10 Causes of Ear Pain
Ear pain can be a distressing issue. Most assume that it is an issue that affects only children. However, it can also occur in adults.
Ear pain can affect one or both ears with the character of the pain being sharp, dull, throbbing, constant, or temporary.
There are many causes of ear pain. It usually resolves once the underlying issue has been treated. However, those who experience persistent ear pain should seek professional medical advice.
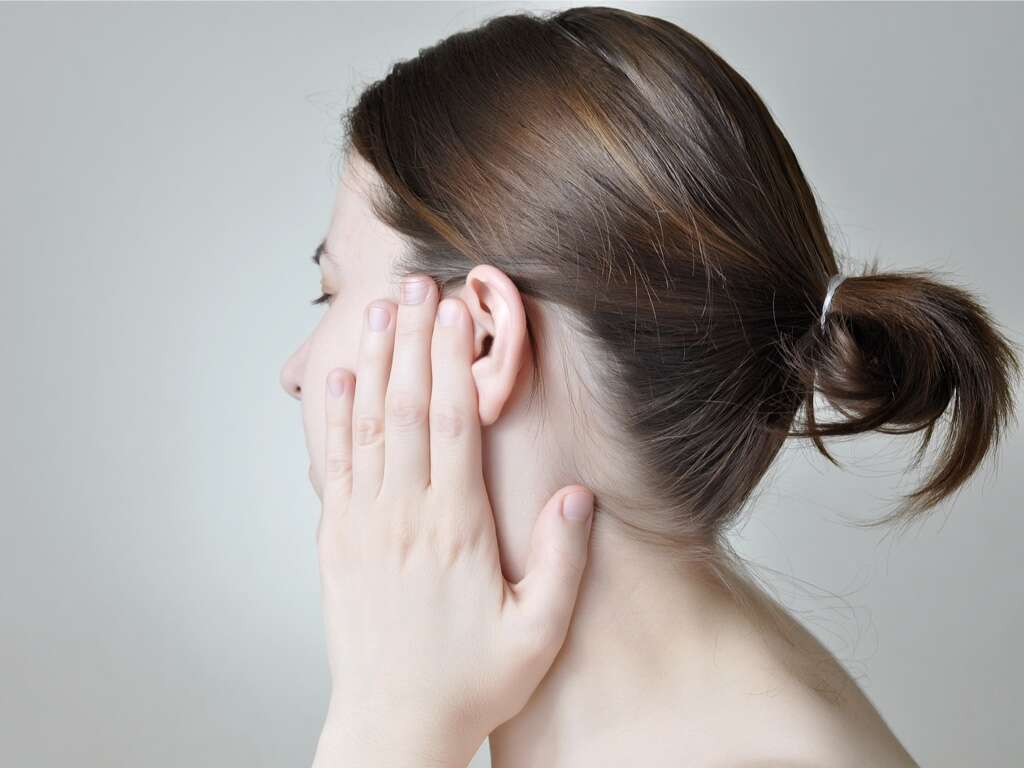

Cause #1: Acute Otitis Media
Acute otitis media (AOM) is an ear infection that results in severe ear pain. It occurs when the middle ear becomes infected and inflamed. In children, it can lead to intense crying, fits of fussiness, and clutching of the ear while wincing in pain. Those affected may experience headache, neck pain, fever, vomiting, irritability, crying, sleeplessness, hearing loss, lack of balance, and pain upon swallowing.
This condition is more prevalent in young children as their eustachian tube is shorter and more horizontal compared to adults, increasing the likelihood of infection.

