10 Foods That Fight Inflammation
Inflammation is one of the ways the body defends itself. It begins with a process where the immune system recognizes the harmful stimuli, tries to remove it, and begins the healing process. Inflammation can be broadly categorized into acute and chronic inflammation.
Acute inflammation can be induced by noxious compounds, trauma, and microbial invasion. It generally begins rapidly and can become severe in a short time. Subacute inflammation usually last between 2 to 6 weeks. Chronic inflammation refers to the slow and long-term state of inflammation that can last from months to years. Inflammation can be due to the failure of elimination of an agent that caused the acute inflammation, prolonged exposure to foreign materials or irritant, autoimmune disorder, recurrent episodes of acute inflammation, or the presence of biochemical or inflammatory inducers that cause mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress.
Chronic inflammatory disease has been identified as the world’s most significant cause of death. It has been ranked by the World Health Organization as the greatest threat to human health. The prevalence of diseases that cause chronic inflammation is estimated to rise steadily in future years. In 2000, surveys found that about 125 million Americans had chronic conditions with 61 million suffering from more than one. In 2014, almost 60 percent of Americans were estimated to suffer from at least one chronic condition. Globally, 3 out of every 5 individuals die due to chronic inflammatory diseases such as cancer, stroke, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, arthritis or joint disease, asthma, and other chronic respiratory disease. Besides the conventional treatment and medication, many experts believe that adopting an anti-inflammatory diet may also be beneficial.
Inflammation Fighting Food #1: Fish Oil
Fish oil refers to oil that is obtained from the tissues of oily fish. It contains omega-3 fatty acids such as docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). These compounds are believed to help improve hypertriglyceridemia (high triglyceride levels) and reduce inflammation in the body. The efficacy of fish oils has been widely studied with the most promising evidence showing support for the prevention of cardiac death.
The commonest dietary source of DHA and EPA is oily fish from cold water such as sardines, salmon, mackerel, herring, and anchovies. Tuna also contains omega-3 fatty acids but in a lesser amount. The fish obtains omega-3 oils from the plankton and algae in their diets. High intake of omega-3 fatty acids has been found to help reduce inflammation as it lowers the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha.

Inflammation Fighting Food #2: Curcumin
Curcumin is a naturally occurring chemical found in plants. It has a bright yellow color and is often sold as a food flavoring, herbal supplement, or ingredient in cosmetics. Chemically, it belongs to the curcuminoids, which are natural phenols that provides the yellow color.
Despite many efforts via clinical and laboratory research to confirm its medical use, there is little to no evidence that supports it. This can be attributed to it being unstable and difficult to study. However, there are many reports where it significantly helps patients by improving their symptoms of inflammatory diseases. Studies of curcumin on animal models have shown significant improvement of inflammatory symptoms.

Inflammation Fighting Food #3: Fiber
Dietary fiber is the part of the plant that cannot be broken down completely by human digestive enzymes. It can be divided into soluble and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and is easily fermented into gases by gut bacteria. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and provides bulking, absorbs water, and helps ease defecation.
Fiber can help fight inflammation as a high intake of both soluble and insoluble fiber helps to reduce levels of TNF alpha and IL-6. Besides being available in food, there are also fiber supplements that are readily available in stores.

Inflammation Fighting Food #4: Fruits
Fruits refer to seed-bearing structures that help with the dissemination of seeds. Edible fruits are an important part of the human diet. Fruits can be eaten fresh or made into preserves such as jams. They can also be used in desserts, beverages, and manufactured foods like yogurt, ice cream, cakes, muffins, and cookies.
Fresh fruits are usually high in water, vitamin C, and fiber. Various studies have concluded that the regular consumption of fruits is associated with lower risks of diseases and functional decline linked to aging. Fruits are beneficial to help fight inflammation as they are high in polyphenols, natural antioxidants, and other anti-inflammatory compounds.

