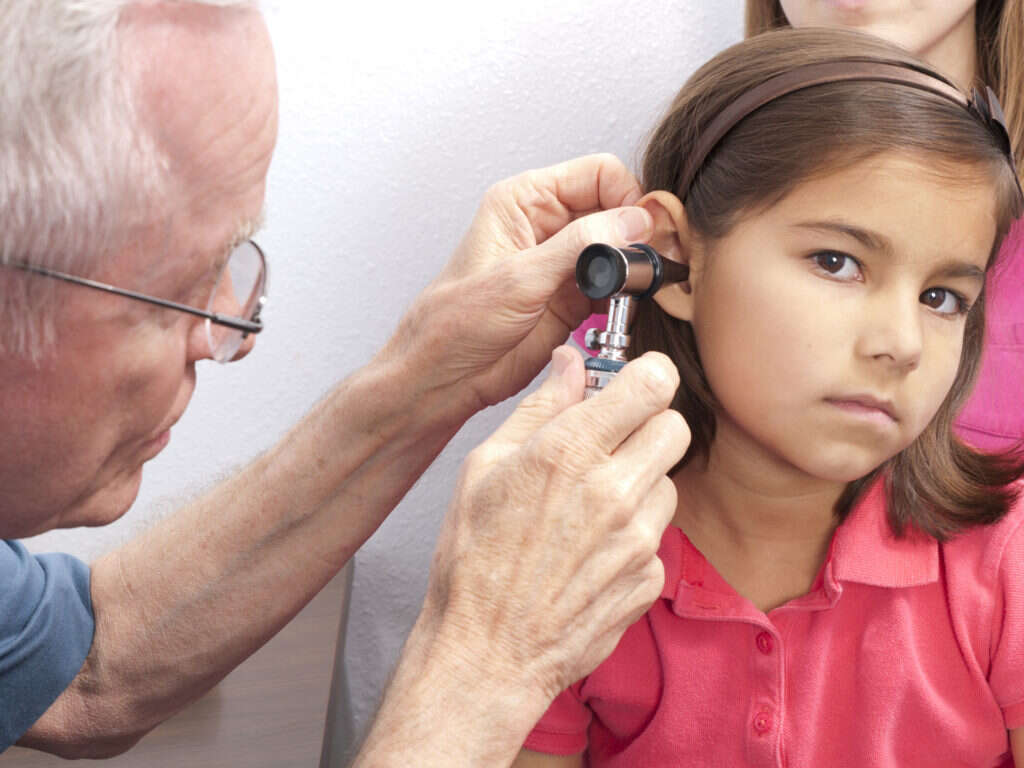
10 Middle Ear Infection Symptoms
Middle ear infections, also known as otitis media, develop most often after an infection of the throat or the upper respiratory tract. The middle ear is the space behind the eardrum and is connected to the throat through the eustachian tube. Inflammation or infection in the upper respiratory tract can spread to the eustachian tube, causing it to swell. This leads to blockage and trapping of fluid in the middle ear, which can serve as a medium for bacterial or viral infection.
Middle ear infections are more common in children under 7 years. This is because the eustachian tube is short, soft, and almost horizontal in young children. According to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, AHRQ, middle ear infections affect nearly 12 percent of children under 18 years 1https://meps.ahrq.gov/data_files/publications/st228/stat228.shtml. The following are the most common symptoms of middle ear infections.

Symptom #1: Dulled Hearing
Dulled hearing is one of the most common middle ear infection symptoms. This occurs when the ear is filled with fluid – the pressure from the fluid on the eardrum interferes with its free vibration. This impaired vibration causes problems in the stimulus transmission that can progress into unilateral and reversible hearing loss.

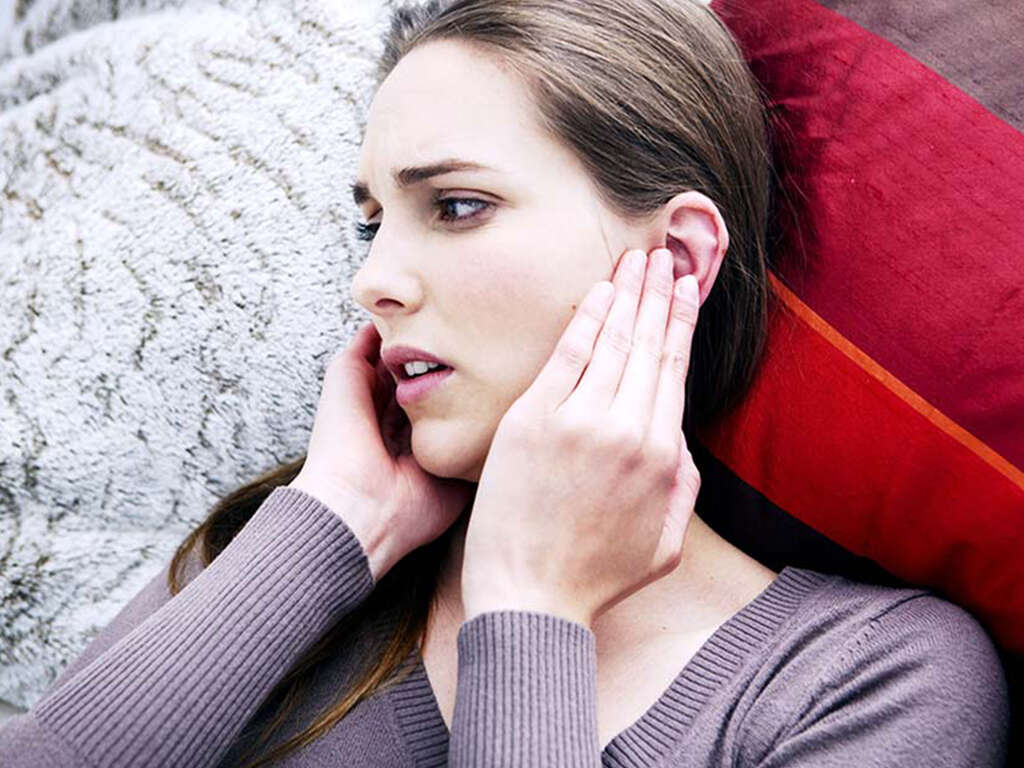
Symptom #2: Earache
Earaches are a common symptom of middle ear infections. Swelling in the eustachian tube causes a blockage which traps fluid within the middle ear. This fluid causes a rise in pressure within the middle ear which may present as an earache. The earache may be more severe and develop into a headache. The pain may worsen when you lie down or alternate in severity.
Earaches due to middle ear infections can clear on their own although this may take a week or two. If the pain persists or if it becomes too intense, it is best to consult a doctor.

