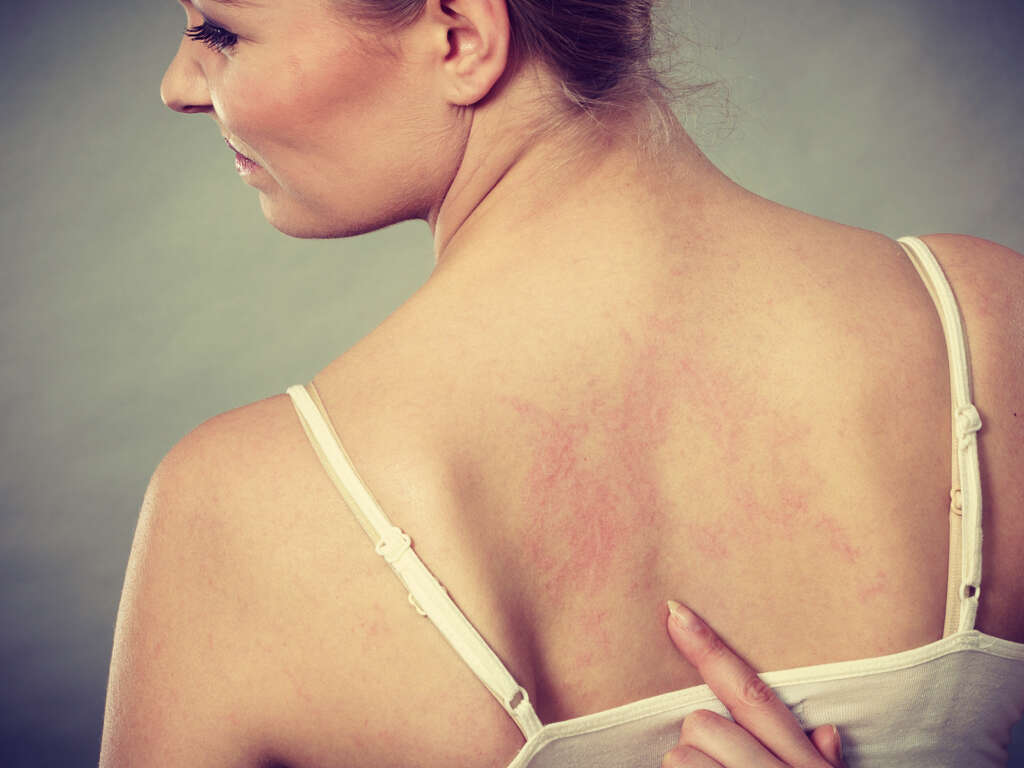
10 Pityriasis Rosea Facts
Fact #10: Is a Clinical Diagnosis
Pityriasis rosea is mostly diagnosed clinically. This means that the diagnosis is achieved based on the patient’s history and physical examination. Most tests are unnecessary or helpful. Literature states that changes in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), white blood cell (WBC) count, globulin level, total serum protein level, and albumin level are rare and minimal.
When a herald patch is first present, a potassium hydrochloride (KOH) test can be used to rule out tinea corporis. A rapid plasma reagin (RPR) or venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test can also be used to rule out secondary syphilis. Another beneficial test is a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) test to rule out the disorder.
Advertisement