10 Symptoms of Angioedema
Angioedema is a condition where there is swelling of the tissue under the skin or mucous membranes. It affects the lower layer of the skin and occurs due to the release of bradykinin or histamine. The onset of angioedema usually ranges from minutes to hours. Angioedema due to an allergic reaction because of foods, medications, and insect bites is related to histamine. In the version that involves bradykinin, it may be due to medications such as angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, hereditary issues like C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, or a lymphoproliferative disorder. To protect the airway, patients may be intubated or a cricothyroidotomy may be performed. Histamine related angioedema may benefit from corticosteroids, antihistamines, and epinephrine.
A C1 esterase inhibitor or medications such as icatibant and ecallantide can be used for bradykinin related angioedema. Fresh frozen plasma is also a viable option. It has been estimated that approximately 100,000 individuals are affected annually in the United States. The diagnosis of angioedema is made based on the patient’s history and physical examination. It is supported through blood tests such as renal function tests, complete blood count, electrolytes, liver enzymes, and more.
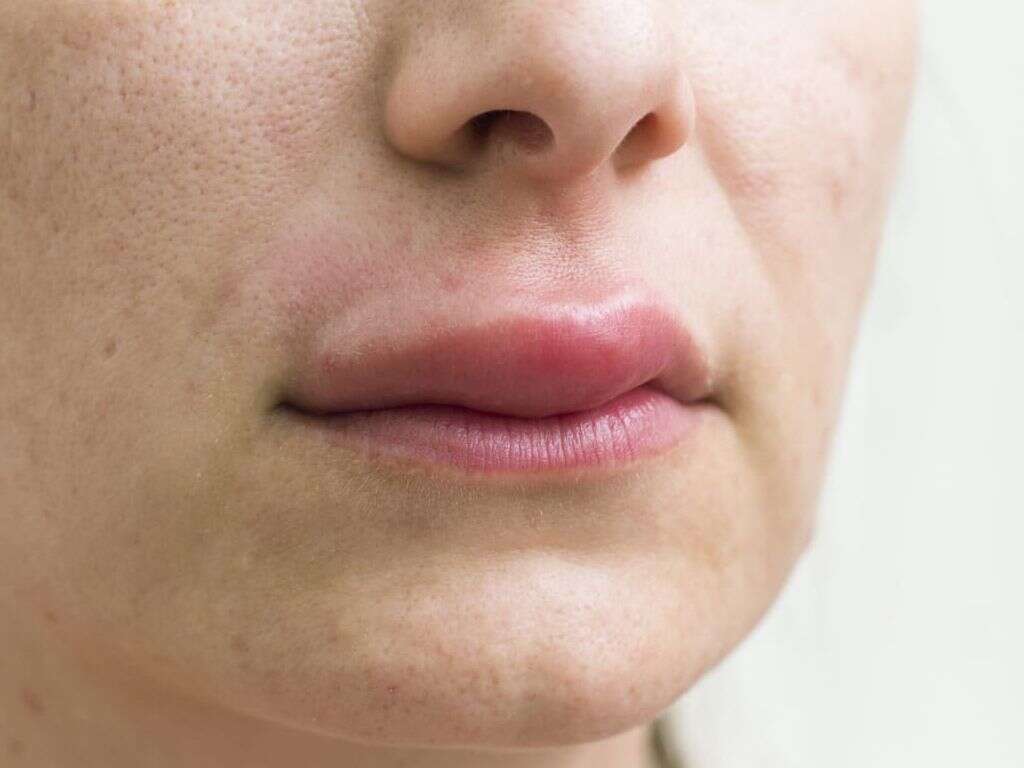
Symptom #1: Swelling
Swelling or edema is one of the cardinal signs of infection. It is a temporary abnormal enlargement of the affected area caused by the accumulation of fluid in the tissues. Swelling usually occurs due to an injury or inflammation in a certain area.
Other associated symptoms of swelling are fever, redness, impaired function, and more. In angioedema, the swelling can also be itchy or painful. The most commonly affected areas in angioedema are the skin of the face, mucosa of the mouth, throat, and tongue.
