10 Signs of Diabetes
Diabetes is a group of metabolic disorders where there are prolonged elevated blood sugar levels. Untreated diabetes can lead to complications such as hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, diabetic ketoacidosis, and death. Long-term, it can cause issues with the kidneys, heart, eyes, and disorders such as foot ulcers and stroke. Diabetes can occur when there is insulin resistance or inadequate insulin production by the pancreas.
There are 3 main types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is usually seen among younger patients and occurs when the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes occurs when there is insulin resistance and is more commonly seen among adult patients. Gestational diabetes is seen among pregnant women without a previous history of diabetes. Control and prevention of diabetes can be done through maintenance of a healthy diet, normal body weight, regular exercise, and avoidance of tobacco. To prevent complications, it is important to teach patients regarding proper foot care and blood pressure control.
Diabetes Sign #1: Weight Loss
Weight loss occurs when there is a total reduction of body mass due to loss of adipose tissue, muscle, fluid, bone mineral deposits, or other connective tissue. Weight loss can occur both intentionally and unintentionally. Unintentional weight loss usually occurs due to malnourishment or underlying disorder such as cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, gastritis, pancreatitis, diarrhea, infection, renal disease, diabetes, and more.
Weight loss can occur when there is impaired intake of food, impaired absorption or digestion, altered metabolic demands, or excessive nutrient loss.
Diabetes Sign #2: Polydipsia
Polydipsia refers to excessive thirst and drinking. It is a non-specific symptom that is seen in various medical disorders. It is one of the main characteristics seen among patients with undiagnosed diabetes or uncontrolled diabetes.
Polydipsia occurs due to the change of osmolality of the extracellular fluids, decreased blood volume, hypokalemia, and more. Polydipsia can be differentiated into psychogenic and non-psychogenic polydipsia. Psychogenic polydipsia is seen among patients with mental illnesses while non-psychogenic polydipsia can be seen among those with organic disorders.

Diabetes Sign #3: Polyuria
Polyuria refers to an abnormally excessive passage of urine. By definition, it occurs when urine output is more than 2.5 to 3 liters over 24 hours in adults. The large volume of urine is often accompanied by frequent urination and increased thirst.
Polyuria is often a symptom or sign of a disorder. It can be seen in uncontrolled diabetes, caffeine consumption, use of diuretics, hypokalemia, hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism, hyperglycemia, heart failure, and many more. in diabetes, polyuria occurs due to osmotic diuresis. This is when the glucose levels are so high that it is excreted in the urine along with water which leads to polyuria.
Diabetes Sign #4: Polyphagia
Polyphagia is a term that refers to increased appetite or excessive hunger. Polyphagia can be seen in various disorders such as diabetes, anxiety, depression, hyperthyroidism, hypoglycemia, stress, fatigue, premenstrual syndrome, bulimia, and more.
In uncontrolled diabetes, glucose cannot enter the cells due to insulin resistance or lack of insulin. This means that the body is unable to convert the consumed food into energy. The lack of energy results in severe hunger.

Diabetes Sign #5: Lethargy
Lethargy refers to a state of weariness, tiredness, lack of energy, and fatigue. Lethargy can be accompanied by decreased motivation, depression, and apathy. It can also be a normal response to overexertion, sleep deprivation, lack of exercise, overworking or improper nutrition.
In normal cases, lethargy usually resolves with a combination of rest, adequate sleep, nutrition, and physical exercise. Lethargy in diabetes can occur when there is low blood sugar, especially in Type I diabetes.
Diabetes Sign #6: Worsening Vision
Diabetes is a condition that can have a significant impact on your eyesight. The persistent state of hyperglycemia leads to permanent damage within the blood vessels. When this happens in the retina, it is called diabetic retinopathy. It is the most common cause of vision loss among diabetics.
Other diabetic eye diseases include diabetic macular edema, cataract, and glaucoma. All diabetics are at risk for diabetic retinopathy. It is important for diabetic patients to maintain regular checkups with an ophthalmologist to prevent any complications.

