Excess Gas Causes, Remedies & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Gas and Gas Pains - Symptoms and Causes.' Mayo Clinic, 3 Mar. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gas-and-gas-pains/symptoms-causes/syc-20372709.
- 2. 'Gas in the Digestive Tract.' Johns Hopkins Medicine, Based in Baltimore, Maryland, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/gas-in-the-digestive-tract.
- 3. 'Should You Take Daily Fiber Supplements?' Mayo Clinic, 25 Oct. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/fiber-supplements/faq-20058513.
- 4. 'Are You Passing Too Much Gas? 6 Tips for Relieving Flatulence.' Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, 9 Mar. 2021, www.health.clevelandclinic.org/what-causes-flatulence-and-what-to-do-when-its-a-problem-for-you/.
- 5. 'How To Decrease Bloating | Natural Remedies for Gas and Bloating.' Boston Hospital & Medical Center - Brigham and Women's Hospital, www.brighamandwomens.org/patients-and-families/meals-and-nutrition/bwh-nutrition-and-wellness-hub/special-topics/gas-beat-the-bloat.
- 6. 'Practical Tips to Reduce Bloating, Belching and Gas.' Mayo Clinic, 13 Feb. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gas-and-gas-pains/in-depth/gas-and-gas-pains/art-20044739
The process of digestion involves the production of gas. The body gets rid of the gas when a person passes gas (flatus) or burps. When gas becomes trapped or fails to move properly in the digestive system, a person may experience gas pain.
Consumption of foods that produce gas may cause gas or gas pain to increase. In general, making changes to one's diet can alleviate some of the symptoms of excess gas. Excess gas and increased gas pain are among the signs and symptoms of certain digestive system disorders, such as celiac disease or irritable bowel syndrome.
1. Symptoms
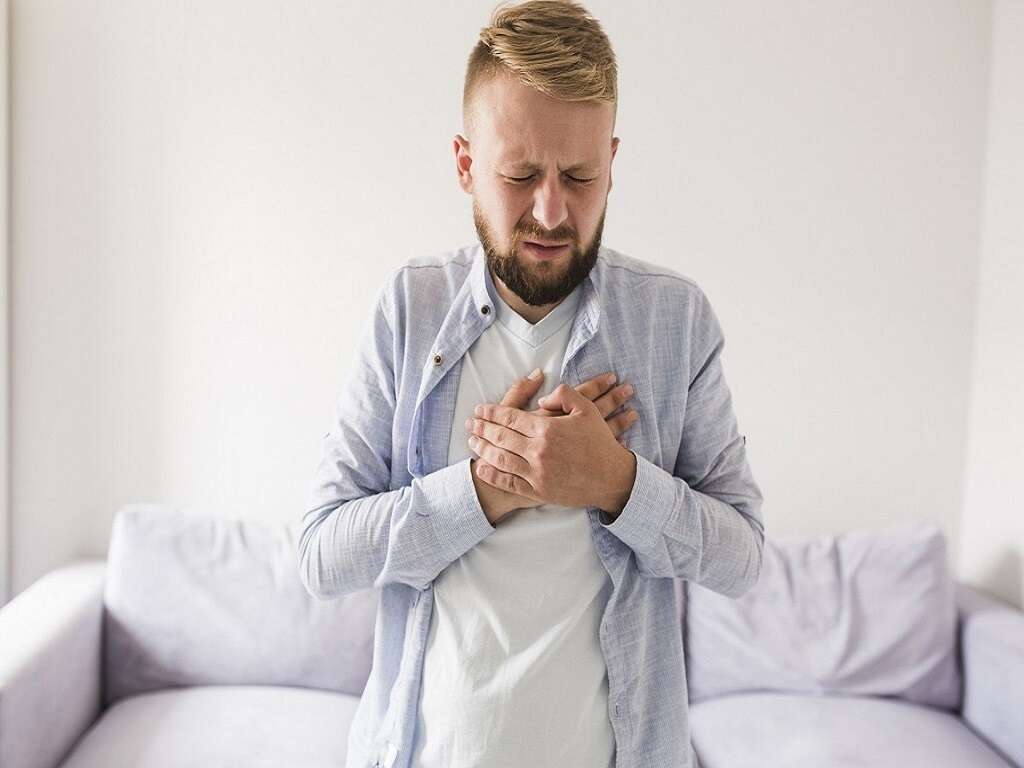
Excess gas presents several symptoms. The most common are burping and passing gas, along with cramps, pains, or a knotted feeling in one's stomach area.1‘Gas and Gas Pains - Symptoms and Causes.’ Mayo Clinic, 3 Mar. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gas-and-gas-pains/symptoms-causes/syc-20372709. One may experience bloating, a feeling of pressure or fullness in the lower abdomen.
Another common symptom is distention, which is characterized by a noticeable increase in the size of the abdomen. Burping during or immediately after a meal is normal. Likewise, most people pass gas several times every day. For these reasons, the presence of these two symptoms (burping and passing gas) by themselves should not be cause for concern, unless there is excessive burping or flatulence.