Inflammation Fighting Food #5: Vegetables
Vegetables are edible plants and can include the roots, flowers, stems, leaves, fruits, and seeds. They can be eaten cooked or raw. Vegetables play a crucial role in the human diet as they contribute significantly to human nutrition. Vegetables are generally low in carbohydrates and fat while being high in dietary fiber, minerals, and vitamins.
Nutritionists often encourage the consumption of 5 or more portions of vegetables a day. Studies have shown that individuals who eat 5 or more portions of vegetables a day have 20 percent lesser risk of developing a stroke or cardiovascular disease. The consumption of vegetables can help fight inflammation as they contain various anti-inflammatory compounds, polyphenols, and natural antioxidants.

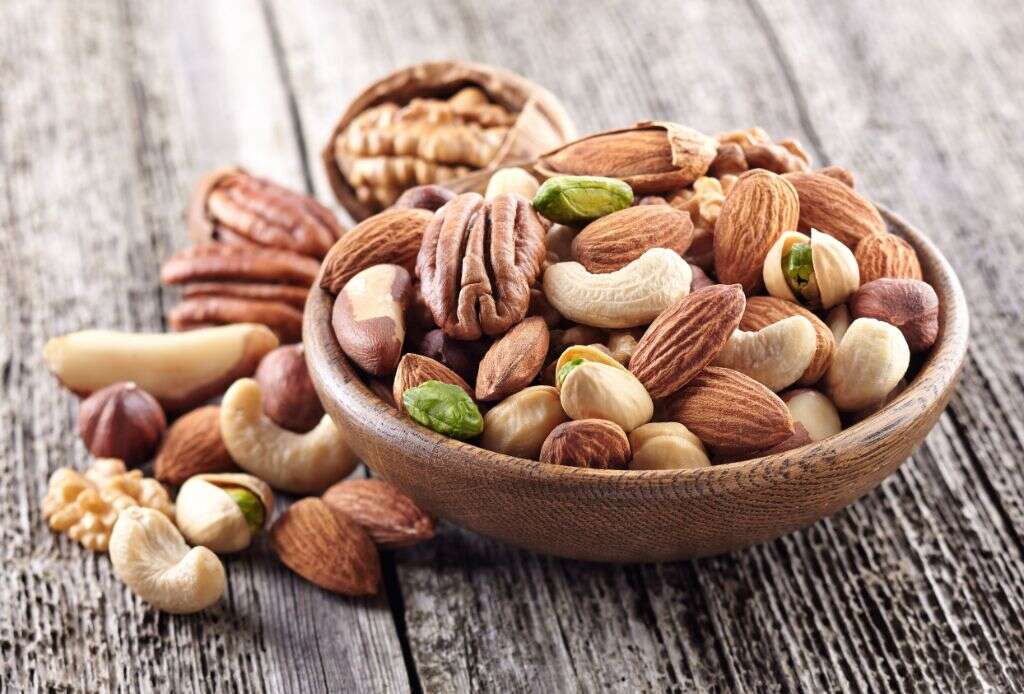
Inflammation Fighting Food #6: Nuts
Nuts are generally fruits contained in a hard shell. They are a nutrient-rich and energy-dense food source due to their high oil content. Nuts are important for both humans and wildlife. They can be eaten raw, used in cooking, roasted as a snack, or pressed for oil that can be found in both cosmetics and cooking.
Nuts are one of the commonest food allergens. Nuts also contain essential monounsaturated and unsaturated fats such as linolenic and linoleic acid, essential amino acids, vitamins, phosphorus, magnesium, folate, fiber, vitamin B2, vitamin E, selenium, copper, and potassium. Nuts have been found to be beneficial in helping fight inflammation as they lower the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.