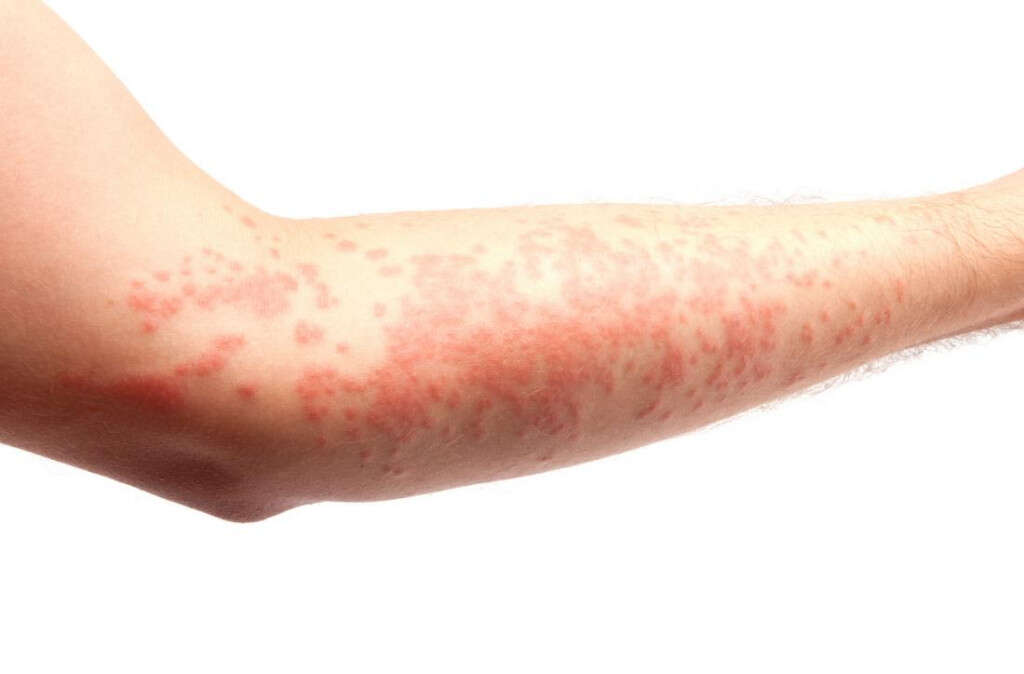
Symptom #2: Hives or Urticaria
Hives or urticaria occurs when there is skin rash that is erythematous, raised, and itchy. These lesions can also feel like burning or stinging. Hives or urticaria usually last approximately several days and do not leave a permanent mark.
It usually occurs after an infection or as a result of an allergic reaction to food, insect bites, medication, stress, cold temperature, and more. To prevent the development of hives or urticaria, patients should try to avoid the trigger. It can be treated with antihistamines, corticosteroids, and leukotriene inhibitors.
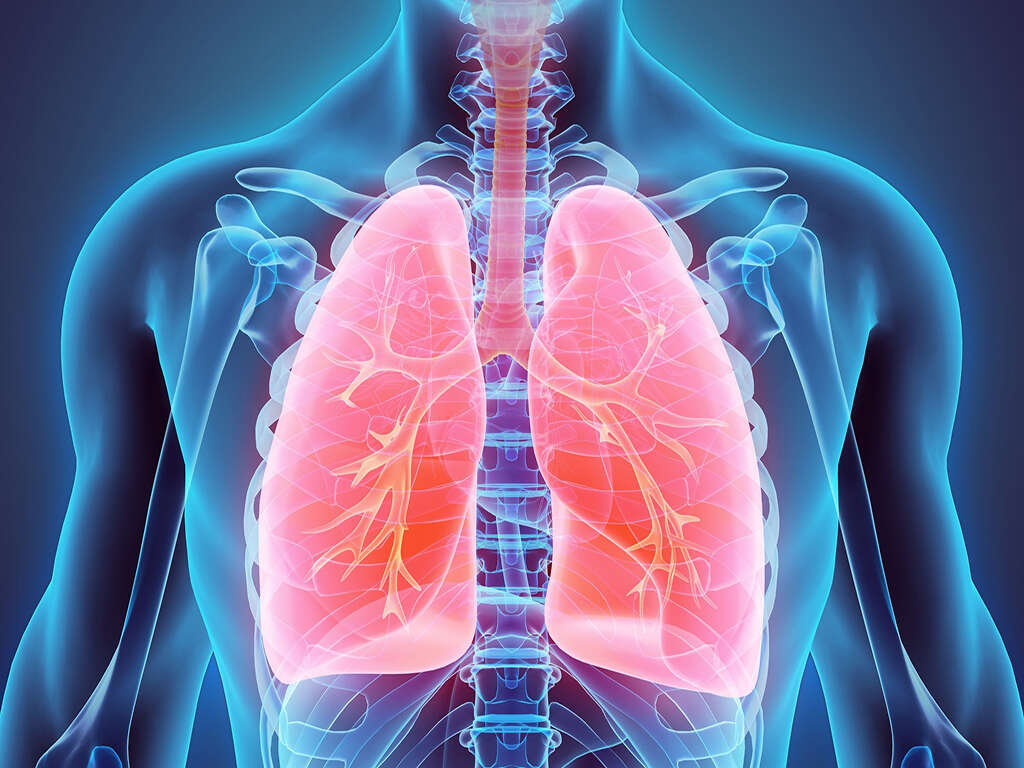
Symptom #3: Stridor
Stridor is a term that describes the high-pitched sound that occurs when there is turbulent air flow in the low bronchial tree or larynx. The presence of stridor usually means that the airway is narrowed or obstructed. It can occur during inspiration, expiration, or biphasic (both inspiration and expiration).
