Myotonic Dystrophy Definition, Causes and More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/muscular-dystrophy/
- 2. 'Myotonic Dystrophy.' Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10419/myotonic-dystrophy.
- 3. 'The Myotonic Dystrophies.' Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.
Muscular dystrophy is a group of rare genetic diseases that gradually cause muscles to weaken.1NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/muscular-dystrophy/ Myotonic dystrophy is the most common form of muscular dystrophy to start affecting people in adulthood. Usually starting in their 20s or 30s, people with myotonic dystrophy may notice progressive muscle weakness as well as being unable to relax some muscles after use.2‘Myotonic Dystrophy.’ Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10419/myotonic-dystrophy.
The severity of myotonic dystrophy varies widely from life threatening to barely noticeable. Although there is currently no cure, there are treatments available. Understanding this rare disease and the resources available can be helpful for those with myotonic dystrophy and their loved ones.3‘The Myotonic Dystrophies.’ Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.

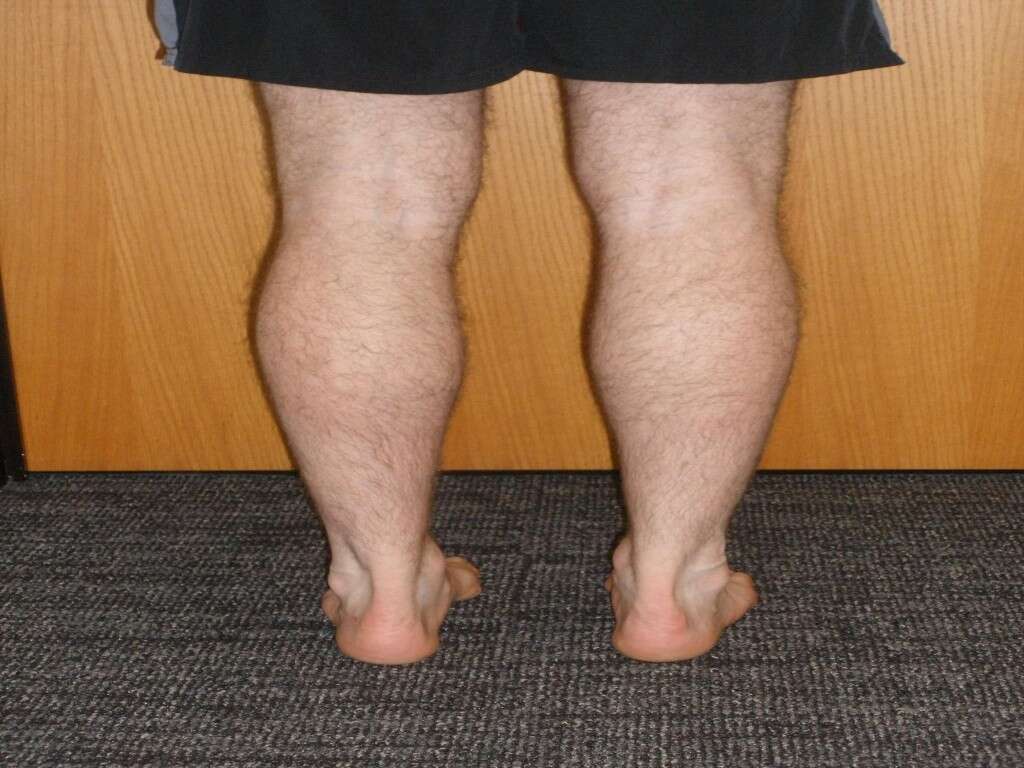
1. Muscular Symptoms of Myotonic Dystrophy
The age at which symptoms start and their severity vary widely depending on the type of myotonic dystrophy a person has. The earlier symptoms begin, the more severe they're likely to be.
Typically, a person with myotonic dystrophy notices weakness in smaller muscles, such as the ones in their face, eyelids, jaw and neck. They may have difficulty gripping objects or trip over their own feet. They may also notice muscle stiffness in their hands and jaw. These symptoms often start in adulthood and progress very slowly. Some people with myotonic dystrophy never experience severe symptoms and their lifespan is not affected.3‘The Myotonic Dystrophies.’ Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.

