Facial Cellulitis Causes, Treatments and More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Graham, Bettie J. 'Bacteria.' Genome.gov, National Human Genome Research Institute, www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Bacteria.
- 2. Raff, Adam B. 'Diagnosis and Treatment of Cellulitis.' JAMA, JAMA Network, 19 July 2016, www.jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2533510.
- 3. 'What Is Sepsis?' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 27 Jan. 2021, www.cdc.gov/sepsis/what-is-sepsis.html.
Bacteria are everywhere on Earth, including in and on the human body. It's estimated that human bodies contain more bacterial cells than human cells, but most bacteria never cause disease. Bacteria found on the skin are harmless unless they enter the skin through cuts, bites or skin irritations and cause an infection.1Graham, Bettie J. ‘Bacteria.’ Genome.gov, National Human Genome Research Institute, www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Bacteria.
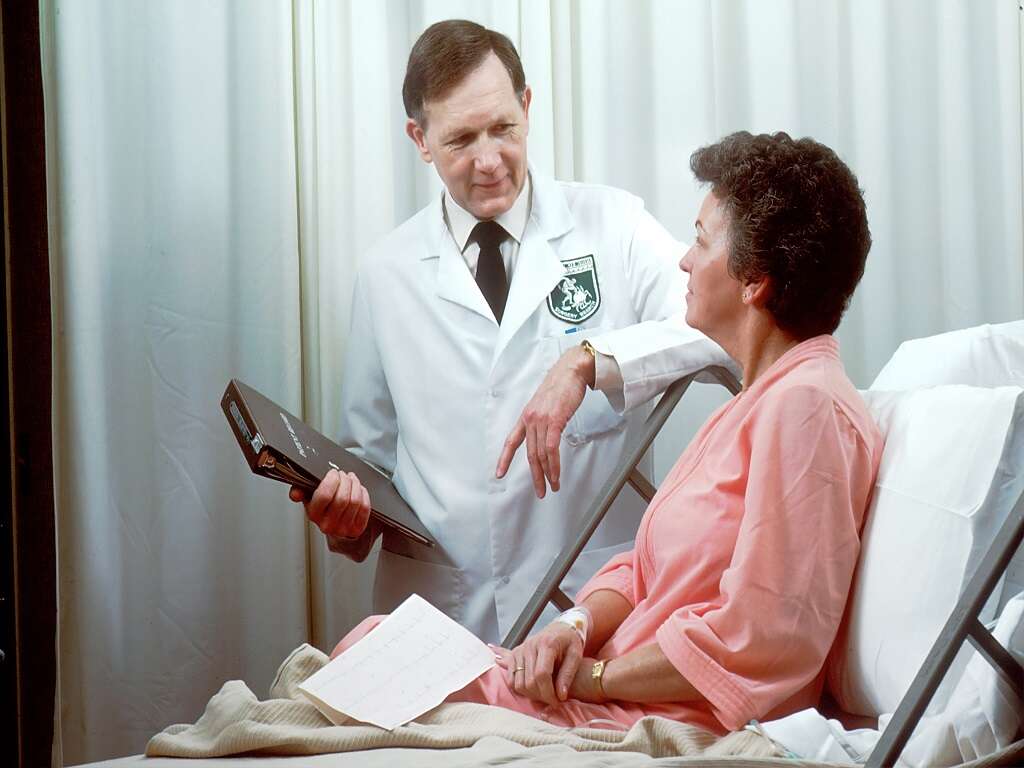
Cellulitis is an infection of the skin and subcutaneous tissue caused by bacteria or fungi. Cellulitis may spread, entering the bloodstream and lymph nodes. Cellulitis affects 14.5 million people in the United States each year.2Raff, Adam B. ‘Diagnosis and Treatment of Cellulitis.’ JAMA, JAMA Network, 19 July 2016, www.jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/2533510. Continue reading to learn about the symptoms, causes and treatments for facial cellulitis.

1. What is Cellulitis?
The most common bacteria that cause cellulitis are in the strep and staph family. These painful bacterial infections run deep under the skin, appear quickly and are easy to treat if they remain local. Rapidly spreading cellulitis infections can lead to sepsis, a blood infection that could be life-threatening.3‘What Is Sepsis?’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 27 Jan. 2021, www.cdc.gov/sepsis/what-is-sepsis.html. How quickly and extensively a cellulitis infection or sepsis spreads depends partly on an individual's immune system.
One of the most important factors affecting the outcome and recovery from cellulitis is early treatment. Learning about cellulitis and signs that it's quickly spreading can help determine when to seek treatment by a physician.