Cause #2: Otitis Media with Effusion
Otitis media with effusion (OME) refers to an accumulation of noninfectious fluid in the middle ear due to an upper respiratory tract infection, sore throat, or cold. It is usually a self-limiting condition where the disorder resolves within 4 to 6 weeks. In some cases, the fluid can persist longer leading to temporary loss in hearing and ear pain.
It is most commonly seen in children between the ages of 6 months to 3 years. It is also more prevalent during fall and winter. It is believed to be caused by poor function of the eustachian tube resulting in prevention of normal fluid drainage and accumulation of fluid.
Cause #3: Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media
Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is a type of middle ear inflammation that occurs for more than 2 weeks, resulting in episodes of discharge from the ear. While ear pain may be present, it is rare. It is associated with hearing loss.
It is an important condition as it can lead to complications such as disability, poor performance in school, acute mastoiditis, and fatal intracranial infections. Treatment may involve topical antibiotics, topical corticosteroids, ear cleansing, and more. The aim of treatment is to heal perforations, improve hearing, reduce otorrhea, and reduce complications.
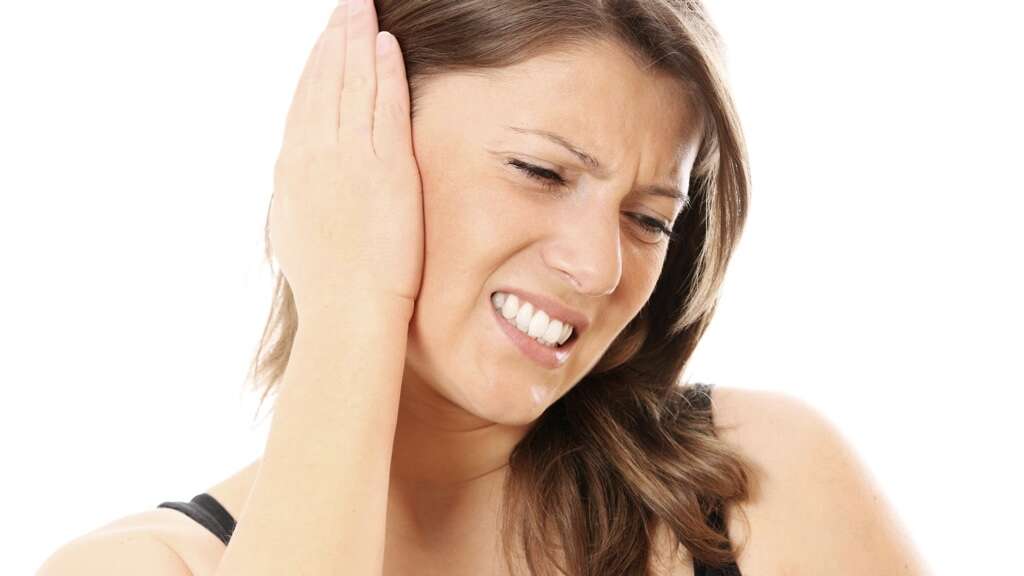

Cause #4: Impacted Earwax
The ear canal produces cerumen, a waxy oil also known as earwax. It functions to protect the ear from microorganisms, dust, and foreign particles. Normally, excess wax finds its way out of the canal naturally into the ear opening and is then washed away.
Glands that produce more earwax than necessary can cause impacted earwax. When one cleans the ears, the wax can be accidentally pushed deeper resulting in a blockage. It is also a common reason for temporary hearing loss. Treatment is simple and generally has great prognosis. It can also cause tinnitus, ear pain, drainage from the ear, and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Cause #5: Air Pressure
Air pressure or ear barotrauma occurs when there is discomfort or pain in the ear due to pressure differences in the outside and inside of the ear. The eustachian tube is a connection between the back of the nose or throat and middle ear. Swallowing or yawning will help to equalize the pressure on either side of the ear drum.
When it is blocked, the pressure in the middle ear is different than that on the outside and can result in barotrauma. This is often seen among those who encounter altitude changes such as driving in the mountains, flying, scuba diving, congestion, or an upper respiratory tract infection. Those affected will experience ear pain, dizziness, hearing loss, stuffiness in the ears, and nosebleeds.

