Anencephaly Definition, Causes & More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. 'Facts about Anencephaly.' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 28 Dec. 2020, www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/anencephaly.html.
- 2. 'Facts about Anencephaly.' Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 28 Dec. 2020, www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/anencephaly.html.
- 3. 'Anencephaly: MedlinePlus Genetics.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 18 Aug. 2020. medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/anencephaly/#synonyms.
- 4. 'Anencephaly.' Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment for Newborns | St. Louis Childrens Hospital, www.stlouischildrens.org/conditions-treatments/anencephaly.
- 5. 'Anencephaly: Neural Tube Defect, Birth Defect, Causes, Prevention.' Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15032-anencephaly.
6. How Is Anencephaly Diagnosed?
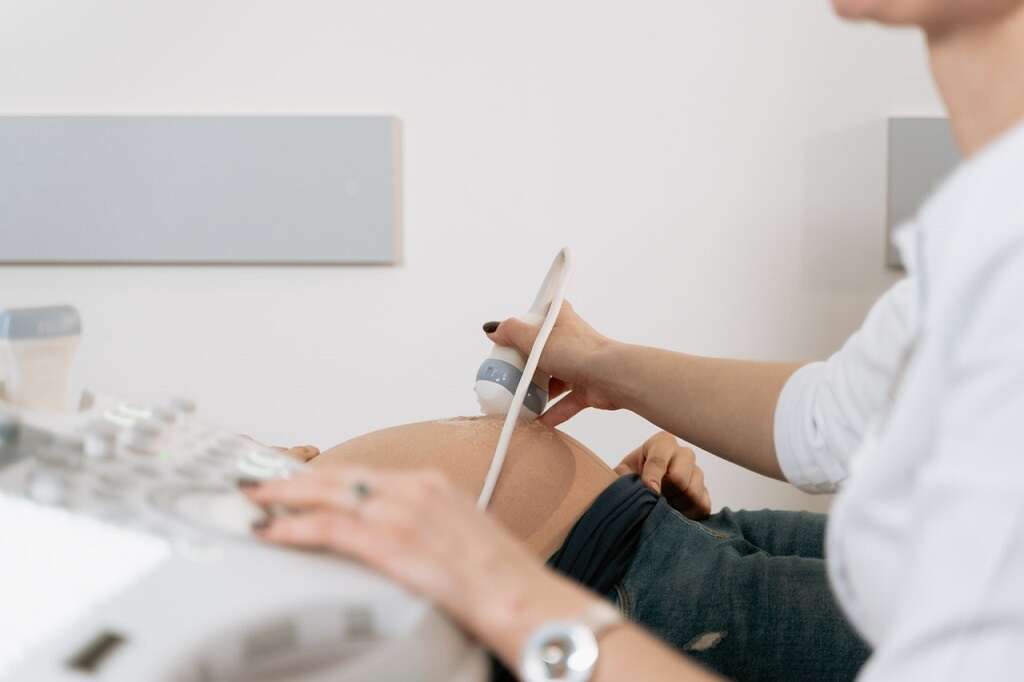
Anencephaly is often diagnosed in the womb, though it may sometimes be diagnosed at birth. The condition may show up on an ultrasound as early as eight weeks into a pregnancy.2‘Facts about Anencephaly.’ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 28 Dec. 2020, www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefects/anencephaly.html.
A blood test in the first few months of pregnancy can measure levels of a protein made by the baby growing in the womb. High levels of this protein do not mean that the baby has anencephaly, only that there’s a higher risk. An ultrasound and further tests can help confirm.4‘Anencephaly.’ Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment for Newborns | St. Louis Childrens Hospital, www.stlouischildrens.org/conditions-treatments/anencephaly.
Advertisement