Hyperventilation Definition, Causes & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Hyperventilation.' Michigan Medicine, University of Michigan, www.uofmhealth.org/health-library/hypvn.
- 2. 'How Correct Breathing Reduces Anxiety.' No Panic, 6 Mar. 2020, nopanic.org.uk/important-breathe-properly-help-anxiety.
- 3. 'Causes of Hyperventilation.' Alberta.ca, myhealth.alberta.ca/health/Pages/conditions.aspx?hwid=aa141603.
- 4. Robson, Andrew. 'Dyspnoea, Hyperventilation and Functional Cough: a Guide to Which Tests Help Sort Them out.' PubMed Central, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5343732.
- 5. Tilles, Ira H. 'Hyperventilation Syndrome Symptoms, Causes, Effects & Treatment.' EMedicineHealth, www.emedicinehealth.com/hyperventilation/article/em.htm.
- 6. 'Diabetic Ketoacidosis.' Nhs.uk, www.nhs.uk/conditions/diabetic-ketoacidosis.
- 7. Bogossian, Elisa G., et al. 'Hyperventilation in Adult TBI Patients: How to Approach It?' Frontiers, www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2020.580859/full.
- 8. Pantelyat, Alexander, et al. 'Central Neurogenic Hyperventilation: A Sign of CNS Lymphoma.' PubMed Central, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5759985.
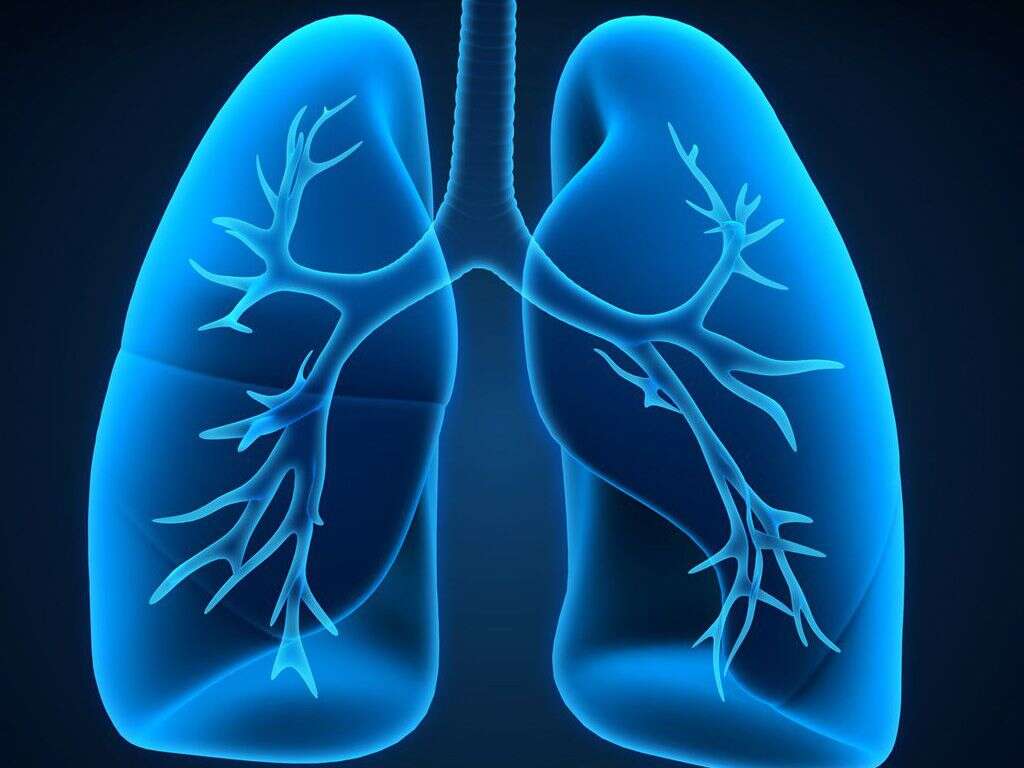
6. Respiratory Diseases
When hyperventilation syndrome is diagnosed, patients go through a series of tests to rule out respiratory disease as the underlying condition. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, or COPD, and asthma are two of the most common respiratory causes of hyperventilation.
COPD is a chronic condition where lung function deteriorates over time, and the reduced lung capacity can cause delays in the response to breathing triggers. Pulmonary fibrosis occurs when lung tissue is scarred or damaged and may also cause hyperventilation.4Robson, Andrew. ‘Dyspnoea, Hyperventilation and Functional Cough: a Guide to Which Tests Help Sort Them out.’ PubMed Central, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5343732.
Advertisement