10 Pyelonephritis Symptoms
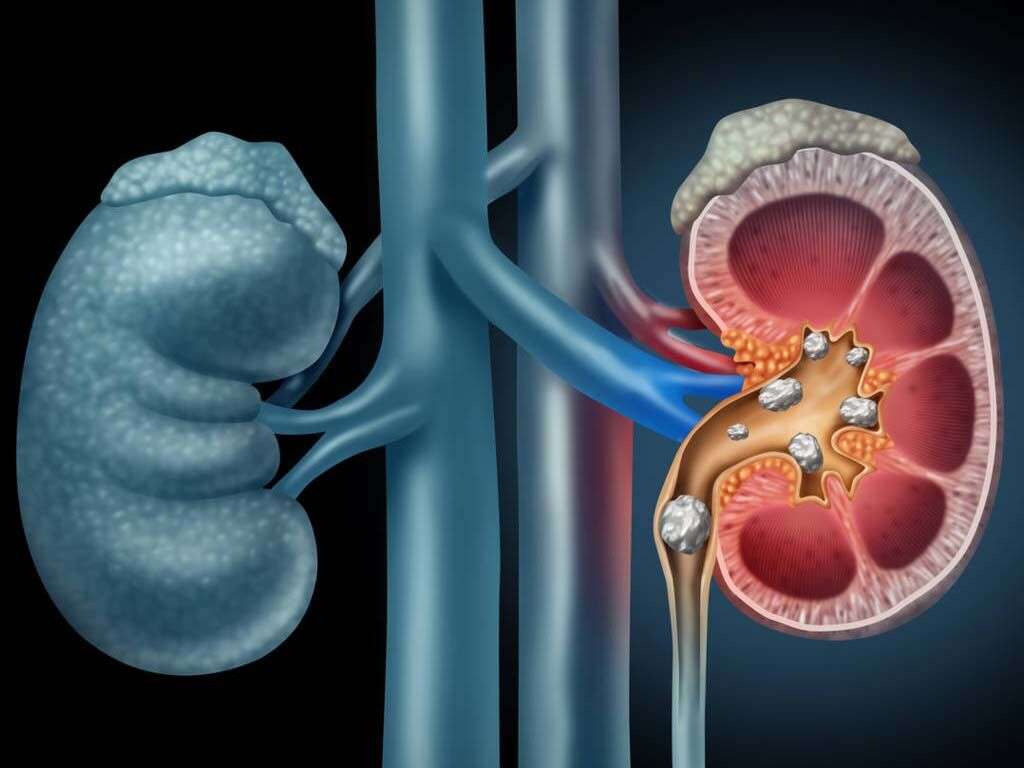
Pyelonephritis is a condition where the affected kidney is inflamed usually because of a bacterial infection such as Escherichia Coli. The risk factors of pyelonephritis include diabetes, sexual intercourse, structural issues with the urinary tract, previous urinary tract infections, spermicide use, and more. Pyelonephritis usually occurs when the infection spreads up the urinary tract. Another possible less common route of infection is through the bloodstream. Pyelonephritis diagnosis can be achieved based on the patient’s symptoms and tests such as urinalysis. Medical imaging may be required.
Treatment of pyelonephritis usually involves the use of antibiotics such as ceftriaxone and ciprofloxacin. Severe cases may require in-patient treatment. Patients with kidney stones or structural issues of the urinary tract may require surgery. Pyelonephritis is a common condition where it affects 1 to 2 per 1000 women and slightly under 0.5 per 1000 men annually. Pyelonephritis most commonly affects young adult females. Prognosis is usually good among young adults.
Symptom #1: Fever
Fever occurs when the set point of body temperature increases beyond the normal range. It is also known as a febrile response or pyrexia. The increase in the set point of body temperature leads to muscle contractions and a feeling of coldness. This causes an increase in the production and conservation of body heat.
Fever is a very common symptom that can usually be seen in any infection (viral, bacterial, or parasitic). It can also be seen in non-infectious causes such as deep vein thrombosis, vasculitis, cancer, and side effect of medication. Antipyretics such as paracetamol (acetaminophen) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help to lower the temperature.

