than two days, or If you’re not able to keep liquids down for 24 hours.

Symptom #4: Rash
Rash is an uncommon symptom of gastroenteritis. The presence of a rash may indicate that the cause of the stomach flu is bacterial.
Salmonella is a bacterium that can cause acute gastroenteritis, and enteric fever. Salmonella typhi causes typhoid fever. Symptoms for this disease include high fever, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, malaise, myalgias, headache, cough, diarrhea or constipation, and delirium. Patients with typhoid fever may develop a rash in the form of rose spots, usually located in the chest or abdomen.

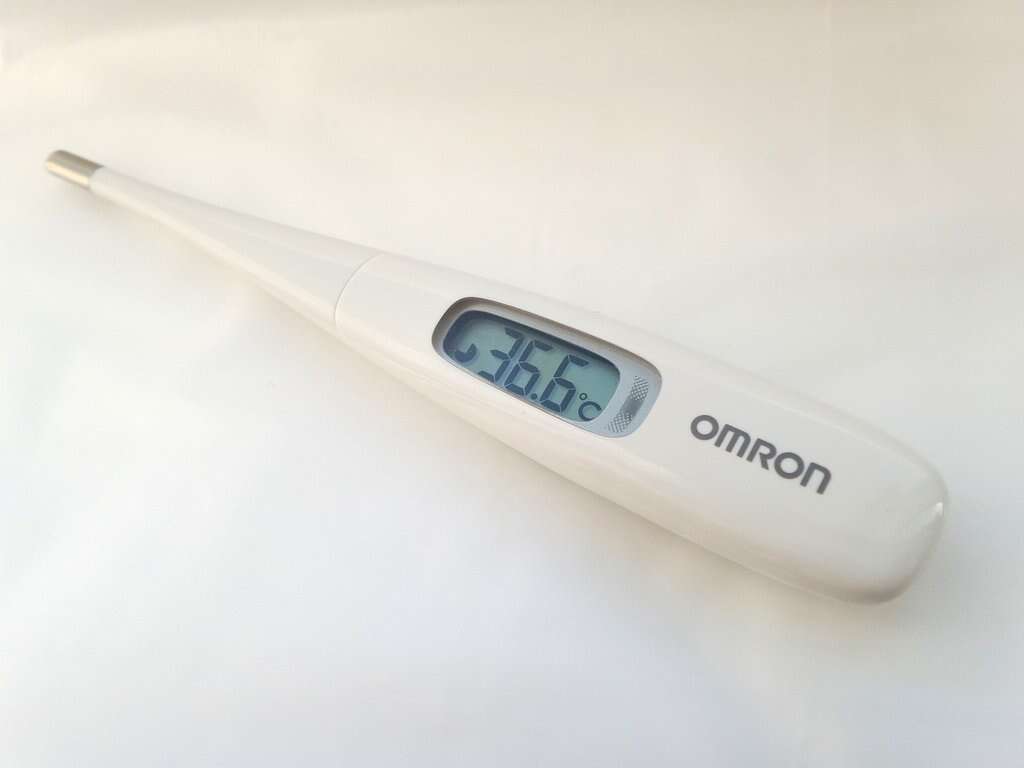
Symptom #5: Fever
Fevers are another very common symptom of the stomach flu. A fever occurs when the body’s internal temperature rises above its regular level and can be indicative of a number of problems.
In this case, the fever usually occurs because of an immune response. In the stomach flu, temperature may be slightly elevated and can be accompanied by chills. This can present as a prodrome, before the onset of watery diarrhea. Note that high fever may suggest bacterial infection. Consult with a physician if you exhibit fever above 104 F (40 C).
Symptom #6: Headaches
Headaches can be a symptom of the stomach flu. Most importantly, they can also be a sign of dehydration in the patient.
Acute gastroenteritis can cause fluid depletion through profuse diarrhea and vomit. This can decrease the body’s blood volume and cause dehydration and consequent hypotension, particularly when standing up after lying down (orthostatic hypotension). It can be accompanied by headaches, lightheadedness or dizziness. This can be especially dangerous in infants and elderly patients.

Symptom #7: Fatigue
Fatigue can be a common symptom, especially in viral gastroenteritis. Patients define it as tiredness or a complete lack of physical energy. It can occur with other nonspecific symptoms like fever, headache, body aches and chills. Therefore, the presence of fatigue can lead to confusion between the flu and gastroenteritis. The flu is a respiratory illness caused by influenza virus and it rarely causes vomiting and diarrhea.
Fatigue can persist for several weeks after the illness has resolved.

Symptom #8: Lethargy
Lethargy is a medical term to describe a pathological state of deep unresponsiveness and inactivity or sleepiness. This symptom can be a consequence of severe dehydration that can ensue with persistent diarrhea and vomit.
This symptom is most likely seen, and especially dangerous, in young children and older adults. When lethargy is observed, the patient is severely dehydrated and must receive medical attention. Other symptoms of dehydration in children include dry mouth, absence of tears when crying, absence of urine (measured by number of wet diapers) for several hours, sunken eyes, irritability or lethargy, and sunken soft spot on the top of the skull (sunken fontanelles).
Symptom #9: Weight Loss
The stomach flu can cause weight loss. The degree of weight loss can be related to the duration of the diarrhea and dehydration. In children, recent weight loss can be a good indicator of the degree of dehydration (or fluids lost), but this information is rarely available.
Another cause of stomach flu is giardiasis, a parasitic (protozoal) intestinal infection caused by Giardia intestinalis. Infection is more common in children than in adults, and it can be asymptomatic, acute or chronic. It can cause intestinal malabsorption with diarrhea, anorexia, malaise and weight loss. In adults, weight loss occurs in more than half of patients and averages 10 pounds. In chronic illness adults may present with long-standing malabsorption syndrome and children, with malnutrition and failure to thrive. Bacterial chronic gastroenteritis can also be a cause of these symptoms.

Symptom #10: Bloody stools
Acute gastroenteritis can be also caused by bacteria or parasitic infections. Some of these pathogens commonly produce inflammatory diarrhea, which usually suggests that they have an invasive mechanism of infection. Some of them can invade the intestinal mucosa and produce high fever and diarrhea associated with the presence of blood or mucous. Some invasive bacteria are salmonella, shigella or campylobacter. Infections caused by parasites (i.e. Entamoeba histolytica can cause amebiasis) or intestinal viruses (cytomegalovirus or adenovirus) can also cause this symptom.
On the other hand, a patient can suspect a viral cause of acute gastroenteritis when there is low-grade fever (or none), vomiting is prominent, in the presence of frequent watery stools, and when there is a short duration of the symptoms (less than 14 days). Most importantly, if you have severe symptoms that include bloody stools, seek medical attention for adequate antimicrobial therapy.