Large Intestine Function Overview
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Quigley, Eamonn M M. 'Gut Bacteria in Health and Disease.' Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Millennium Medical Publishing, Sept. 2013, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3983973
- 2. Rinninella, Emanuele, et al. 'What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases.' Microorganisms, MDPI, 10 Jan. 2019, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6351938
- 3. Sender, Ron, et al. 'Revised Estimates for the Number of Human and Bacteria Cells in the Body.' PLoS Biology, Public Library of Science, 19 Aug. 2016, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4991899
- 4. Hsiao, William W L, et al. 'The Microbes of the Intestine: an Introduction to Their Metabolic and Signaling Capabilities.' Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America, U.S. National Library of Medicine, Dec. 2008, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4411945
- 5. Sears, Cynthia L. 'A Dynamic Partnership: Celebrating Our Gut Flora.' Anaerobe, Academic Press, 27 June 2005, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1075996405000685
Gut Bacteria and Fiber
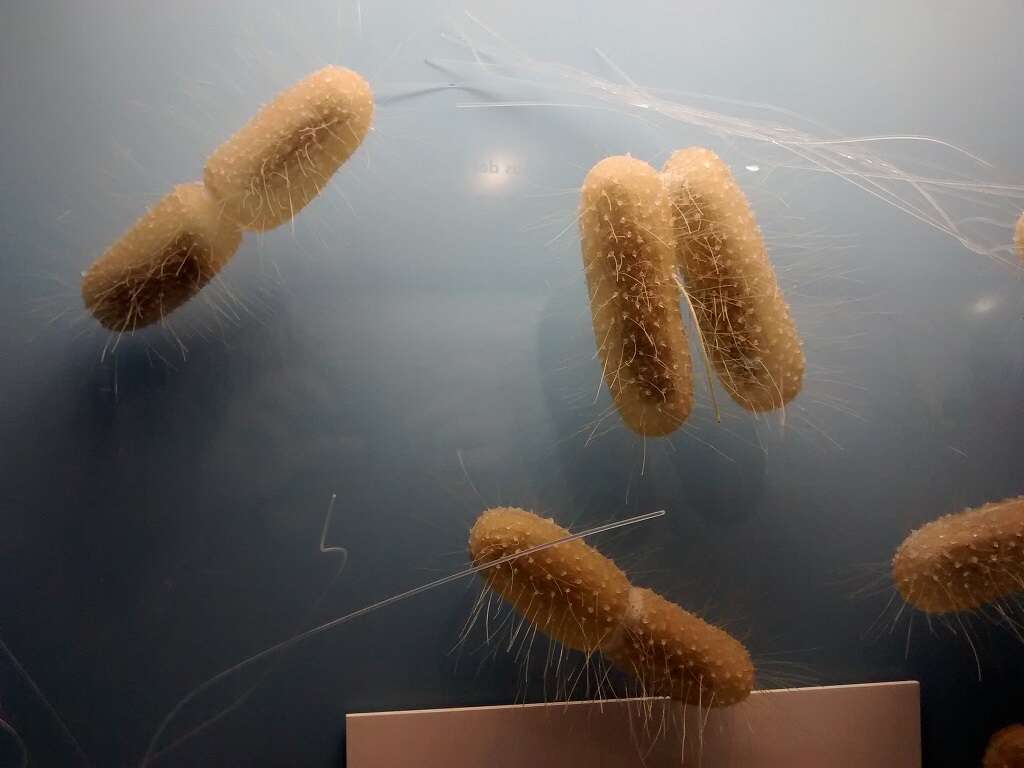
The large intestine contains the human body's largest bacterial ecosystem, which plays several important roles. Several hundred species of bacteria live in the large intestine.1Quigley, Eamonn M M. ‘Gut Bacteria in Health and Disease.’ Gastroenterology & Hepatology, Millennium Medical Publishing, Sept. 2013, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3983973 These microorganisms perform various functions.
Some of these functions include forming products that the gut absorbs. For example, the bacteria in the large bowel metabolize undigested fiber and turn it into short fatty acids. The large intestine absorbs these acids through a process known as passive diffusion.
Advertisement