10 Hepatitis C Symptoms
Hepatitis C is a condition caused by the hepatitis C virus and most commonly affects the liver. Most individuals have mild or no symptoms in the early stages of the infection. In 75 to 85 percent of those infected, the virus continues to persist and can lead to complications, including liver disease, liver failure, liver cancer, cirrhosis, and esophageal varices.
The hepatitis C virus is spread via intravenous drug use, needle-stick injuries, poorly sterilized equipment, and transfusions. It can also be passed on from mother to child during birth. Sexual transmission is also possible but it is not as common. The diagnosis of hepatitis C infection can be achieved via blood screening. Blood screening is recommended for all individuals who are at risk.
There is currently no vaccine for hepatitis C. Efforts to prevent hepatitis C include reducing needle sharing among intravenous drug users and testing donated blood. Ninety-five percent of individuals with a chronic infection can be cured using antiviral medications, such as simeprevir and sofosbuvir. Earlier generation treatments have a lower cure rate with greater side effects. However, the newer treatments are often expensive. Individuals with liver cancer or cirrhosis can also benefit from a liver transplant.
Most cases of hepatitis C occur in Africa, East Asia, and Central Asia. In 2015, approximately 143 million individuals worldwide were infected with hepatitis C. There were also 167,000 deaths due to liver cancer and 326,000 deaths due to cirrhosis.
Symptom #1: Loss of Appetite
Loss of appetite is known medically as anorexia. It is often seen in many conditions, such as pregnancy, pneumonia, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), viral hepatitis, cancer, anxiety, dehydration, and celiac disease.
It is commonly associated with other constitutional symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and weight loss. Those with a prolonged loss of appetite are susceptible to electrolyte imbalances and sudden cardiac death. Care should be taken to avoid refeeding syndrome.

Symptom #2: Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is a sensation of unease and discomfort that often includes an urge to vomit. Vomiting is the involuntary and forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth and sometimes the nose. It is also known as barfing, puking or throwing up.
Both nausea and vomiting are nonspecific symptoms that are often seen in various conditions, such as viral infections, bacterial infections, parasitic infections, pregnancy, and food poisoning, or as side effects of medications.
Symptom #3: Myalgia
Muscle pain is known medically as myalgia. It is a non-specific symptom associated with many conditions. Patients suffering from a hepatitis c infection may experience muscle pain as one of the early symptoms associated with the infection.
It is usually located in the legs and arms and it is mild to moderate in intensity. This symptom is present in more than 15% of patients with hepatitis c.
Symptom #4: Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of tiredness that is distinct from weakness because it can be alleviated with rest. It is a nonspecific symptom that can be due to many conditions, such as increased stress, overworking, jet lag, depression, inadequate sleep, boredom, and disease.
Fatigue has a gradual onset and can be physical or mental. Physical fatigue occurs when the body’s muscles are unable to maintain their optimal performance while mental fatigue is a temporary decrease in cognitive performance.

Symptom #5: Cognitive Problems
Patients with chronic hepatitis C may develop liver cirrhosis, which can result in hepatic encephalopathy. It is estimated that more than 40 percent of individuals with cirrhosis develop hepatic encephalopathy. In hepatic encephalopathy, the affected individual has an altered level of consciousness, which can be either sudden or gradual.
It is believed to be due to the buildup of ammonia in the blood. Some of the issues associated with hepatic encephalopathy are changes in mood or personality and movement problems. Advanced cases can result in a coma.

Symptom #6: Ascites
Ascites is the abnormal buildup of fluid in the abdomen. To be precise, once there is more than 25 mL of fluid in the peritoneal cavity, it is considered ascites. Patients with ascites may experience increased abdominal size, abdominal discomfort, shortness of breath, and increased weight. In hepatitis C, ascites occurs as a result of liver cirrhosis.
However, it is also associated with cancer, tuberculosis, heart failure, blockage of the hepatic vein, and pancreatitis. Testing of the fluid in the abdominal cavity can help determine the underlying cause of ascites. Management of the condition includes a low-salt diet, diuretics, peritoneal tap, and a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.

Symptom #7: Easy Bruising or Bleeding
Easy bruising or bleeding is known as coagulopathy. It affects the way the blood clots. There are many causes of coagulopathy, such as anemia, leukemia, vitamin K deficiency, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), inherited bleeding disorders (like hemophilia and von Willebrand disease), and cirrhosis of the liver.
In a hepatitis C infection, which can lead to liver disease, the synthesis of clotting factors, fibrinolytic proteins, and coagulation inhibitors is affected and can result in coagulopathy.