It can be seen in cases such as croup, epiglottitis, lodged foreign body in the airway, laryngeal tumor, airway edema, and more. In angioedema, the swelling of the airway due to the allergic reaction can result in stridor. Tracheal intubation may be required to prevent respiratory arrest.
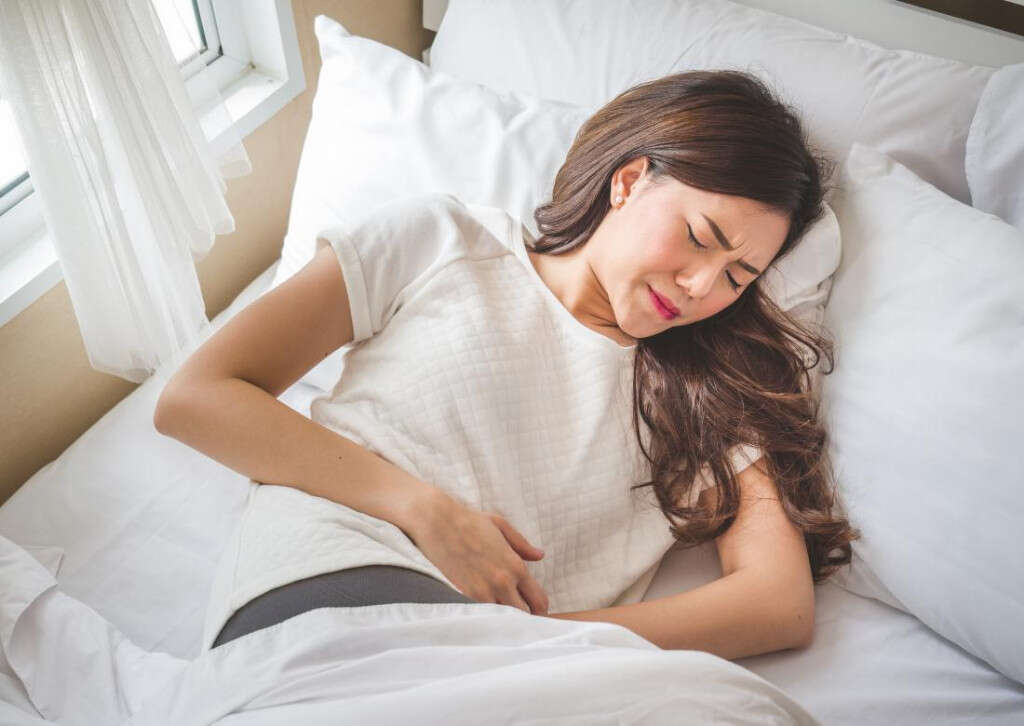
Symptom #4: Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain or stomach ache is a common and non-specific symptom that is often seen in serious and non-serious conditions such as gastroenteritis, irritable bowel syndrome, food poisoning, appendicitis, diarrhea, diverticulitis, ectopic pregnancy, and more. The abdomen can be divided into nine regions: right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypogastric, left lumbar, umbilical, right lumbar, right iliac, suprapubic, and left iliac.
Based on pain that is felt in the different regions, the physician can usually tell what may be causing the abdominal pain. Patients with hereditary angioedema can experience recurrent attacks where there is abdominal pain with associated symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. The pain usually lasts one to five days and may require hospitalization.

Symptom #5: Nausea
Nausea is an unpleasant and uncomfortable sensation where there is an involuntary urge to vomit. It is a non-specific and common symptom that can be seen in pregnancy, food poisoning, gastroenteritis, motion sickness, dizziness, extreme pain, and more. In hereditary angioedema, nausea can occur as part of the recurrent episodes that lasts several days along with associated symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and weakness.
