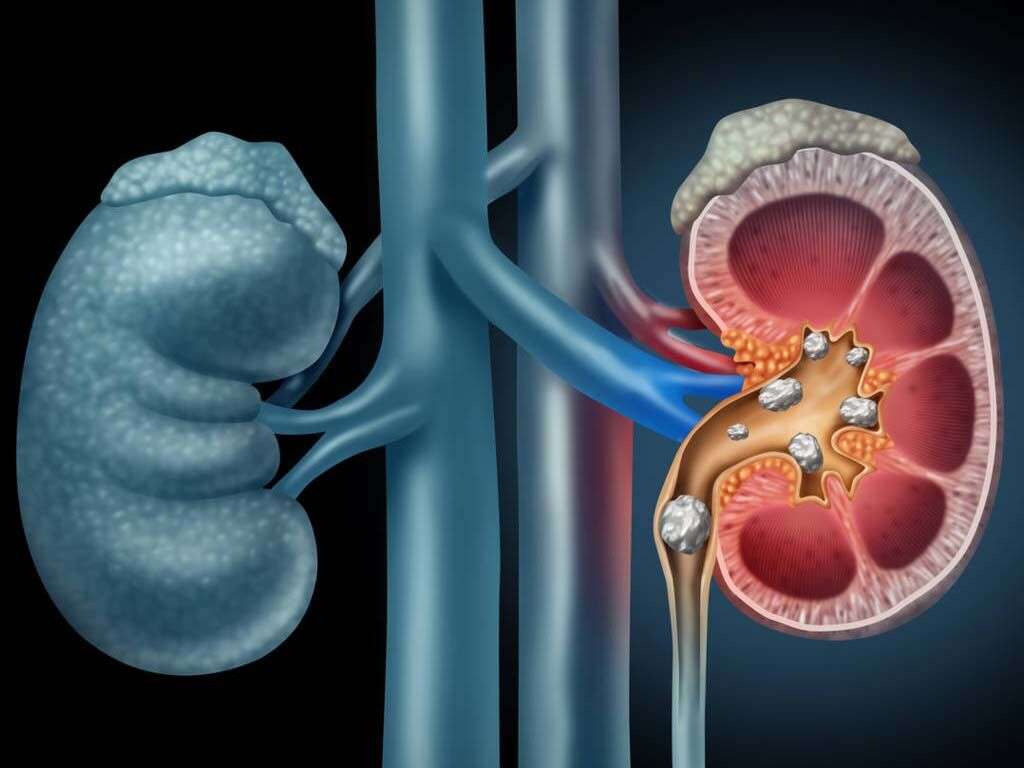
10 Signs of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are small stones that usually form in one or both kidneys due to the crystallization of certain salts. The majority of kidney stones are made of calcium salts that accumulate in the kidney. This condition is also known as renal calculi or nephrolithiasis and affects roughly 2 million people in the US each year. This condition is fairly common and it is seen more frequently in males.1Chirag N Dave, M. (2020, February 28). Nephrolithiasis https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/437096-overview
Scientific data suggests that the most important factor leading to kidney stones is having concentrated urine. Insufficient water intake is going to cause the concentration of calculi-forming salts in the kidneys, leading to nephrolithiasis. Certain drugs, particularly antibiotics and protease inhibitors used in the treatment of conditions like HIV, are known to cause kidney stones as well. A certain hereditary factor is also believed to play a role in the disease process.
Depending on the size and location of the kidney stones, they can cause different signs and symptoms. Usually, kidney stones cause no symptoms if they are small enough to be able to leave the body through the urine. Most of the symptoms associated with this condition are due to stones that become trapped in some portion of the urinary tract (usually the ureters, which are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder).
1. Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. The location and characteristics of the pain can help to distinguish between different pathologies and it can be very useful information to the clinicians in order to provide an accurate diagnosis.
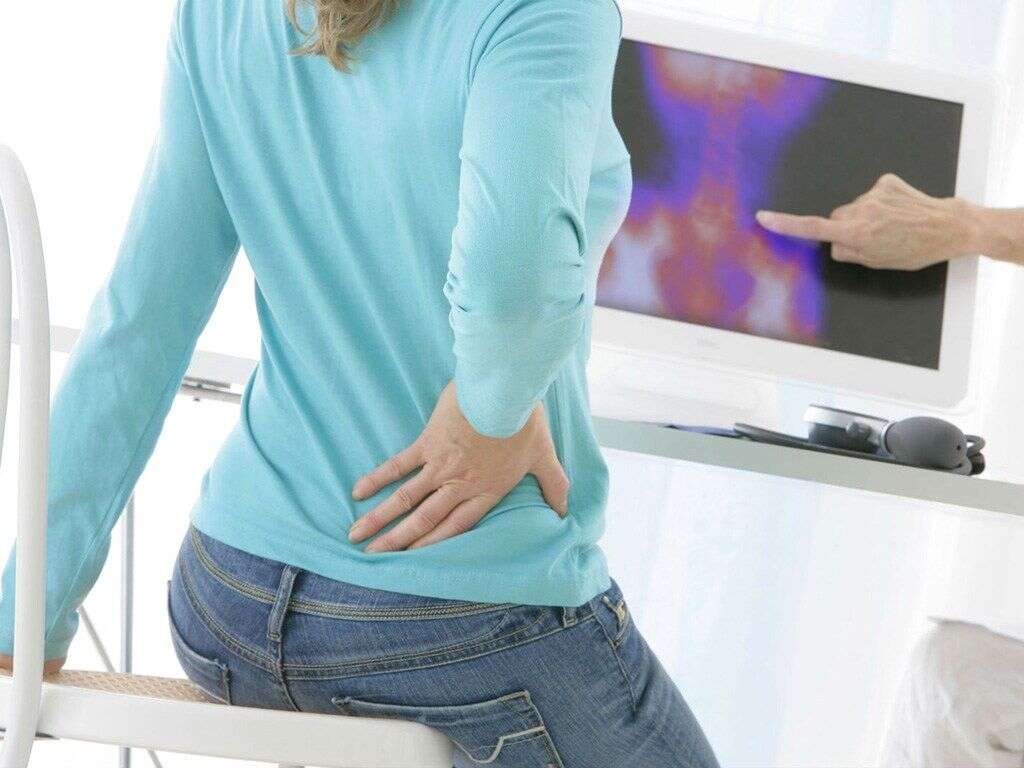
When a kidney stone becomes trapped in the urinary tract it can cause a great amount of pain. The stones usually get trapped in the ureters, which are the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Once a stone becomes trapped, the ureter is going to spasm causing the classic renal colic. Renal colic is characterized by sharp and sudden pain in the affected side of the abdomen. Usually, the pain comes and goes as the ureter spasms repeatedly. This pain is known to be quite severe and may last a few hours until it starts to calm down.