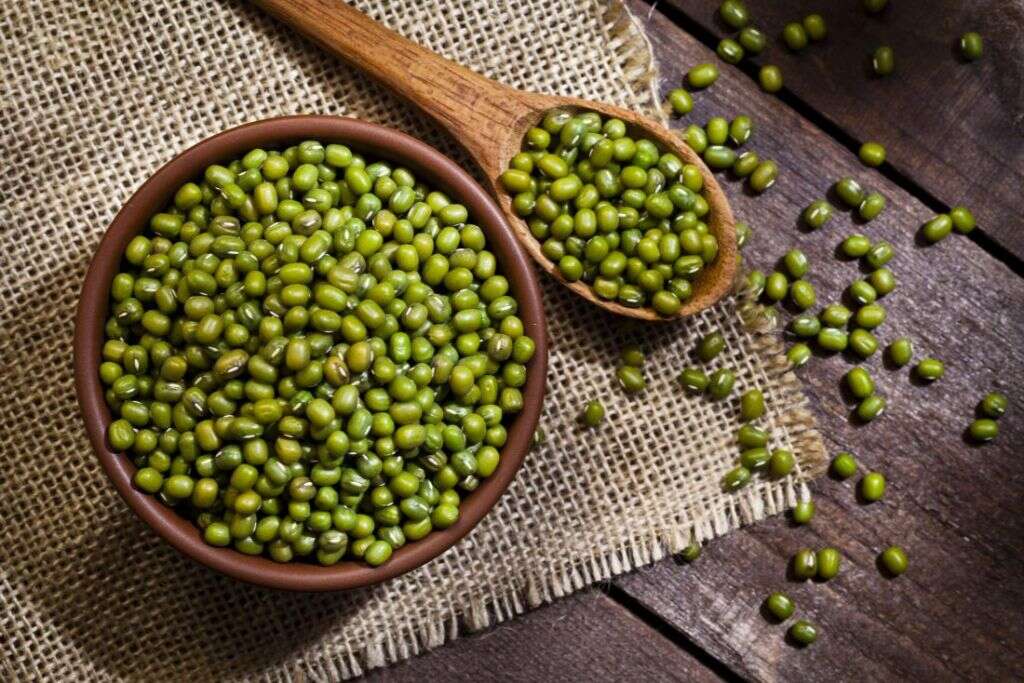
Inflammation Fighting Food #7: Mung Beans
Mung beans, or green gram, are from the legume family. They are mainly cultivated in Southeast Asia and India. Mung beans have a high nutritional value and contain nutrients such as magnesium, manganese, potassium, folate, essential B vitamins, and zinc. They also provide dietary fiber and protein.
Due to their nutritional content, mung beans have been shown to help with decreasing cholesterol levels, decreasing blood pressure, preventing type 2 diabetes, fighting off cancer, and helping to boost immunity. They can also help fight inflammation as they are rich in flavonoids. They have long been used in herbal and traditional medicine due to their anti-inflammatory properties.

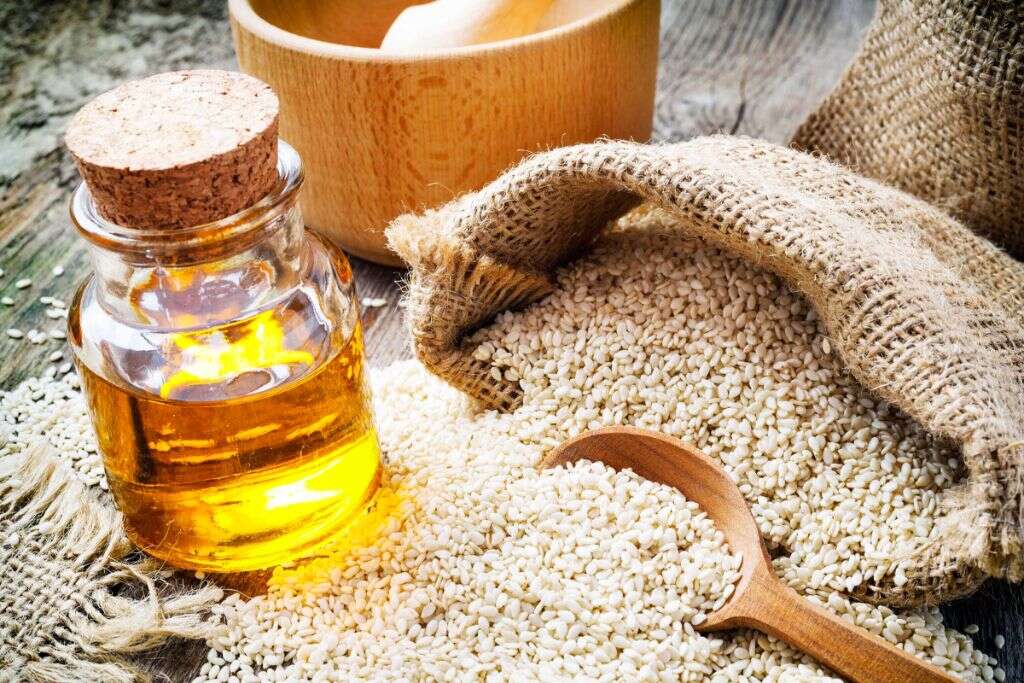
Inflammation Fighting Food #8: Sesame Oil
Sesame oil is an oil extracted from sesame seeds. It is often used for cooking purposes in Indian, African, Middle Eastern, and Southeast Asian cuisines. Besides cooking, it is also used in Ayurvedic medicine for massaging purposes as it is believed to help rid the body of heat.
Just like nuts and seeds, sesame oil can produce an allergic reaction. However, it is rare and is estimated to affect only 0.1 percent of the population. It may help fight inflammation as sesame oil consumption have been shown to reduce the production of thromboxanes, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes.