Symptom #2: Flank Tenderness
Flank tenderness is also known as costovertebral tenderness or Murphy’s punch sign. It means that there is pain when the area on the back overlying the kidney or costovertebral angle is percussed.
This area can be elicited by looking for the angle made by the costal margin and vertebral column. Flank tenderness is found in patients with perinephric abscess, renal stones, and pyelonephritis.
Symptom #3: Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is an uncomfortable and unpleasant sensation where it results in an urge to vomit. Although there is no pain, nausea can be debilitating as it causes discomfort in the upper abdomen, chest, and throat. It is the body’s way to discourage the person to not repeat their actions that may have resulted in nausea.
Vomiting is the involuntary expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth and nose. Both nausea and vomiting are non-specific symptoms that can be caused by motion sickness, migraine, hypoglycemia, dizziness, fainting, food poisoning, and more. Symptomatic treatment may include the use of antiemetics such as ondansetron or metoclopramide.

Symptom #4: Burning Sensation During Urination
A burning sensation during urination is also known as dysuria. The term “dysuria” can also be used to describe painful urination or difficult urination. It is one of the hallmarks of irritation in the bladder.
Other associated symptoms may include increased urinary frequency and nocturia. Dysuria can be seen in bladder tumors, sexually transmitted diseases, bladder stones, urinary tract infections, pyelonephritis, and more.

Symptom #5: Frequent Urination
Frequent urination occurs when the affected individual notices that he or she has a need to urinate more frequently. It is usually associated with urinary urgency where the patient often has an urgent need to urinate.
It can occur in urinary tract infection, interstitial cystitis, urethral inflammation, bladder cancer, diabetes mellitus, pregnancy, pyelonephritis, and more. Alcohol or caffeine use are also common causes.

Symptom #6: Tachycardia
It is usual for a patient suffering from an infectious disease to have an increased heart rate. The fever seen in patients with pyelonephritis is the main cause for this symptom to appear, although sympathetic activation due to the pain caused by the infection can also cause it.
The increase in heart rate may be an early sign that the infection is progressing, therefore, if you are having this symptom it is important to seek medical attention to prevent further complications like sepsis.

Symptom #7: Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort where there is pain or uneasiness. It is usually one of the first indications of disease or infection. It is a non-specific symptom that can be observed in even the slightest ailment such as hunger and feeling faint. It is also seen in serious conditions such as stroke, cancer, internal bleeding, heart attack, and many more.
Patients with malaise often express it as “feeling that something is not right”. Experts believe that malaise is due to the activation of an immune response and pro-inflammatory cytokines.

Symptom #8: Loss of Appetite
Loss of appetite or anorexia is believed to be part of the acute phase response when there is an infection. It is thought to be triggered by peptidoglycans and lipopolysaccharides from bacterial cell walls, DNA, viral DNA, and viral glycoproteins.
The release of proinflammatory cytokines enhances the production of leptin which suppresses appetite. Appetite loss is seen in pneumonia, viral hepatitis, anxiety, cancer, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, dehydration, dementia, fever, hypothyroidism, and more. Appetite loss usually leads to weight loss.

Symptom #9: Hematuria
Hematuria is the medical term used when there is presence of blood in the urine. Gross hematuria is hematuria that is visible to the human eye where the urine is seen to be pinkish, red, or brown. Microscopic hematuria is blood in the urine that is only visible through urinalysis or dipstick test.
There are many causes of hematuria such as bladder cancer, kidney stones, renal cancer, prostate cancer, testicular cancer, urinary tract infection, pyelonephritis, and more. In pyelonephritis, other associated symptoms of hematuria include flank pain and fever.

Symptom #10: Tachypnea
Tachypnea refers to abnormally fast breathing. In a normal adult, the respiratory rate per minute ranges from 12 to 20. Causes of tachypnea include pneumonia, carbon monoxide poisoning, pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, foreign body aspiration, heart failure, anxiety, laryngospasm, and sepsis.
Tachypnea is one of the symptoms in pyelonephritis that has progressed to sepsis. Other signs and symptoms of septic shock include low blood pressure and delirium.