10 Fibromyalgia Symptoms In Women
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition where there is heightened pain response and widespread pain. While the cause of fibromyalgia is unknown, experts believe that it may be due to a combination of environmental and genetic factors. The condition has been found to be more common among family members, with the involvement of many genes. Some environmental factors that have been thought to cause fibromyalgia include certain infections, psychological stress, and trauma.
The pain seems to be due to processes in the central nervous system and is referred to as “central sensitization syndrome.” The diagnosis is based on the patient’s history and physical examination of the patient. There are no diagnostic tests available (except to rule out other conditions) for the diagnosis of fibromyalgia. Treatment can be difficult and often includes lifestyle changes such as having a healthy diet, getting adequate sleep, and regular exercise. Cognitive behavioral therapy has also been found to be beneficial. Medications that may be used are pregabalin, duloxetine, and milnacipran.
Although it is a chronic condition, researchers have not found any evidence of tissue damage or death. Fibromyalgia has been estimated to affect about 2 to 8 percent of the population, with women twice as likely to be affected compared to men.

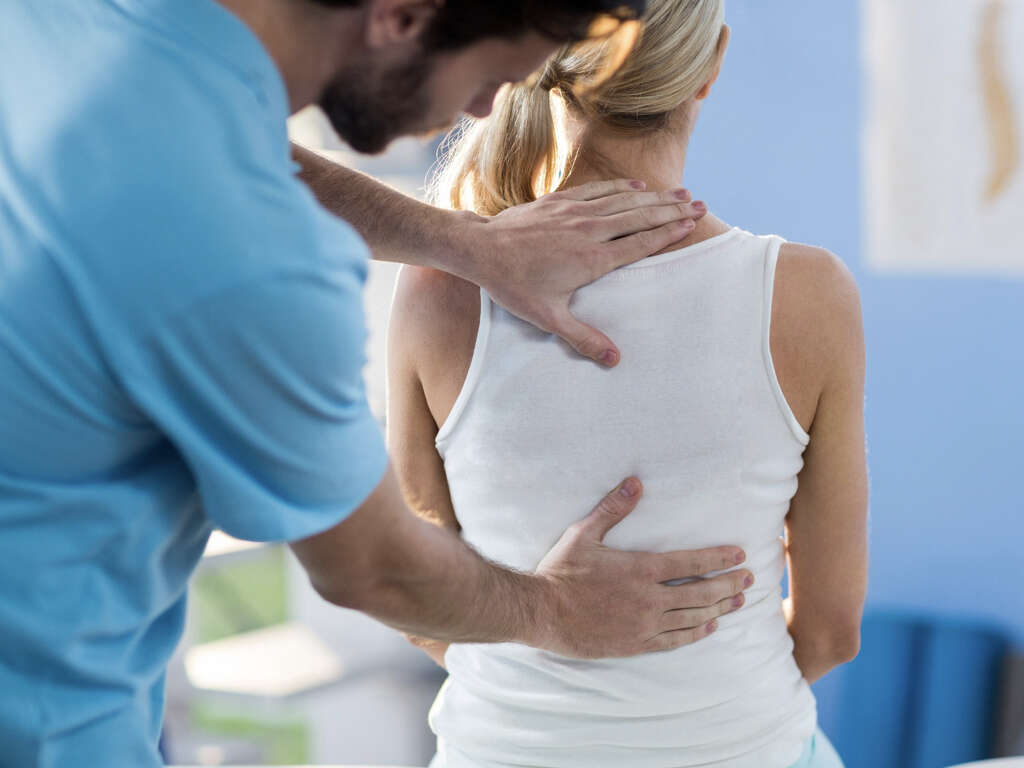
Symptom #1: Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can be defined as pain that lasts more than 12 weeks. Pain is a subjective and personal experience. There are no tests available that can locate or measure pain. This is why medical professionals rely on the patient’s description of timing, characteristic, and location of pain.
Pain can be described as constant, intermittent, sharp, dull, throbbing, or burning. In fibromyalgia, patients often experience chronic pain that is widespread. There may be tender points that continue to hurt despite medication. Research has suggested that the pain in fibromyalgia may be cause by a “glitch” in the way the body processes the pain, resulting in hypersensitivity to stimuli that are usually not painful.

Symptom #2: Fatigue
Severe fatigue is one of the main symptoms often seen among patients with fibromyalgia. It has been estimated to affect about 80 percent of patients with fibromyalgia. This has been attributed to the sleepless nights that often leave patients exhausted and drained.
Despite how patients feel, regular exercise can be beneficial for patients with fibromyalgia. Many patients often report being too tired to exercise but this results in greater muscle weakness. With regular exercise, there can be less fatigue. It may also be possible that exercise creates a chain reaction that boosts brain function. To start out, patients are encouraged to work with a physical therapist.

