10 Radiation Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Lanes, Olivia, and David Cheng. 'Radiation Sickness.' NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), 21 July 2015, rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/radiation-sickness/
- 2. 'Radiation Therapy Side Effects.' American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html
- 3. 'Radiation-Induced Vasculopathy.' A Non-Profit Hospital in Los Angeles | Cedars-Sinai, 11 2020, www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/r/radiation-induced-vasculopathy.html
- 4. 'Radiation - Radiation Sickness.' Encyclopedia Britannica, www.britannica.com/science/radiation/Radiation-sickness
- 5. Acute Radiation Syndrome. Professor Robert B. Laughlin, Department of Physics, Stanford University, large.stanford.edu/courses/2017/ph241/bae1/
Radiation sickness, radiation poisoning or acute radiation syndrome, also known as ARS, happens when the body is exposed to radiation for a short period of time, but long enough for it to penetrate the skin and reach the organs.1Lanes, Olivia, and David Cheng. ‘Radiation Sickness.’ NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), 21 July 2015, rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/radiation-sickness/ Historical examples include the bombing of Hiroshima and the reactor explosion at Chernobyl.
While radiation sickness is rare, there are instances where patients may be exposed to radioactive substances. Radiation is also used in the treatment of certain diseases such as cancer. Depending on the area of treatment, the symptoms may vary. For instance, radiation of the mouth could lead to tooth decay.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html

Diarrhea
Diarrhea is one of the early signs of exposure to radiation. The effects can take place within minutes to days of exposure, and the severity will depend on the level of exposure and type of radiation. Severe diarrhea can lead to dehydration, which needs immediate medical intervention.
Those undergoing radiation therapy may need to follow a special diet to counter the effects of diarrhea. Liquid diets and frequent small meals may help, and when diarrhea improves, meals can include small amounts of low-fiber foods. It's also important to take in enough potassium as it allows the body to absorb nutrients better.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html

Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is a common symptom of radiation exposure and can start within minutes. It's critical to get medical help as soon as the symptoms appear in order to effectively treat this problem. If nausea is accompanied by vomiting, it's important to replace the fluids to avoid dehydration.
Those undergoing radiation therapy are often advised not to eat before the procedure to reduce vomiting. Medication may help manage the symptom if it persists. Bland snacks such as toast might help manage nausea.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html

Fever
Fever is the body's way of fighting off infection. Radiation may cause inflammation in the body, such as radiation pneumonitis, which happens with radiation to the chest or breasts. The body's natural response is a low-grade fever as the radiation damages the lung tissue.
This symptom doesn't always appear immediately and can take up to 3 to 6 months to appear. Other symptoms that may accompany fever include a cough, pink-tinged sputum and weakness.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html

Headache
Radiation can cause headaches which should go away after a short while. It may cause temporary swelling of the brain, which leads to pressure.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html
Radiation therapy is also known to cause vasculopathy, which is a condition that affects blood vessels. It causes lesions or narrowing of the blood vessels and limits the blood supply to the brain, which is called ischemia. The condition is reversible in some cases through certain procedures.3‘Radiation-Induced Vasculopathy.’ A Non-Profit Hospital in Los Angeles | Cedars-Sinai, 11 2020, www.cedars-sinai.org/health-library/diseases-and-conditions/r/radiation-induced-vasculopathy.html

Fatigue
Exposure to enough radiation means that healthy cells in the body get destroyed. The body works hard to replace or repair these cells, which could lead to fatigue as all the energy is channeled to the affected areas.
Fatigue is also a symptom of radiation therapy, even though the radiation is medically controlled. This is because the therapy doesn't only destroy affected cancerous cells but healthy cells too. While fatigue can't be measured, the patient needs to alert medical professionals when it becomes debilitating.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html

Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, of being unwell and weak physically and/or emotionally. Malaise may also be accompanied by confusion and fatigue.
Radiation therapy can cause malaise and is often referred to as cancer fatigue. Both cancer and its treatment cause foreign responses in the body, which means that the body is constantly fighting off foreign bodies. Once the treatment is complete, the malaise will improve.4‘Radiation - Radiation Sickness.’ Encyclopedia Britannica, www.britannica.com/science/radiation/Radiation-sickness