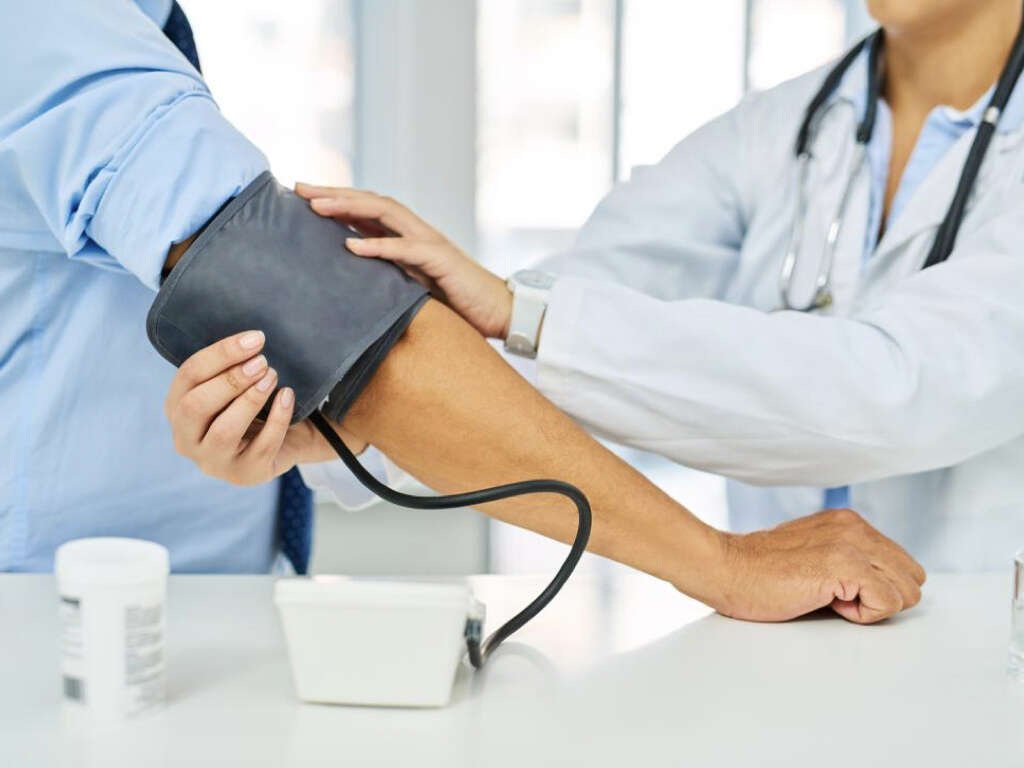
Diabetes Sign #7: Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a chronic condition where the blood pressure in the arteries is consistently high. Long-term high blood pressure can increase the risk of stroke, heart disease, atrial fibrillation, heart failure, kidney disease, peripheral vascular disease, dementia, and more.
Factors that increase the risk of hypertension include smoking, excess body weight, alcohol use, and excessive salt in the diet. Studies have observed that about 33 percent of patients with diabetes also have hypertension. Chronic diabetes that affects the kidneys can also cause hypertension.
Diabetes Sign #8: Yeast Infections
Diabetic patients are more prone to suffer from yeast infections.
Yeast lives in our bodies without causing any harm, but given the immunocompromised state and the increased glucose levels seen in diabetics, yeasts can grow at a faster rate and cause complications.

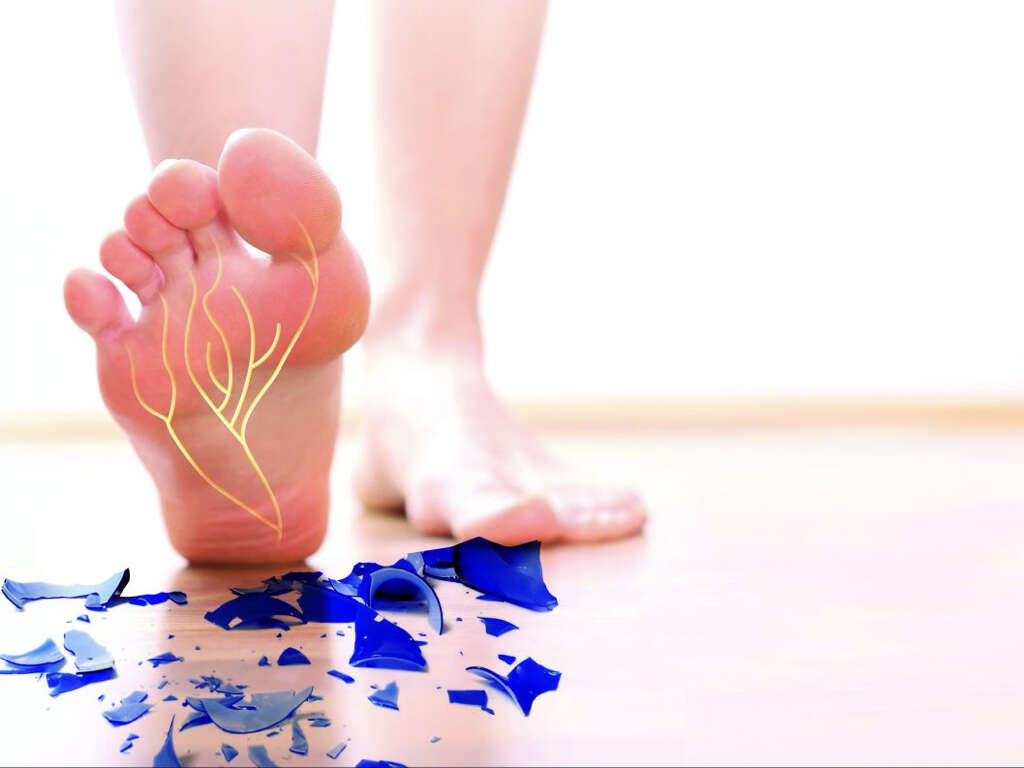
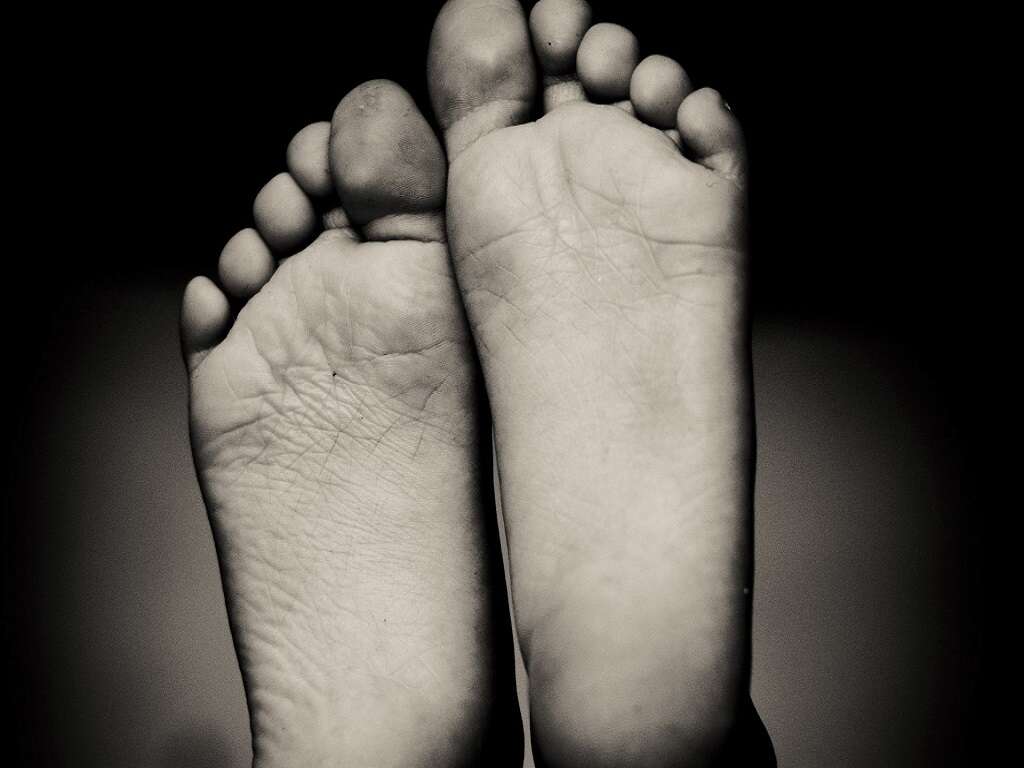
Diabetes Sign #9: Foot Numbness
Diabetes is also a condition that is associated with poor circulation causing red blood cells to move more slowly. The poor circulation and poor blood sugar control can cause nerve damage which leads to foot numbness. This is also known as diabetic neuropathy.
If left uncontrolled, it can lead to serious complications such as numbness and pain. Foot numbness also makes it hard for diabetics to tell if there is a wound, increasing the risk of infection and amputation.
Diabetes Sign #10: Poor Healing
Diabetes is a condition that can cause wounds to heal more slowly. Since cuts and wounds can be a part of life, it can be detrimental for diabetics as these issues can fester and become infected. some diabetics even have wounds that never heal. The infection can even spread to the surrounding bone and tissue causing sepsis that may result in death.
This is why diabetics should check their foot for wounds and ulcers as the poor healing can lead to amputation. Poor healing occurs as the high blood glucose impairs the function of white blood cells impairing their ability to fight bacteria.