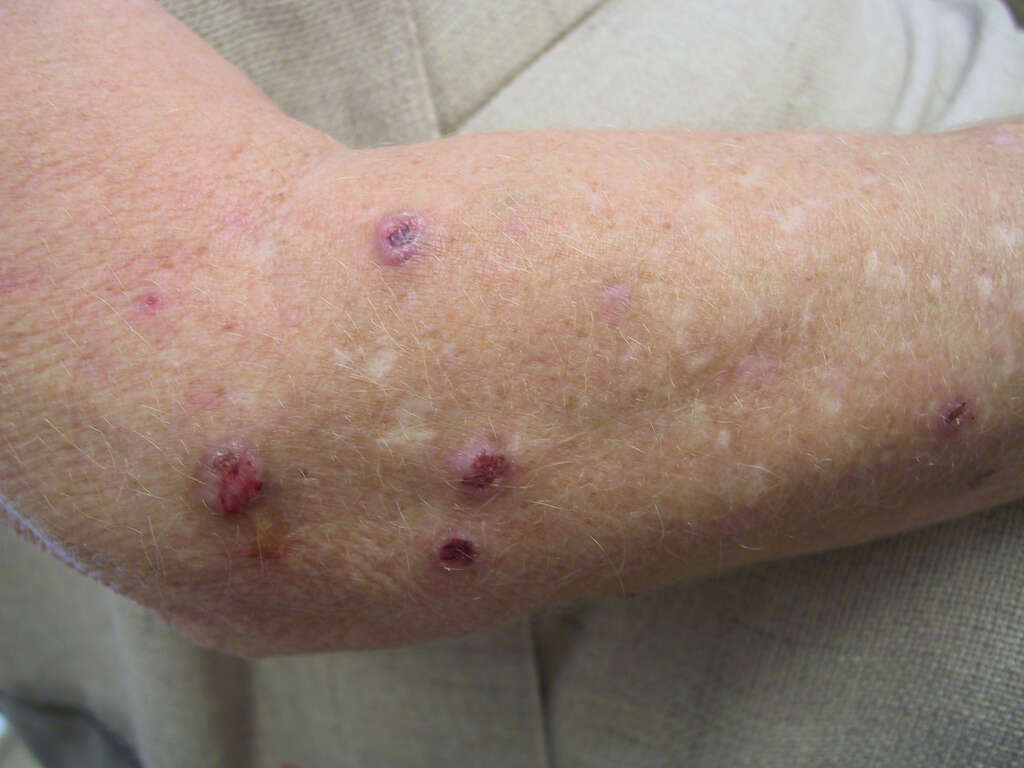
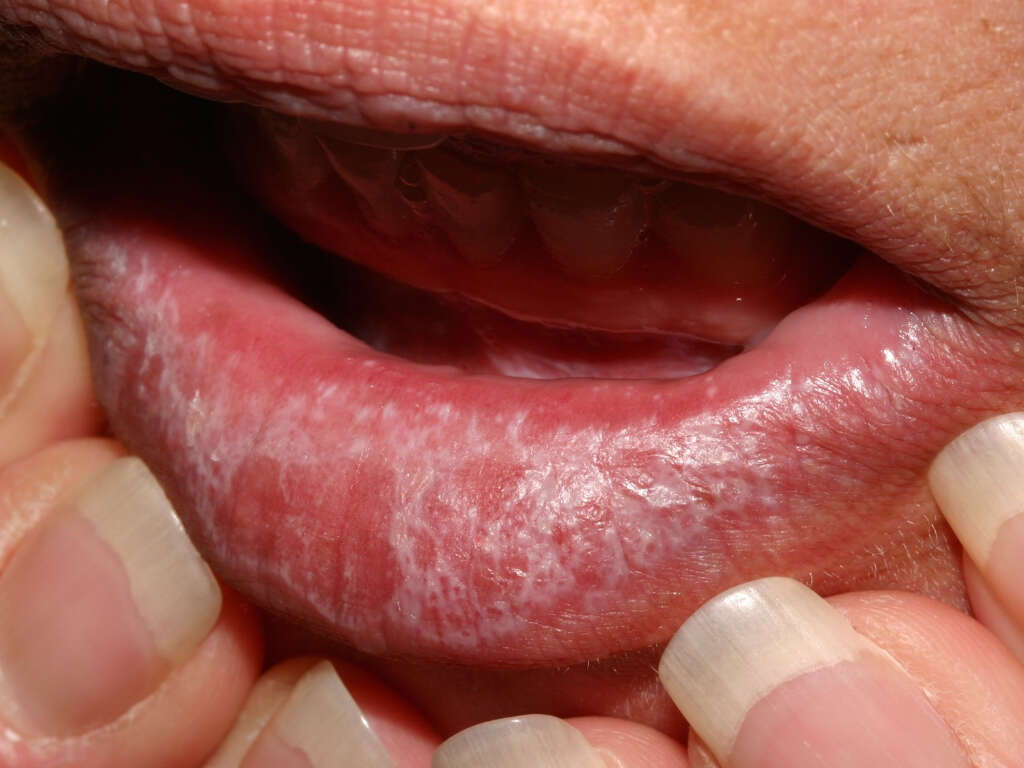
Symptom #8: Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is a condition that causes reddish-purple, polygonal skin lesions. These lesions are commonly found on the wrists, ankles, and lower back. It also causes itching and may present as a burning sensation in the mouth.
It is associated with hepatitis C, autoimmune disorders, the side effects of dental materials or medications, and graft-versus-host disease. The characteristics of lichen planus are known as “The Six Ps”: the lesions are purple, planar (flat-topped), pruritic, polygonal, plaques, and papules.
Symptom #9: Arthralgia
Arthralgia is the medical name for joint pain. It is a non-specific symptom that is associated with many conditions.
This symptom is seen in more than 20% of patients with hepatitis c and it is one of the early symptoms associated with this disease.
Symptom #10: Pruritus
Pruritus is the medical name for itchiness. This is a non-specific symptom that occurs in almost 15% of patients suffering from a hepatitis c infection.
It usually appears as an early symptom of the disease and it is quite annoying for the affected person.