Symptom #3: Loss Of Balance
Loss of balance can be a symptom of a middle ear infection. This happens because the ear contains the equipment necessary for the maintenance of balance. The balance sensors help you to stand or walk in an upward position or carry out other activities without feeling awkward.
Normally, pressure in the middle ear is balanced with the pressure in the outer ear due to air exchange through the eustachian tube. However, inflammation, swelling, or infection can cause a blockage of the eustachian tube. This interferes with the air exchange and the working of the balance maintenance sensors, resulting in a loss of balance.

Symptom #4: Fever
Fever is yet another symptom of a middle ear infection, especially in children. As with other infections, otitis media can lead to a rise in body temperature as the body’s defense system fights against the pathogens causing the infection. The patient may also get chills.
When a fever is a result of middle ear infection, it is accompanied by other symptoms such as ear pain, swelling, and a feeling of dulled hearing. Children also tend to tug at their ear as a response to the discomfort they experience.

Symptom #5: Inability To Sleep
Another middle ear infection symptom is the inability to sleep. This is obvious whether it relates to a grownup or a child. Illnesses often cause pain, swelling, or other discomfort. In such a state, it becomes difficult to fall or remain asleep.
A young child with a middle ear infection may simply fail to sleep or have disturbed sleep. When we lay down for sleeping, the pressure within the ear may shift, causing the pain to exacerbate at night. Because young children are unable to express themselves, it falls upon the caregiver to watch out for other symptoms. A child with a middle ear infection may rub the ear against the bedding or rub it. A baby may also tug at the ear or cry.

Symptom #6: Warm Drainage
Drainage of warm fluid from the ear is a symptom of middle ear infections. The fluid may be clear, yellowish or bloody. This happens in the event that the eardrum ruptures due to the increased pressure in the middle ear. It can also occur as a result of altitude changes or some activities under pressure such as scuba diving. Eardrum rupture is usually accompanied by pain.
When there is a rupture in the ear drum, the fluid in the middle ear drains through the ear canal and comes out of the outer ear. If this happens, it is important to consult a doctor for assessment and treatment without delay, because a ruptured eardrum can lead to a more extensive infection or long-term hearing problems.

Symptom #7: Nausea
Patients suffering from otitis media may develop nausea. This is not a very common symptom but it can appear as in any other infectious disease. The balance disturbance and vertigo seen in patients suffering from otitis media may lead them to feel nauseated.
Vomiting is uncommon in these patients. If you are suffering from these symptoms, you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.

Symptom #8: Irritability
This is a common symptom associated with otitis media in young children. It is a non-specific symptom because many other conditions may cause this to happen. In very young children irritability can translate into excessive crying and unrest.
Older children lack the communication skills to convey distress, therefore they can behave abnormally as a sing of irritability due to otitis media.

Symptom #9: Poor Appetite
Similar to other health conditions, a middle ear infection can lead to poor appetite. This happens because a lot of energy is being directed to fighting the infection. Additionally, eating may increase the feelings of discomfort and earache. Many people may therefore minimize eating to avoid the increase in pain.
Otitis media may also present with flu-like symptoms like fever and headache. This can mean that you do not feel like eating. However, it is important that you eat regularly even during the illness in order to provide the body with the energy and nutrients needed to fight the infection.

Symptom #10: Ringing In The Ears
If you experience ringing or a buzz sound in one or both ears, it could mean that you have a middle ear infection. These sounds occur due to the fluid that collects within the middle ear, which leads to increase in pressure. This affects the way the eardrum works. It can cause the eardrum to become more sensitive to movement and to sound because any small movement or sound causes an exaggerated vibration of the eardrum.
Because sounds are everywhere around us, it is impossible to avoid a ringing or buzzing in the ears if you have an infection. However, this ringing or buzzing may come and go or be more pronounced at different times of the day. Because this condition can affect your hearing significantly, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.