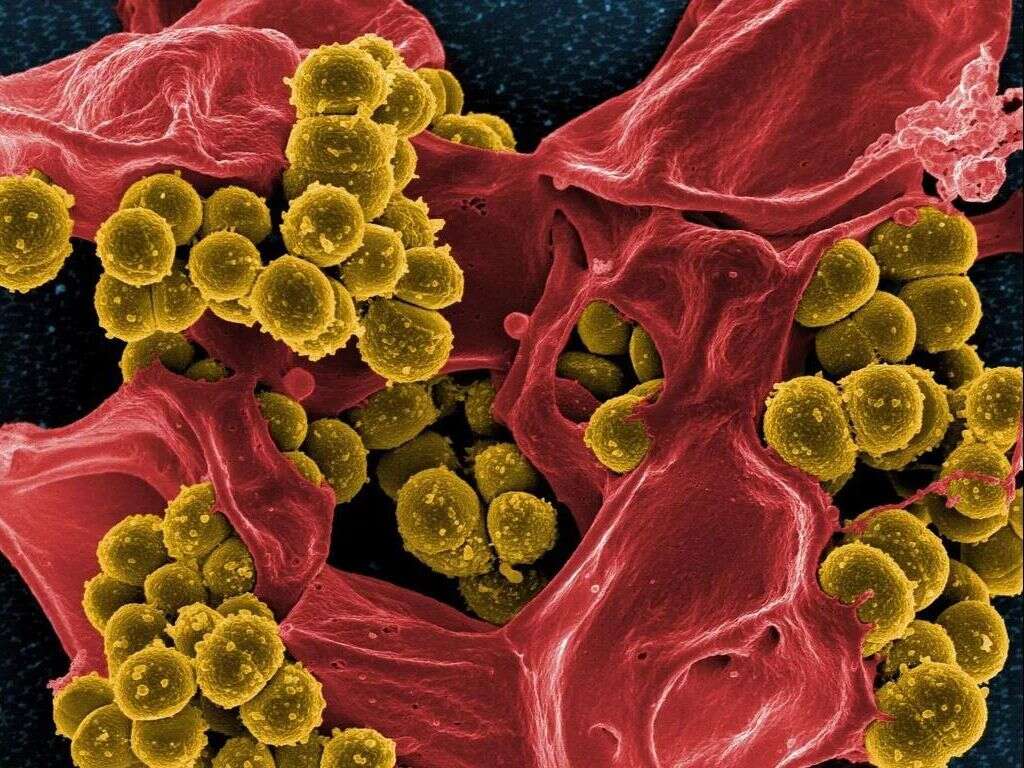
Staph Infections Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
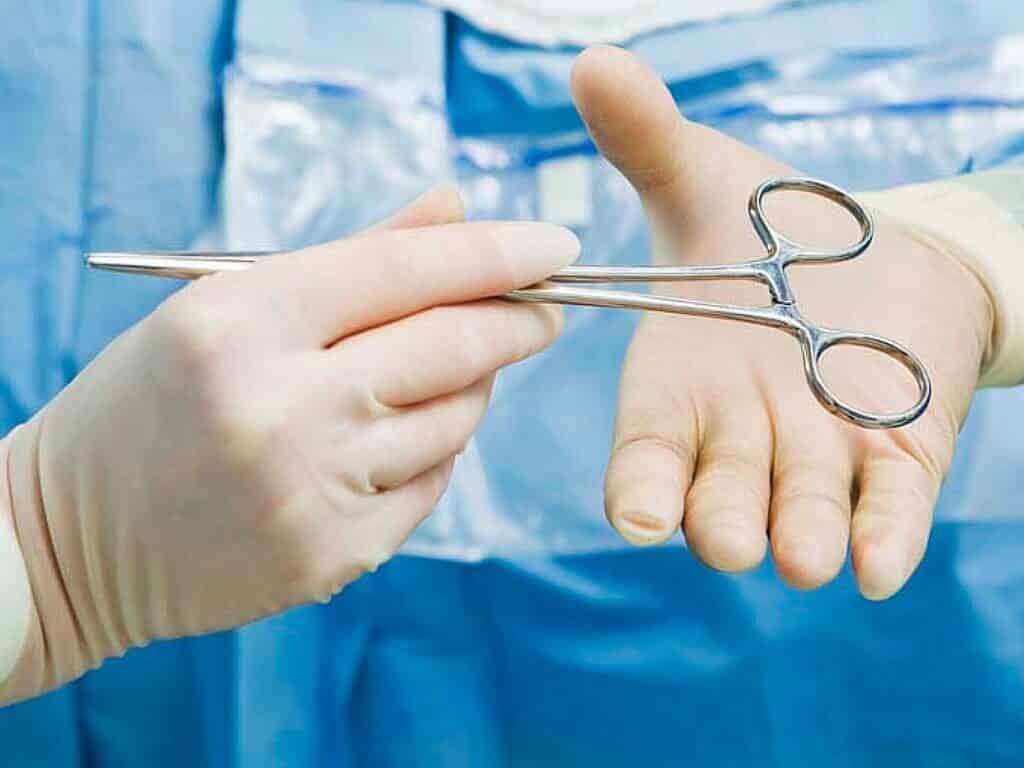
Treatment #2: Surgical Care
Surgical care for staph infections includes the drainage of abscesses, if any. Abscesses are full of bacteria, pus, and debris. The pocket of pus has to be drained to clear the infection; otherwise, the abscess may grow until it bursts on its own, causing extreme pain and allowing the infection to spread or recur. Without treatment or drainage, most abscesses will worsen, causing the infection to spread to deeper tissues and possibly the bloodstream.
Patients should not attempt to drain the abscess themselves because it may push the infection deeper. Sharp instruments should not be introduced since they can injure a blood vessel and cause the infection to spread into the bloodstream. If a prosthetic such as an artificial hip is infected, the prosthetic may need to be removed.
Advertisement






-06.jpg)