2. What is Facial Cellulitis?
Facial cellulitis occurs anywhere on the face, often caused by strep and staph bacteria around the nose and mouth. These bacteria don't usually cause an infection unless a cut, scrape or small area of open skin allows the bacteria to get into the fat and tissue underneath, where the bacteria can multiply and lead to an infection.
Facial cellulitis that becomes swollen, red, hot and painful is uncomfortable and unsightly. Treatment can help clear the infection; however, facial cellulitis around the eyes may become dangerous.

3. What Causes Facial Cellulitis?
Facial cellulitis may appear on areas of the face affected by eczema or, in children, chickenpox sores. Scratching and rubbing these sores can break the skin and allow bacteria to get underneath. Any surgery performed on the face may also allow bacteria to travel under the skin to the tissues underneath, resulting in cellulitis.
Individuals with red, swollen painful areas on the face after surgery or from eczema and other sores should consult with the doctor right away.
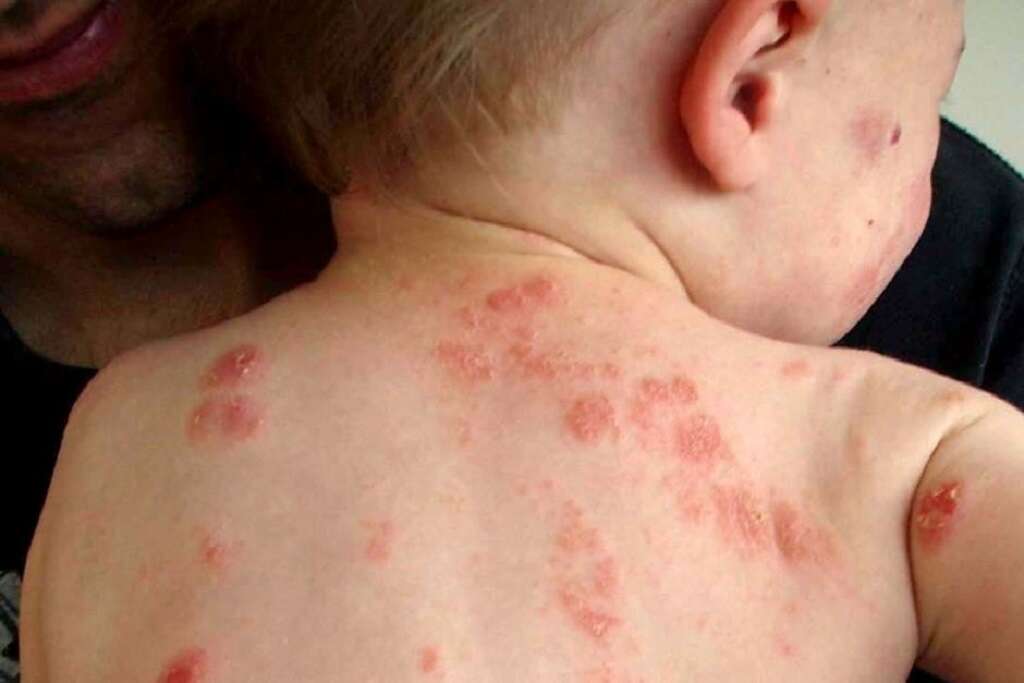
4. What are the Symptoms of Facial Cellulitis?
The initial symptoms of facial cellulitis may begin with a skin sore and redness. The area quickly swells and spreads, becoming increasingly hot and painful. The skin in the area takes on a glossy sheen from the swelling, and the tongue may become swollen and sensitive, as well,
Other symptoms that cellulitis is getting worse and spreading include chills, weakness, dizziness or sweating. It's important to see a doctor immediately if additional symptoms develop, such as red streaks under the skin or drowsiness.

5. What does Facial Cellulitis Look Like?
Facial cellulitis that develops around the eyes often results in the eye swelling shut until the infection resolves. Swelling and redness under the eyes may spread down into the cheek.
When facial cellulitis develops around the lips, the swelling may spread to the upper or lower lip and both sides, causing cracked skin and sores. If facial cellulitis develops on the nose, it may cause the nostril area to close up and make it difficult to breathe, requiring immediate medical care.