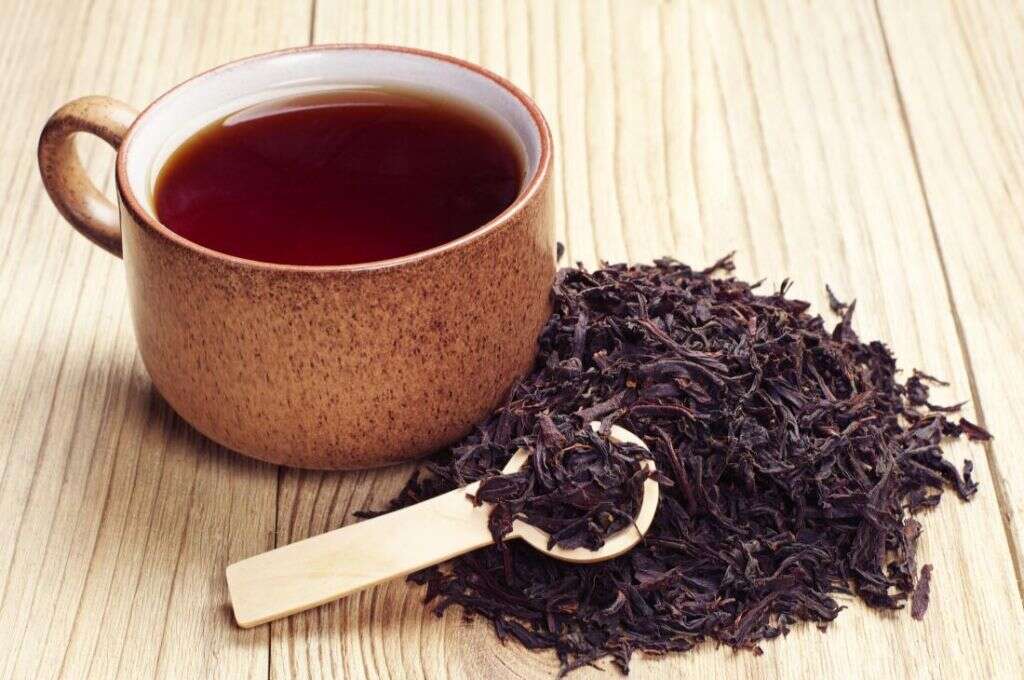
Inflammation Fighting Food #9: Green and Black Tea
Green tea is a type of tea made from buds that have not undergone the same oxidation and withering process as black tea. Despite many claims regarding its health benefits, clinical research has not been able to provide definitive evidence for any of these claims. However, it is believed to be beneficial for enhancing mental alertness, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Black tea is tea that has been oxidized more compared to other teas. Both green and black tea is thought to help fight off inflammation as the tea polyphenols have been found to decrease C-reactive protein levels in human clinical research.

Inflammation Fighting Food #10: Micronutrients
The micronutrients that can help fight inflammation include vitamin D, vitamin E, magnesium, selenium, and zinc. Magnesium is one of the best anti-inflammatory micronutrients as the intake of magnesium has been linked with reduced levels of IL-6, TNF-alpha, and high sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Vitamin D also has anti-inflammatory properties as it helps suppress nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells and prostaglandins. Zinc, selenium, and vitamin E also helps as they act as antioxidants in the body. Some foods rich in these micronutrients include spinach, avocado, and shellfish.