10 Angelman Syndrome Symptoms
Angelman syndrome is a genetic condition where the nervous system is affected. Children affected by Angelman syndrome tend to have a happy personality and have a tendency to enjoy water. Symptoms of Angelman syndrome tend to become more noticeable by one year of age.
Angelman syndrome is thought to be due to a new mutation that has been inherited from a parent. It occurs when there is a lack of function of part of chromosome 15 inherited from the maternal side. In most situations, it occurs due to a mutation or deletion of the UBE3A gene on the chromosome. In some cases, it is due to the inheritance of two copies of chromosome 15 from the father and none from the mother. Since the father’s abnormal genes are inactivated by genomic imprinting, there are no functional version of the abnormal gene that remains.
The diagnosis of Angelman syndrome can be made based on the symptoms of the patient and genetic testing. Although there is no cure, the treatment of Angelman syndrome is supportive with options of anti-seizure medications, bracing, and physical therapy. The life expectancy of those affected is usually normal. Angelman syndrome affects about 1 in 12,000 to 20,000 individuals with equal frequency between males and females.

Symptom #1: Microcephaly
Microcephaly is a term that describes the improper development of the brain, which results in a smaller than normal head. Microcephaly can be present at birth or develop in the first few years of life.
Individuals who have microcephaly often experience poor motor function, intellectual disability, seizures, dwarfism, abnormal facial features, and more. Some causes of microcephaly include autosomal dominant microcephaly, autosomal recessive microcephaly, x-linked microcephaly, Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, and more. Microcephaly is also a feature of Angelman syndrome.
Symptom #2: Intellectual Disability
Intellectual disability or general learning disability refers to generalized neurodevelopmental disorder where there is significantly impaired adaptive and intellectual functioning. It can be defined as an intelligence quotient (IQ) below 70 with two or more additional deficits in adaptive behaviors that affect general or everyday living.
Some disorders with intellectual disability include individuals with fragile X syndrome and Down syndrome. Intellectual disability affects an estimated 2 to 3 percent of the general population. It is also seen in Angelman syndrome.

Symptom #3: Developmental Disability
Developmental disability refers to a diverse group of chronic disorders that are caused by physical or mental impairments that begin before adulthood. These disabilities result in difficulties especially in language, self-help, learning, mobility, and independent living. These disabilities can be detected in the early stages of life and persist throughout the affected individual’s lifespan. If it affects all areas of development, it is referred to as global developmental delay.
Some of the patients affected experience fragile X syndrome, Down syndrome, pervasive developmental disorders, cerebral palsy, fetal alcohol spectrum disorders, intellectual disability, and Angelman syndrome.

Symptom #4: Short Attention Span
Attention span is measured by the amount of concentrated time one individual can spend on one task without becoming distracted. Most experts believe that the ability to focus and sustain attention needed is crucial to achieve one’s goals. Some also believe that part of education consists of attention training especially when students are to remain focused on a specific topic for a long period of time.
The estimated length of human attention span is variable and ultimately depends on the definition of attention used. Individuals with Angelman syndrome are thought to have a short attention span.

