Leg Pain Causes, Treatments & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Don't Let Foot Cramps and Charley Horses Slow You Down.' Cleveland Clinic, health.clevelandclinic.org/dont-let-foot-cramps-charley-horses-slow.
- 2. 'About Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD).' Heart.org, heart.org/en/health-topics/peripheral-artery-disease/about-peripheral-artery-disease-pad.
- 3. 'What is Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)?' Heart.org, heart.org/en/health-topics/venous-thromboembolism/what-is-venous-thromboembolism-vte.
- 4. 'Shin Splints.' NHS.UK, www.nhs.uk/conditions/shin-splints.
- 5. 'Leg Fracture.' Harvard Health, health.harvard.edu/a/to/z/leg-fracture-a-to-z.
- 6. Jadhav, S. P., et al., 'Comprehensive Review of the Anatomy, Function, and Imaging of the Popliteus and Associated Pathologic Conditions.' Radiological Society of North America, pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/rg.342125082.
- 7. 'Hamstring Injury.' NHS.UK, www.nhs.uk/conditions/hamstring-injury.
- 8. 'Leg Pain: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.' MedlinePlus, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003182.htm.
Leg pain can have many causes. Some of the most common causes include excessive stress on the leg and injuries from a fall or other trauma, such as a sports-related injury. It can also be caused by health issues related to bones, soft tissues, joints, muscles, nerves and blood vessels.
The cause of the leg pain determines the appropriate treatment, and home treatment is often adequate. However, if the pain is persistent, severe and sudden or other symptoms are present alongside the pain, it may indicate a severe health issue that requires immediate medical attention.

1. Causes
The causes of leg pain can be vascular, musculoskeletal, neurological or a combination of all three. Vascular causes include peripheral artery disease, deep vein thrombosis, infections, cellulitis, varicose eczema and varicose veins. These conditions often result in the discoloration of the skin.
Musculoskeletal causes include crepitus and arthritis. Crepitus involves a cracking or popping sound in the knee. Arthritis is a degenerative disease of the joints, such as the ankle, knee or hip. A fall that strains a ligament, tendon or muscle may also cause musculoskeletal leg pain. Neurological causes include sciatic nerve pain, nerve damage and restless leg syndrome.

2. Charley Horse
A charley horse is a muscle cramp that is common in the legs but can occur in any muscle.1‘Don’t Let Foot Cramps and Charley Horses Slow You Down.’ Cleveland Clinic, health.clevelandclinic.org/dont-let-foot-cramps-charley-horses-slow. The pain can become severe if the contractions occur over several seconds. Severe charley horses can cause muscle soreness that may last for up to a day.
As long as the pain doesn't recur and is not prolonged, there is no cause for worry, and home treatment is often adequate. However, frequent charley horses may indicate an underlying health issue.

3. PAD
PAD, or peripheral artery disease, refers to a common circulatory problem that involves narrowing of the arteries that deliver blood to the limbs.2‘About Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD).’ Heart.org, heart.org/en/health-topics/peripheral-artery-disease/about-peripheral-artery-disease-pad. Clogged arteries are the most common causes of PAD.
When an individual develops PAD, their legs or arms do not receive enough blood to perform their functions. As a result, they experience claudication, which is pain when walking. Claudication may also cause momentary leg cramps when a person walks.

4. DVT
DVT, or deep vein thrombosis, results from a blood clot forming in one of the deep veins in the body.3‘What is Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)?’ Heart.org, heart.org/en/health-topics/venous-thromboembolism/what-is-venous-thromboembolism-vte. If it forms in a deep vein in the leg, DVT may cause leg pain or swelling. However, a person may not experience any symptoms.
Medical conditions that affect the clotting process may cause DVT. Extended periods of inactivity, such as the recovery period following surgery, bed rest and long-distance travel, may also lead to a blood clot in the leg.

5. Shin Splints
Also referred to as medial tibial stress syndrome, shin splints occur due to excess stress on the shinbone and the surrounding tissue that attaches to the bones and muscles.4‘Shin Splints.’ NHS.UK, www.nhs.uk/conditions/shin-splints.
Common causes of shin splints include having flat feet, wearing ill-fitting shoes, failing to stretch and warm-up before a workout and having weak core hips, weak core muscles or weak ankles. Active individuals can get shin splints when they suddenly start doing longer or more intense workouts.

6. Fractures
A leg fracture is a crack or break in one of the leg bones.6Jadhav, S. P., et al., ‘Comprehensive Review of the Anatomy, Function, and Imaging of the Popliteus and Associated Pathologic Conditions.’ Radiological Society of North America, pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/rg.342125082. The most common causes of leg fractures are falls, sports injuries and car accidents. The severity and location of the fracture determine the treatment.
Severe fractures may require surgery to implant a device into the affected bones to help with healing. However, a splint or cast may be sufficient for less severe fractures. Doctors perform a diagnosis to determine the severity of the fracture before deciding on the best treatment.