2. When to Seek Medical Help
When the excess gas symptoms become persistent, it is advisable to contact a doctor immediately. In some cases, the symptoms may get in the way of daily activities. If other symptoms occur alongside excess gas, it may indicate a severe condition.
These additional signs and symptoms include changes in the stool, which may become bloody change consistency. Other symptoms are weight loss, change in frequency of bowel movements, recurrent/persistent nausea or vomiting, and constipation/diarrhea. Chest pain or prolonged abdominal pain requires medical attention.

3. Causes of Excess Gas
Swallowing air as one eats or drinks is the main cause of gas in the stomach.2‘Gas in the Digestive Tract.’ Johns Hopkins Medicine, Based in Baltimore, Maryland, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/gas-in-the-digestive-tract. The body releases much of the gas through burping. Gas also forms in the digestive system as a result of the fermentation of carbohydrates by bacteria.
This happens when the small intestine fails to digest these carbohydrates, including fiber and some sugars and starches. Some of that gas is consumed by the bacteria and the rest comes out of the body through flatulence.

4. Foods That Cause Excess Gas
Foods that are high in fiber, like legumes, vegetables, fruits and whole grains, tend to cause gas and some may cause excess gas. Although these foods are considered healthy, a person with food intolerances or IBS may temporarily need to remove them from the diet, until he/she is able to tolerate them again.
Foods containing a lot of fiber also assist in regulating cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Consult your doctor or nutritionist before making any serious changes to your diet.

5. Other Dietary Factors
Several other dietary factors play a role in the production of gas in the digestive system. Consumption of carbonated beverages often leads to excess gas and certain eating habits lead to the swallowing of more air. These habits include talking while chewing, chewing gum, using drinking straws, and eating too quickly.
Fiber supplements that contain psyllium may cause increased gas and gas pains.3‘Should You Take Daily Fiber Supplements?’ Mayo Clinic, 25 Oct. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/fiber-supplements/faq-20058513. Excess gas may also occur as a result of consuming sugar-free beverages and foods that contain artificial sweeteners and sugar substitutes.

6. Medical Conditions That Cause Excess Gas
Certain medical conditions can cause increased gas and gas pains. Excess gas is usually one of the signs and symptoms of chronic intestinal conditions.4‘Are You Passing Too Much Gas? 6 Tips for Relieving Flatulence.’ Health Essentials from Cleveland Clinic, 9 Mar. 2021, www.health.clevelandclinic.org/what-causes-flatulence-and-what-to-do-when-its-a-problem-for-you/. Weight loss, diarrhea, and excess gas may occur as a result of change or increase in intestinal bacteria.
Food intolerance in which the digestive system is unable to digest certain foods like gluten (a protein found in grains) and lactose (a sugar found in dairy products) may cause excess gas. Lastly, constipation may also hinder the passing of gas.