Coma
There are three main syndromes associated with acute radiation syndrome, depending on the radiation threshold: hematopoietic (affecting bone marrow), gastrointestinal (major changes in the digestive system) and neurovascular syndromes. Patients who go into a coma caused by radiation fall within the neurovascular category, which usually takes place with a 30 to 50 Gray exposure.
Other symptoms in this category include convulsions. This level of exposure is almost always fatal and patients can go into a coma within three days. Death follows soon after.5Acute Radiation Syndrome. Professor Robert B. Laughlin, Department of Physics, Stanford University, large.stanford.edu/courses/2017/ph241/bae1/

Seizures
The severity of seizures, when exposed to radiation, depends on the radiation dose and type. Those undergoing radiation therapy for diseases, such as brain cancer, might experience mild seizures after treatment. This is usually a short-term problem, and once treatment stops, the seizures will stop.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html
Radiation that leads to neurovascular syndrome, however, is more serious. These lead to convulsions. Other symptoms of this syndrome include coma and death.5Acute Radiation Syndrome. Professor Robert B. Laughlin, Department of Physics, Stanford University, large.stanford.edu/courses/2017/ph241/bae1/
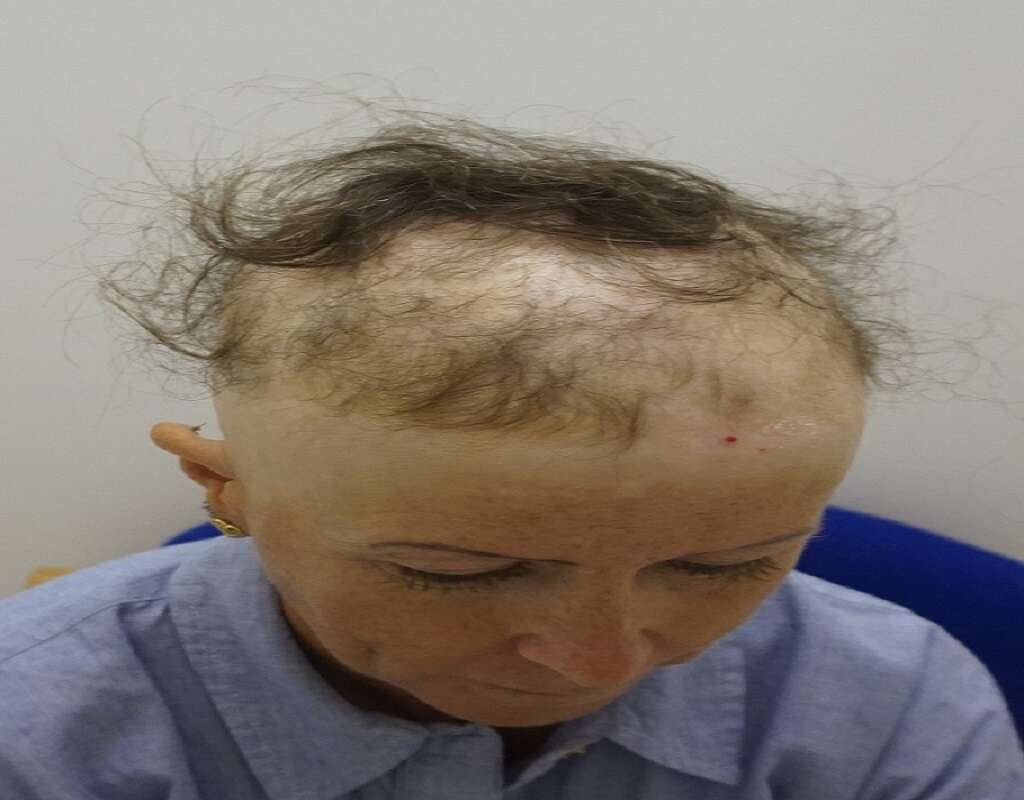
Hair Loss
Radiation therapy can lead to hair loss or alopecia. The hair loss may be limited to the area that receives the radiation, however other courses of cancer management may lead to total hair loss, such as chemotherapy.
Once the radiation therapy is complete, it can take up to three to six months for the hair to grow back. It's not uncommon for the hair to grow back thinner or different texture.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html
Skin Damage
Radiation dermatitis is often a side effect of radiation therapy. This can leave the skin swollen, sensitive, red or darkened. It's important to manage the effects of dermatitis to protect the skin in the long term.
The radiation medical team will provide information on skin best practices. After the radiation therapy ends, the skin might still feel sensitive, dry and flaky. Peeling is a common symptom of radiation dermatitis.2‘Radiation Therapy Side Effects.’ American Cancer Society | Information and Resources About for Cancer: Breast, Colon, Lung, Prostate, Skin, www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/treatment-types/radiation/effects-on-different-parts-of-body.html