6. How is Facial Cellulitis Treated?
Oral antimicrobial antibiotics that treat facial cellulitis include cefazolin, cefuroxime and oxacillin. Cellulitis usually shows signs of improvement within three days of starting the antibiotics. A doctor will explain how long to take the prescription and when to let them know if there's no improvement.
Treatment for pain and fever includes over-the-counter medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, and cold compresses to help with swelling and discomfort from the heated infected area.
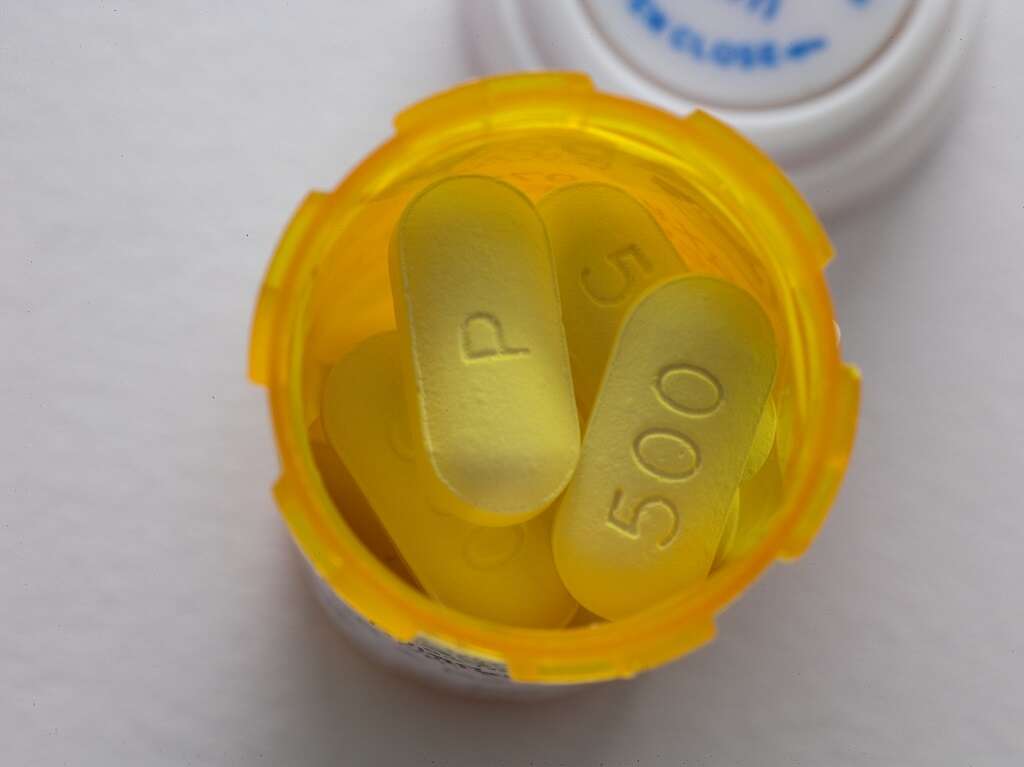
7. How Long Does it Take for Facial Cellulitis to Go Away?
Once treatment begins, facial cellulitis symptoms may show improvement within one to three days, and complete healing may take seven to 10 days. Often, facial cellulitis completely heals before the antibiotics are finished. Prescribing doctors and pharmacists usually recommend completing the medication, regardless of improvement or complete healing.
Sometimes symptoms may temporarily worsen as the antibiotics kill the infection, releasing toxins. If the symptoms do not resolve or continue to worsen, it's important to let the doctor know.

8. Is Facial Cellulitis Contagious?
Facial cellulitis is not usually contagious. Other bacterial skin infections may be transferable; however, cellulitis cannot be spread to other people. It's important to practice frequent hand washing and avoid touching the affected areas. Anyone helping care for facial cellulitis also needs to wash their hands.
If an individual has an open wound and their skin comes into contact with a person's skin who has facial cellulitis, there is a slight risk of spread. Always ensure that no one touches open wounds from cellulitis.

9. Will Facial Cellulitis Leave Permanent Scarring?
When facial cellulitis is developing, painful red rashes typically occur that can blister and scab over. Scabs and blisters may leave scarring if picked at or not treated with proper medications, such as antibiotics. If the cellulitis occurred due to surgery, the wound may split open and not heal correctly.
Often, facial dermatitis is treated by a dermatologist, who can provide treatment plans to prevent or reduce permanent scarring. If cellulitis is severe, it may require surgery to drain the infection, which may leave scarring.

10. How to Prevent Facial Cellulitis
It's helpful to use moisturizers on dry facial skin and sunscreen when outside. Cuts or scrapes on the face should be washed with soap and water, and a doctor should be consulted if the area quickly reddens or swells. Any facial cuts deeper than one-half inch require examination by a physician or dermatologist.
If a cut or abrasion comes in contact with saltwater or frostbite occurs on an area of the face, it's important to see a doctor for treatment to prevent infection.