Nausea can be managed using antiemetics such as metoclopramide, promethazine, and ondansetron. Patients with nausea can find the symptom to be debilitating as it greatly affects the quality of life for them.
Symptom #6: Diarrhea
Diarrhea is the occurrence of three or more loose stools per day. It can last several days and result in dehydration, decreased urination, tachycardia, decreased responsiveness, loss of skin color, and more. Causes of diarrhea include infection of the intestines due to a viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection. It can also be caused by irritable bowel syndrome, lactose intolerance, celiac disease, hyperthyroidism, and more.
Management of diarrhea may include oral rehydration solution, zinc tablets, intravenous fluids, and in some rare cases, antibiotics and loperamide. In hereditary angioedema, diarrhea is one of the symptoms seen in the recurrent episodes.

Symptom #7: Vomiting
Vomiting is the involuntary expulsion of stomach contents from the mouth and nose. It may or may not be preceded by nausea. It is a common and non-specific symptom that can be seen in motion sickness, gastroenteritis, food poisoning, pregnancy, gastritis, and more. Like nausea, it can be suppressed using antiemetics.
Excessive vomiting may also lead to dehydration and may require hospitalization and intravenous fluids. In hereditary angioedema, vomiting occurs as part of the symptoms experienced in recurrent attacks. It is accompanied by abdominal pain, nausea, watery diarrhea, weakness, and a non-pruritic rash.
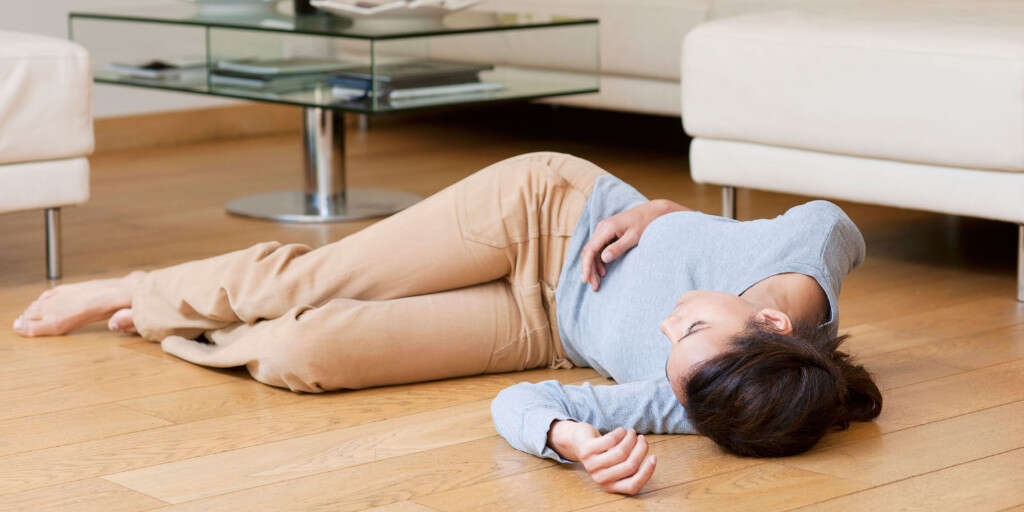
Symptom #8: Dizziness and Fainting
Dizziness is a common and non-specific symptom where one feels off balanced or lightheaded. Most cases of dizziness usually resolve on its own. Patients should try to rest and lie down until the dizziness passes as it increases the risk of injuries and falls especially among the elderly.
Fainting or syncope is a transient loss of consciousness that usually results in a fall. Some of the associated symptoms of fainting include nausea and clammy sweat. Both dizziness and fainting are less common symptoms of angioedema.

Symptom #9: Dyspnea
Dyspnea or shortness of breath describes the feeling where one feels unable to breathe well enough. It can impact the activities of daily living. Patients with dyspnea may describe the need for increased effort to breathe, air hunger, and chest tightness.
Dyspnea can be seen in congestive heart failure, cardiac ischemia, pneumonia, interstitial lung disease, anxiety, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and more. In angioedema, the swelling of the airway can cause shortness of breath.
Symptom #10: Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis can be caused by allergies or infection. It is also known as pink or red eye. It can cause the affected eye or eyes to appear bloodshot, itch, water, produce pus, or have a gritty or burning sensation.
To help relieve and ease the symptoms at home, patients can use a clean cotton wool to gently clean the crusts off the eye lashes. Holding a cold flannel over the eyes also helps to soothe the burning sensation. Conjunctivitis is one of the less common symptoms of angioedema.