Cause #6: Toothache
Toothache or dental pain occurs when there is pain in the teeth or supporting structures. Toothache can be so severe that it may disrupt daily activities such as eating and sleeping. Most cases of toothache are due to inflammation of the pulp when there is tooth decay, trauma, dentin hypersensitivity, abscesses, and apical periodontitis.
Symptoms of a toothache include pain, headache, ear pain, and sensitivity to warm or cold food and beverages. Toothache can be prevented through good oral hygiene and avoidance of a cariogenic diet. This includes regular brushing, flossing, visits to the dentist, and reduction of refined sugars.
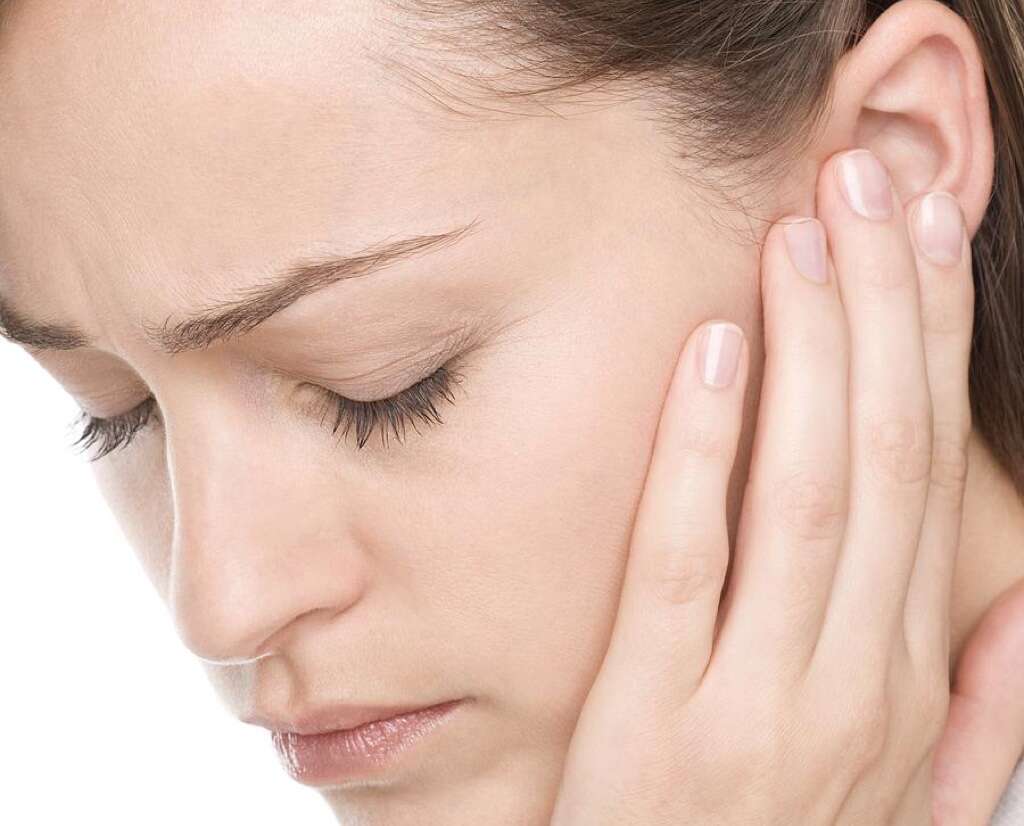

Cause #7: Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis occurs when there is inflammation of the tonsils. Patients with tonsillitis may experience lymphadenopathy, fever, sore throat, enlargement of the tonsils, and ear pain. It can sometimes progress to a peritonsillar abscess. Most cases of tonsillitis are caused by a viral infection. Some causative organisms include Adenovirus, group A Streptococcus, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Corynebacterium Diphtheriae.
Treatment includes the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen), ibuprofen, and antibiotics (for bacterial infections). For those with frequent episodes of tonsillitis, a tonsillectomy is an option as it helps decrease future episodes of tonsillitis.
Cause #8: Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis refers to inflammation of the back of the throat. Patients with pharyngitis also usually experience a fever, sore throat, cough, runny nose, hoarse voice, ear pain, and a headache. Most symptoms last about three to five days.
With pharyngitis, it can result in complications such as acute otitis media, or sinusitis. Most cases of pharyngitis are caused by a viral infection although it can also be linked with allergies, strep throat, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. To help with the pain, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used. If you are suffering from this symptom you should seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.

