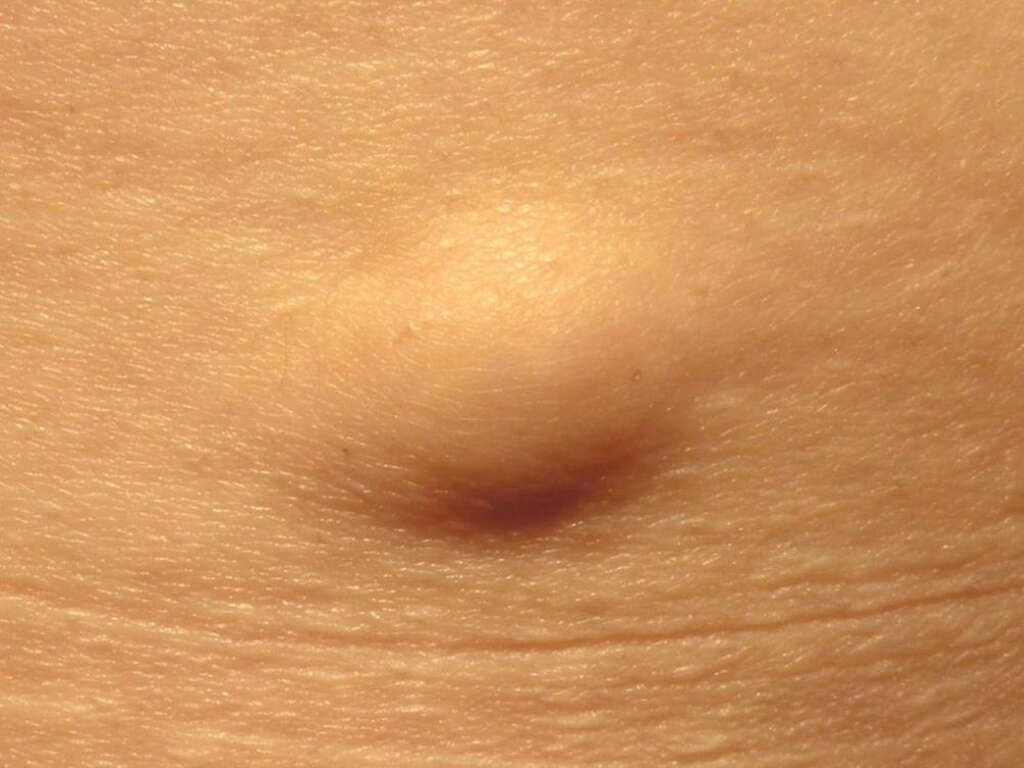
10 Lipoma Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. ’Lipoma | Lipoma, Arm.' MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 16 April 2019. medlineplus.gov/ency/imagepages/1209.htm
- 2. ’Olafsdottir, B. E., Frodadottir, H. K., Runarsdottir, R., & Valsdottir, E. B. (2018). Laeknabladid.’ 104(11), 499–501. www.doi.org/10.17992/lbl.2018.11.204
- 3. Kosztyuova, T., & Shim, T. N. (2017). 'Rapidly enlarging lipoma.’ BMJ Case Reports, 2017, bcr2017221272. www.doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-221272
- 4. Agrawal, Amit, and K J Singh. Symptomatic Intestinal Lipomas: Our Experience. Medical Journal, Armed Forces India, Elsevier, Oct. 2011, [www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4920661/.](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4920661/.)
- 5. Dercum's Disease. NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), 26 Mar. 2020, rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/dercums-disease/
- 6. Singh, Mansher et al. 'Causal Relation between Nerve Compression and Migraine Symptoms and the Therapeutic Role of Surgical Decompression.' Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Global open vol. 3,5 e395. 5 Jun. 2015, doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000345
Lipoma is a benign lump of fatty tissue cells. Lipomas can form on every organ of the body but are most typically seen in the subcutaneous layer beneath the skin. It's a soft, movable lump that develops slowly and isn't usually painful. Lipomas can also be related to other disorders that aren't quite as harmless.