2. Other Symptoms of Myotonic Dystrophy
Some symptoms of myotonic dystrophy may be less predictable. Many people with myotonic dystrophy develop cataracts, which are usually slow to form and can be treated. Weak muscles in the throat may cause difficulty swallowing. Those with myotonic dystrophy may cough or sputter while drinking or eating.3‘The Myotonic Dystrophies.’ Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.
A slow heartbeat, dizziness and fatigue may also cause problems. In some types of myotonic dystrophy, these symptoms can shorten a person's life span, with severely affected people sometimes only living a few years.1NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/muscular-dystrophy/

3. Types of Myotonic Dystrophy
There are two major types of myotonic dystrophy. Type 1, which is the more common form, tends to be more severe than Type 2. People with Myotonic Dystrophy Type 2 may not experience much muscle stiffness if any, and while they are at risk of heart complications, these tend to be milder than in Type 1.3‘The Myotonic Dystrophies.’ Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.
One variation on Type 1, called Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy, causes babies to be born with muscle weakness, breathing problems and delays and is often very severe.1NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/muscular-dystrophy/

4. Causes of Myotonic Dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy is inherited. A mutation of certain genes is passed from parent to child. It's not fully understood how this mutation causes myotonic dystrophy, only that it does.
The gene mutations that cause myotonic dystrophy are dominant, meaning there's a roughly 50/50 chance a parent with myotonic dystrophy passes it on. It also has a trait called anticipation, where the disease can become more severe and present earlier as it's passed down through more generations.2‘Myotonic Dystrophy.’ Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10419/myotonic-dystrophy.

5. Pregnancy and Myotonic Dystrophy
A future parent with myotonic dystrophy may worry about their child inheriting a more severe form or about their own health or their baby's during pregnancy. These worries are understandable, and seeking medical advice can help create the best health outcomes for parent and child.
A doctor who knows a pregnant person has myotonic dystrophy can monitor the pregnancy for complications. A genetic counselor can give a couple insight on how likely certain types or severities of myotonic dystrophy are to affect their children.3‘The Myotonic Dystrophies.’ Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.

6. Diagnosis of Myotonic Dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy is usually diagnosed through a medical exam. Doctors look at which muscles are weakening and whether there is myotonia, or muscle stiffness. Medical history is also considered, and it's important to tell a doctor if myotonic dystrophy runs in the family.
Laboratory tests may be used, including a muscle biopsy and inserting a small needle into the muscle to measure electrical activity. A genetic test on the saliva or blood is the most definitive way to identify myotonic dystrophy.2‘Myotonic Dystrophy.’ Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10419/myotonic-dystrophy.
7. Treatments for Myotonic Dystrophy
While there's no cure for myotonic dystrophy, there are treatments available that can help manage symptoms. Some people's symptoms are so mild they don't require any treatment.
Physical therapy and regular exercise can help strengthen muscles and may slow the progression of the illness. Mobility aids like canes or wheelchairs may also be helpful. Pain medication may be prescribed. Men may need testosterone replacement therapy for infertility. In extreme cases, pacemakers, surgery and medications may be needed to help with heart and eye issues.2‘Myotonic Dystrophy.’ Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10419/myotonic-dystrophy.

8. What To Tell Your Doctor
Because myotonic dystrophy is a rare disorder that can present with mild symptoms, a doctor may not necessarily be aware a person has it until they're told.
If a person with myotonic dystrophy needs surgery, it's especially important that the anesthesiologist and surgeon know. General anesthesia can be extremely dangerous for people with even mild myotonic dystrophy. A person with myotonic dystrophy should carry an alert card so doctors know to provide appropriate emergency care. Issues usually only occur when the doctor is unaware.3‘The Myotonic Dystrophies.’ Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.

9. Research Into Myotonic Dystrophy
Current research is being conducted on how gene editing may be used to remove the mutation that causes myotonic dystrophy.2‘Myotonic Dystrophy.’ Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10419/myotonic-dystrophy. Recent advances have given researchers a lot of important information on the illness and how it's caused, which may one day lead to a cure.
Some potential treatments have had very promising results on mice. However, mice and humans are very different and it may still be some time before it's proven that these treatments are safe and effective for people.3‘The Myotonic Dystrophies.’ Muscular Dystrophy UK, www.musculardystrophyuk.org/about-muscle-wasting-conditions/myotonic-dystrophy/myotonic-dystrophy-factsheet/.

10. Resources for Myotonic Dystrophy
Living with myotonic dystrophy may be isolating and frightening at times. Many people with muscular dystrophy live a full and happy life, but support can be helpful as well.
Myotonic dystrophy associations and support groups exist in the United States and United Kingdom as well as a global Facebook group where those who have myotonic dystrophy can share stories and support. An online myotonic dystrophy support organization may help those with the condition find support and in advocating for themselves.2‘Myotonic Dystrophy.’ Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, rarediseases.info.nih.gov/diseases/10419/myotonic-dystrophy.