Cause #9: Swimmer’s Ear
Swimmer’s ear is also known as Otitis Externa and it is characterized by inflammation and/or infection of the ear canal. It is quite common in patients practicing water sports due to the accumulation of water in the ear canal.
The pain is usually on the affected ear only and it can be triggered by touching the patient’s ear.

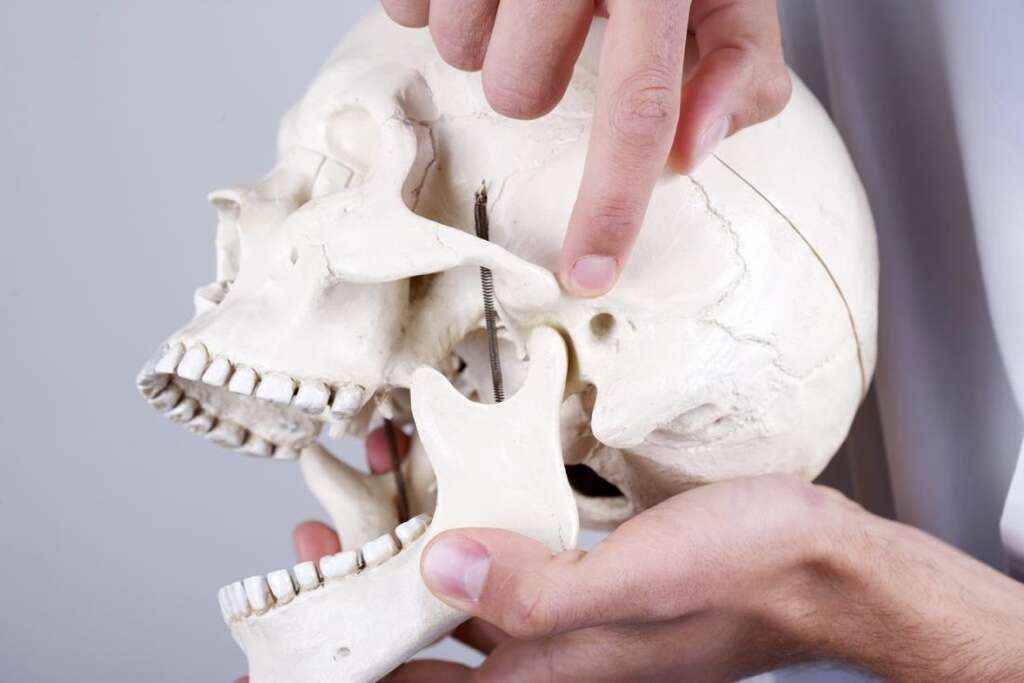
Cause #10: Temporomandibular Joint Disorders
The temporomandibular joint functions as a sliding hinge that connects the jawbone to the skull. With one on each side of the jaw, issues in this joint can lead to pain in the jaw and muscles of mastication. Since the exact cause of temporomandibular joint issues can be hard to determine, the symptoms may be due to a combination of injury, genetics, arthritis, and bruxism.
Most patients experience temporary symptoms where the issue usually resolves on its own without invasive treatment. Surgery is reserved for patients who are still symptomatic after conservative measures. Some symptoms that may be experienced include an aching pain in or around the ear, pain or tenderness of the jaw, pain at the affected temporomandibular joints, difficulty chewing, and locking of the jaw.