2. Back Pain
Pain in the lower back is one of the most common medical complaints worldwide. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. It can have an acute onset which is usually seen in conditions affecting the musculature of the back, but sometimes it can have an insidious onset which makes it harder to diagnose.
Depending on the location of the stone, it may cause different signs and symptoms. Kidney stones that become trapped in the lower portion of the ureter (where the ureter and bladder meet), are known to cause lower back pain. It is also possible for the back to be tender to the touch if the affected kidney is struggling to push urine out due to the blockage in the urinary tract.
3. Groin Pain
Groin pain is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions. Given the many muscles that are located in this region, it is common to experience groin pain due to muscle cramps, tears, and/or strains. Muscle injuries usually have an acute and sudden onset right after the causing trauma takes place. Other conditions like hernias and even nephrolithiasis are also known to cause pain in the groin.
Kidney stones that get trapped in the lower portion of the ureter may cause groin pain. Testicular pain in males and pain in the labia majora for females are also reported by patients with nephrolithiasis. This is called referred pain and it is explained by the shared neural pathway in the region.

4. Dark or Red Urine
Hematuria is the medical term used to describe blood in the urine. When a patient is able to see blood in their urine, this is called macroscopic hematuria. On the other hand, some patients may have blood in their urine but the amount is so low that it is only visible during a urine analysis, this is called microscopic hematuria.
More than 50% of the patients suffering from kidney stones have either macroscopic or microscopic hematuria. As the stone passes through the urinary tract, it may damage it, causing blood to appear in the urine.
5. Pain During Urination
Dysuria is the medical term used to describe the presence of pain during urination. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions such as urinary tract infections (UTI), kidney stones, and sexually transmitted infections (STI) to name a few. This symptom is often described as a burning sensation during urination and it can be quite a painful experience.
This symptom can be seen in patients with kidney stones that are lodged in the point where the ureter joins with the bladder. It can also be a sign that an underlying urinary tract infection might be present as well.

6. Nausea
Nausea is commonly defined as the urge to vomit. It can appear suddenly but in some cases, it has an insidious onset. It is a non-specific symptom that can be associated with many conditions, but it can also be triggered by certain events or things in our surroundings.
Most patients with renal colic are going to experience nausea and even vomiting at some point. As the pain increases over time, the patient is likely to experience certain signs and symptoms that are due to the extreme level of pain. A person with severe abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to prevent further complications.

7. Frequent Urination
An increase in the normal urinary frequency is known as pollakiuria. This is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. It can be a condition on its own, or it can be linked to another condition in the urinary system such as urinary tract infections (UTI), kidney stones, and issues with bladder emptying.
Kidney stones that are located in the lower portion of the ureter are known to cause voiding problems like urinary frequency and pain during urination. Usually, the patient goes many times to urinate but only manages to pass little to none urine at all.

8. Increased Heartrate
Tachycardia is the medical term that describes a rapid heartbeat. It is medically defined as a heart rate that goes above 100 beats per minute. Depending on the situation, an increased heart rate can be perfectly normal. Exercise and extremely stressful situations will cause the heart rate to increase and it is a perfectly normal response to these events. On the other hand, conditions like anxiety and cardiac arrhythmias may also cause a person to experience tachycardia.
During the peak of renal colic, it is normal to experience an increase in the heart rate. This is a normal finding associated with the pain caused by the ureter spasm. Usually, the pain during renal colic increases over time until it reaches a point where it stays the same for a few hours, and then starts to get better.
9. Fever
A fever is an increase in body temperature. Usually, the temperature should be above 38⁰C (100.4⁰F) in order to be considered as a fever, but this depends on the site where the temperature is being measured. A fever is usually a response of the body to a threat. By increasing the body’s thermostat set point, we start to shiver to generate heat in order to reach the new temperature that has been set.
This is not a very common finding associated with kidney stones, nevertheless, it might appear in patients with an underlying urinary tract infection. It can also be seen in patients experiencing complications from nephrolithiasis.

10. Profuse Sweating
Sweating is a normal event for most of us. It is a useful way to dissipate heat and maintain normal body temperature. During exercise, the increased muscle activity causes the body to become increasingly hot. As a thermoregulatory mechanism, we start to sweat to cool down. There are many scenarios where a person might start to sweat without being physically active. Some of these scenarios are normal and others can be associated with many conditions.
During the peak of renal colic, it is quite normal for a person to start sweating profusely. This is a common finding due to the excruciating pain associated with kidney stones. Other symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and tachycardia are also common.