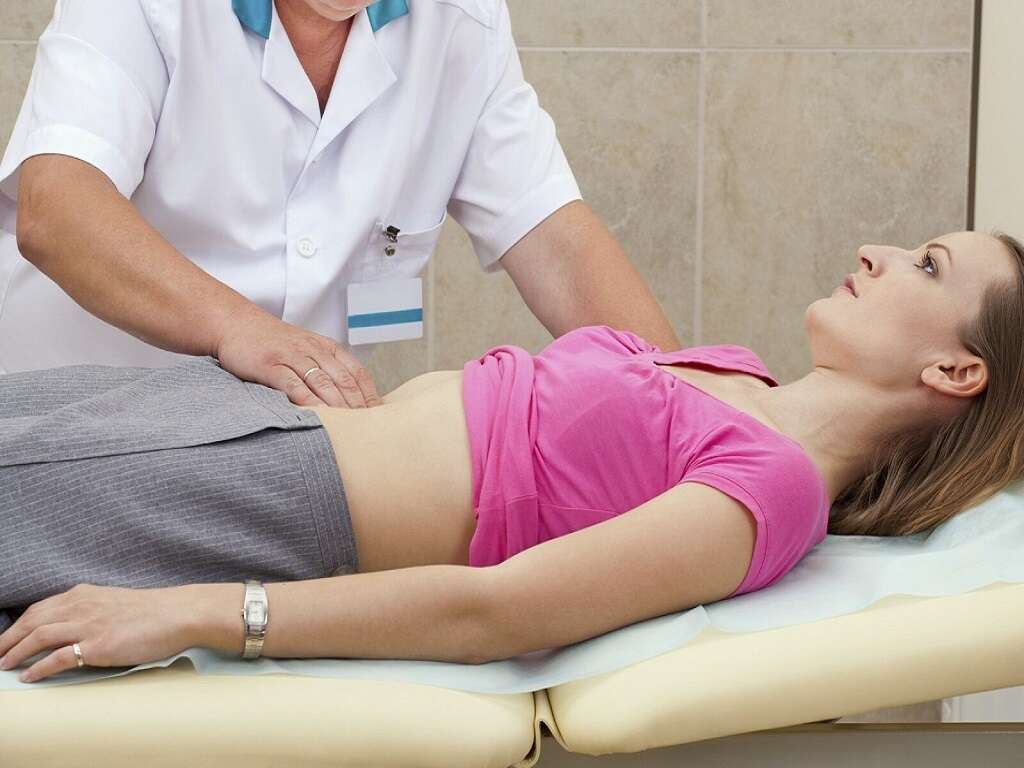
7. Diagnosis
A doctor determines the cause of excess gas by checking a person's medical history, reviewing their diet, and performing a physical examination. The physical examination may involve touching the abdomen to check for tenderness and other irregularities.
The doctor may also use a stethoscope on the abdomen. An additional diagnostic test may become necessary depending on the presence of other signs/symptoms (diarrhea, bloody stool) and the results of the physical exam.
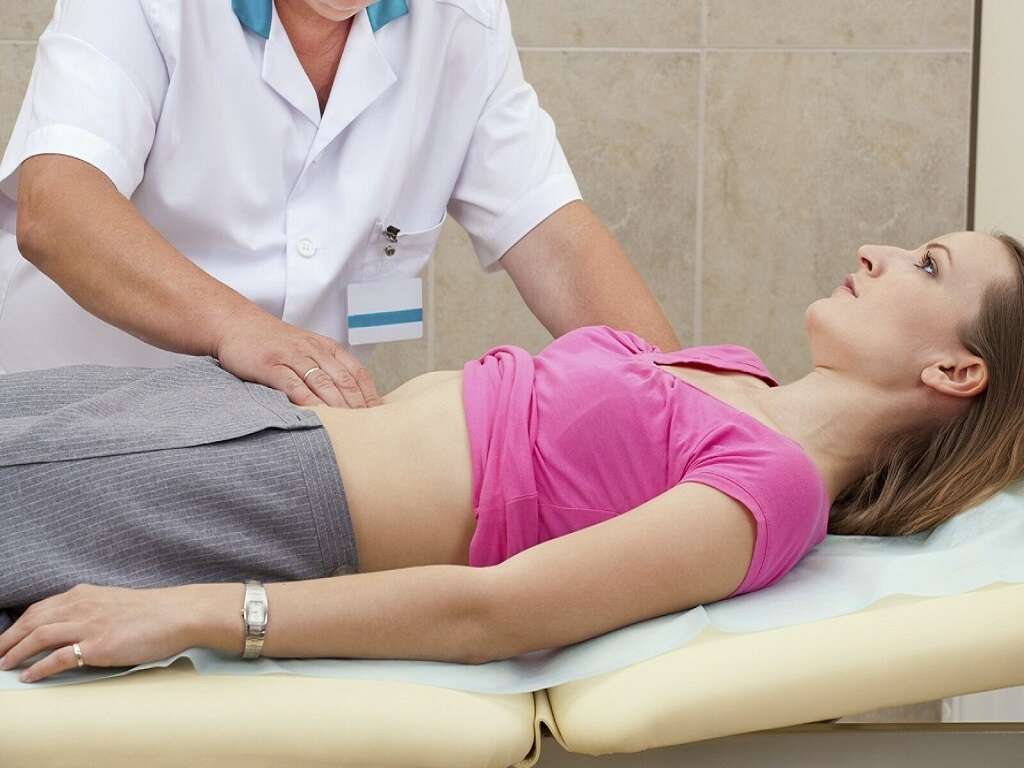
8. Over-The-Counter Remedies
If another health problem is at the root of excess gas and gas pains, treating the underlying problem alleviates the symptoms of excess gas. Otherwise, lifestyle changes, dietary measures, and over-the-counter (OTC) medications may treat excess gas.
Some trial-and-error may be necessary because people's bodies respond differently to different treatments. Some useful OTC remedies include alpha-galactosidase, lactase supplements, simethicone, and activated charcoal.5‘How To Decrease Bloating | Natural Remedies for Gas and Bloating.’ Boston Hospital & Medical Center - Brigham and Women’s Hospital, www.brighamandwomens.org/patients-and-families/meals-and-nutrition/bwh-nutrition-and-wellness-hub/special-topics/gas-beat-the-bloat. Many of these remedies are available at drug stores or pharmacies.

9. Dietary Remedies
Dietary changes can minimize gas production and promote the efficient movement of gas through the digestive system. Journaling one's diet and excess gas symptoms can help the doctor to determine the changes needed. These changes may include the elimination of some items or reduction of the portions.
Some of the foods that may need to be eliminated or reduced include high-fiber foods, dairy, sugar substitutes, fatty or fried foods, carbonated drinks, and fiber supplements. Drinking plenty of water helps prevent constipation.

10. Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Excess Gas
Specific lifestyle changes have proven helpful in alleviating excess gas and its symptoms. Consuming smaller portions can help by not overwhelming the digestive system, as does slow eating and thorough chewing.
Things like drinking through a straw, sucking on hard candies, and chewing gum cause a person to swallow air and should be avoided. Smoking and ill-fitting dentures can also cause gas. As such, smoking cessation and getting well-fitted dentures may help alleviate gas.