7. Popliteus Tendinitis or Tenosynovitis
Popliteus tendinitis, also called popliteus tenosynovitis, is associated with excessive stress on the knee due to extensive activities, such as walking or running uphill or downhill.6Jadhav, S. P., et al., ‘Comprehensive Review of the Anatomy, Function, and Imaging of the Popliteus and Associated Pathologic Conditions.’ Radiological Society of North America, pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/rg.342125082. This uncommon condition typically occurs in athletes.
It may also occur in people who have a history of knee trauma involving the ligaments. The popliteus muscle is located in the back of the knee and stabilizes the knee and facilitates the internal rotation of the lower leg as a person walks.

8. Hamstring Strain
Pain at the back of a person's leg may indicate an injury in the hamstring, a group of muscles behind the thighs.7‘Hamstring Injury.’ NHS.UK, www.nhs.uk/conditions/hamstring-injury. These muscles strain fairly often, especially in athletes. Cold or hot treatment, over-the-counter medications and rest may successfully treat mild hamstring strain, although severe cases may take up to several months to heal.
Risk factors for hamstring strain include exercising tight muscles, muscle imbalances, poor conditioning and muscle fatigue. Active and retired athletes whose exercise involves walking are at higher risk.
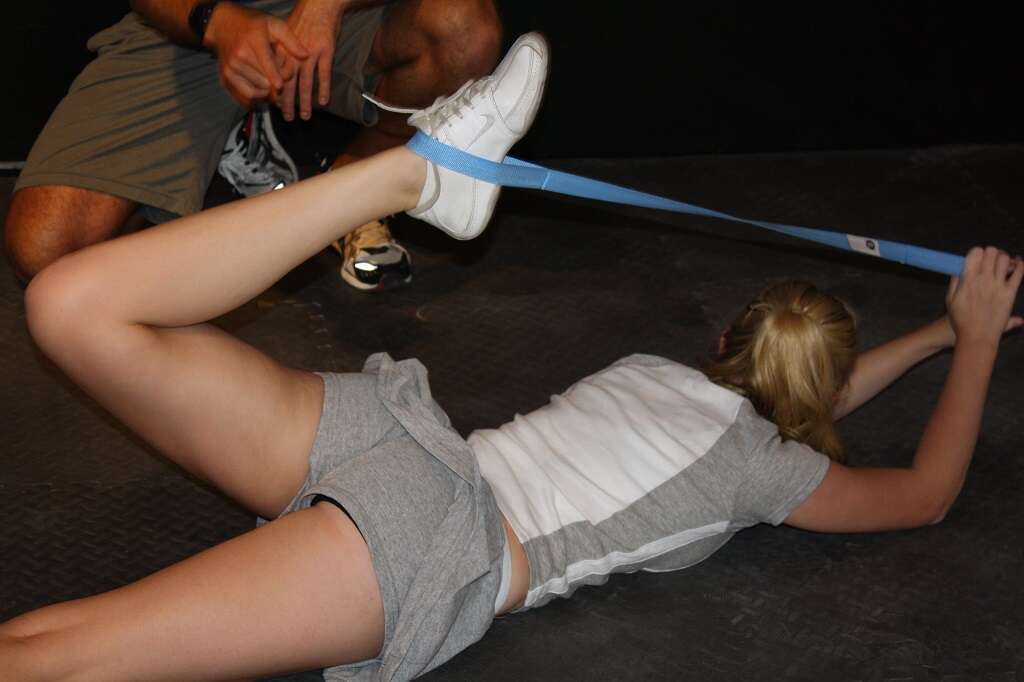

9. Treatment
Minor leg cramps and injuries are usually treatable at home with rest, over-the-counter medications and cold or hot applications.8‘Leg Pain: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia.’ MedlinePlus, medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003182.htm. Applying ice for about 15 minutes at a time, several times throughout the day can relieve leg pain. Taking a warm bath and gently stretching the leg for 5 to10 seconds may also help.
Immediate medical attention is required if the pain persists for several days or if a person experiences unbearable pain while walking, uncomfortable varicose veins or excessive swelling.

10. Prevention
It's advisable to stretch before and after exercising to prevent leg pain. Diets with potassium-rich foods, such as chicken and bananas, may help prevent tendon and muscle leg injuries.
Medical conditions that may cause nerve damage in the legs can be prevented through lifestyle changes. These changes include exercising for at least 150 minutes every week, avoiding cigarette smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy weight and maintaining healthy blood pressure and cholesterol levels.