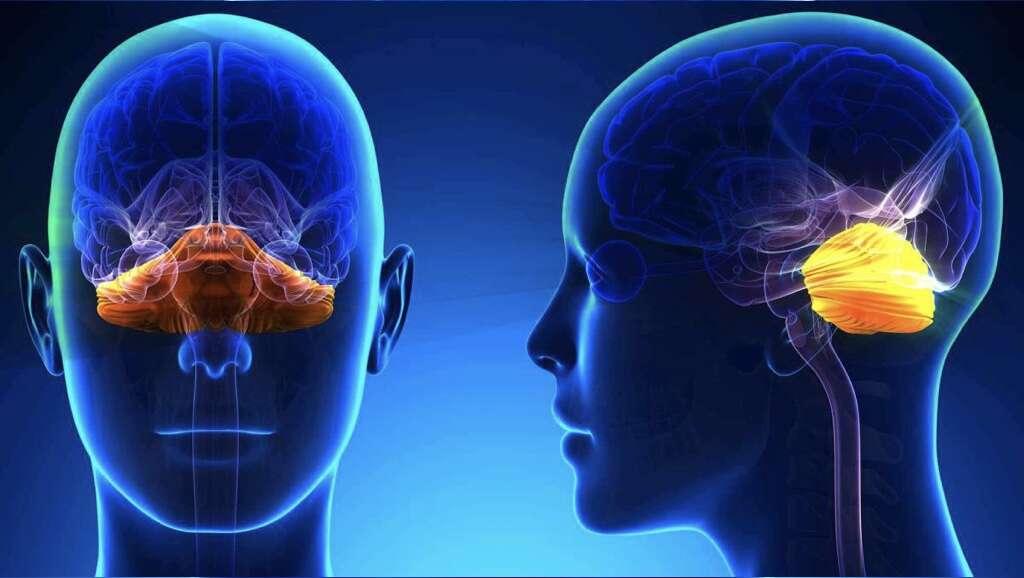
Symptom #5: Ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign where there is lack of voluntary muscle coordination that can result in abnormalities in gait, speech, and eye movements. It is a clinical manifestation which indicates that there is an underlying dysfunction of the nervous system that functions to coordinate movement. It can involve either one or both sides.
In Angelman syndrome, those affected often experience movement or balance disorder where they have gait or limb movement issues. Ataxia can also be seen in any disorders that affect the cerebellum.
Symptom #6: Strabismus
Strabismus is a condition of the eyes where both eyes do not align properly when looking at one object. If present in childhood, it can lead to amblyopia or loss of depth perception. Onset of strabismus during adulthood tends to result in double vision.
Strabismus can occur due to a number of several conditions such as farsightedness, issues in the brain, trauma, muscle dysfunction, infections, premature birth, and more. It can also be observed among those with Angelman syndrome. The treatment of strabismus ultimately depends on the underlying cause. Options include the use of glasses, surgery, and more.
Symptom #7: Seizures
A seizure occurs when there is abnormally excessive synchronous neuronal activity in the brain leading to outward effects where there is uncontrollable shaking and loss of consciousness. Most seizures lasts less than 2 minutes and can take some time to return to normal.
Seizures can be triggered by low blood sugar, hyponatremia, fever, brain infection, concussion, alcohol withdrawal, and more. It is important to note that seizures lasting more than 5 minutes should be treated as a medical emergency. In Angelman syndrome, the seizures can be controlled using anticonvulsant medications.

Symptom #8: Speech Impairment
Child developmental milestones are important for professionals to assess the physical and mental changes in a child that mark the end and beginning of a developmental period. Milestones are important as it indicates a stage of transition. The four main components of language development are phonology, lexicon, morphology, and pragmatics.
In Angelman syndrome, there is absence or near absence of speech. While most are unable to speak, there are a few who have some limited speech. Most children with Angelman syndrome will benefit from speech, physical, and occupational therapy.

Symptom #9: Aggressive Behavior
Aggressive behavior refers to behavior that can cause injury or harm to another individual. While individuals with Angelman syndrome are thought to have aggressive behavior, it does not mean that these individuals are intentionally trying to hurt another person.
A study found that about 7 out of 10 individuals show some degree of aggressive behavior. This research has also observed that individuals with Angelman syndrome are three times more likely to display aggressive behavior compared to others. Some aggressive behavior seen include hair pulling, hitting, scratching, kicking, biting, and more.

Symptom #10: Hypotonia of Trunk with Hypertonia of Limbs
Hypotonia is a term that refers to low muscle tone where there can be reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder but can be seen in various conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, achondroplasia, Down syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, fragile X syndrome, neurofibromatosis, Patau syndrome, and more.
Hypertonia is a term that is sometimes used synonymously with rigidity or spasticity. It usually occurs when there is damage to the central nervous syndrome. However, in individuals with Angelman syndrome, they tend to have hypotonia of the trunk (body) with hypertonia of the limbs (arms and legs).