Symptom #3: Sleep Issues
Sleep issues are a common symptom among patients with fibromyalgia. It is such a prominent symptom that the American College of Rheumatology proceeded to include symptoms such as tiredness, waking unrefreshed, insomnia, and fatigue as part of the 2010 diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia.
While the routine evaluation for fibromyalgia does not include sleep recording, polysomnography may be beneficial in detecting primary sleep disorders such as restless leg syndrome and obstructive sleep apnea. Proposed nonpharmacological management include cognitive behavioral therapy and sleep hygiene.

Symptom #4: Allodynia
Allodynia is a term describing pain felt on the skin caused by triggers that usually do not cause pain. This means that there is increased sensitivity to pain from stimuli that should not provoke pain.
Allodynia has been observed in patients with fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, postherpetic neuralgia, neuropathy, and migraines. Allodynia can be broadly categorized into tactile (touch), mechanical (movement across the skin), and thermal (heat or cold) allodynia.

Symptom #5: Paresthesia
Paresthesia refers to the unpleasant sensations that occur without an apparent physical cause. These sensations have been described to be prickling, crawling, tingling, burning, and numbness. Common descriptions of paresthesia include pins and needles or a limb falling asleep.
Fibromyalgia has been associated with paresthesia. The severity can range from mild to severe and occur at any time. A study has reported that fibromyalgia patients who smoke tend to have more severe paresthesia. Quitting smoking may help reduce the severity of paresthesia.

Symptom #6: Muscle Spasms
A muscle spasm refers to an involuntary and sudden muscle contraction that is sustained and often results in pain. Muscle spasms can occur in any muscle in the body. They may affect both skeletal or smooth muscles. Acute skeletal muscle spasms are often due to overuse or injury and usually improve with gentle stretching, rest, and hydration.
Muscle spasms are a common occurrence among patients with fibromyalgia. Many researchers agree that it is one of the main sources of pain. While the cause is unclear, one study has suggested that the spasms are due to myofascial trigger points.

Symptom #7: Migraines
Migraines are severe recurrent headaches that generally affect one-half of the head and last from 2 to 72 hours. The pain has been described to be pulsatile in nature with other associated symptoms such as vomiting, nausea, photophobia, phonophobia, and increased sensitivity to smell. The pain is usually exacerbated by exertion or any physical activity.
Approximately 33 percent of those with migraines may experience an aura. Migraines have also been linked to fibromyalgia. Studies have found that the frequency of fibromyalgia is much higher among patients with chronic migraines. Patients with chronic migraines have also been reported to have more severe fibromyalgia symptoms.

Symptom #8: Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea can be characterized by lower abdominal pain that occurs before or during menstruation. Studies have reported the prevalence of dysmenorrhea to range from 16 to 91 percent. If there is no underlying cause for dysmenorrhea, it is known as primary dysmenorrhea. Secondary dysmenorrhea describes the condition due to underlying causes such as pelvic inflammatory diseases, fibroids, or endometriosis.
Dysmenorrhea has been shown to have a negative impact on the quality of life. It has been reported as the leading cause of absence from work and school among females in the reproductive age. Severe dysmenorrhea has been commonly reported in patients with fibromyalgia.

Symptom #9: Anxiety and Depression
While occasional anxiety is a normal part of life such as facing issues at work or having to make an important decision, anxiety disorders can lead to disruption and have a negative impact on school, work, and relationships. Anxiety disorder symptoms include irritability, restlessness, feeling on edge, muscle tension, sleep issues, difficulty controlling feeling worried, heart palpitations, tachycardia, and trembling.
Depression is also a normal part of life, especially when something bad happens. However, depression as a disorder occurs when an individual persistently feels low (mood) and experiences symptoms such as tiredness, excessive guilt, anhedonia, feelings of hopelessness, restlessness, and irritability. Patients with fibromyalgia have been reported to experience both anxiety and depression.

Symptom #10: Cognitive and Memory Impairment
Cognitive impairment occurs when an individual experiences difficulty concentrating, remembering, learning new things, or making decisions that make a difference in their life. Cognitive impairment can range from mild to severe. In mild cases, affected individuals may notice changes but are still able to continue their daily routines. Severe impairment can lead to the loss of ability to write, talk, understand, and the inability to live independently.
Memory impairment occurs when there is complete or partial memory loss due to a psychological or physical disorder. Both cognitive and memory impairment are potential symptoms in patients with fibromyalgia.