In rare instances, lipomas can put pressure on nerves resulting in pain. The severity of pain is determined by where it's located in the body and which adjacent tissues or organs it has affected.1’Lipoma | Lipoma, Arm.’ MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine, 16 April 2019. medlineplus.gov/ency/imagepages/1209.htm
Nodule or Bump
The first symptom of lipoma is the formation of a bump or nodule below the skin. This could be the size of a pea or as large as a couple of inches in diameter. There are cases where it has grown four inches and weighs in excess of two pounds.2’Olafsdottir, B. E., Frodadottir, H. K., Runarsdottir, R., & Valsdottir, E. B. (2018). Laeknabladid.’ 104(11), 499–501. www.doi.org/10.17992/lbl.2018.11.204
Soft and normally painless, lipomas move below the skin when prodded with the finger. The condition tends to run in families, passed on from one generation to the next, therefore genetics may play a role. It most commonly appears between 40 and 60 years of age, but can appear in children, too.
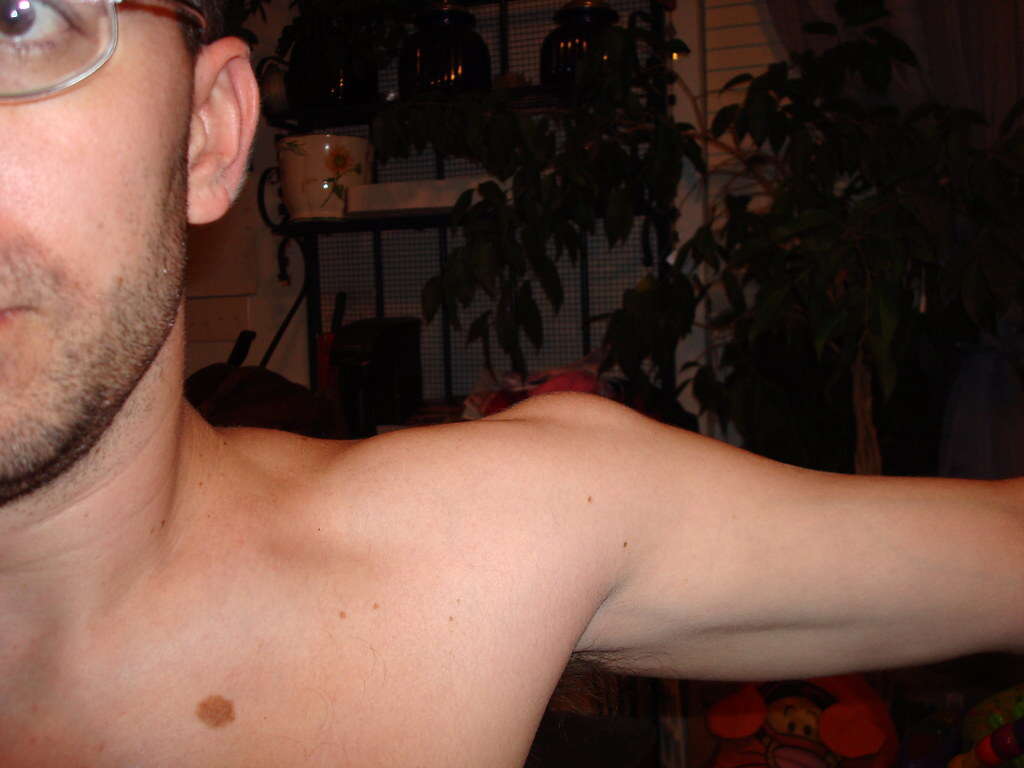

Painless Mass
Lipoma can be present almost anywhere in the body, even in the brain. Because it is non-cancerous, many people unknowingly live with one for many years. As the lump mainly comprises fatty fibers, it presents limited risks if it doesn't grow.
Removal is normally only necessary if it becomes symptomatic and the lump becomes enlarged. A painful lipoma normally indicates associated complications, such as pressure on surrounding nerves. Lipomas may also be removed for cosmetic reasons, especially those on the face and neck.
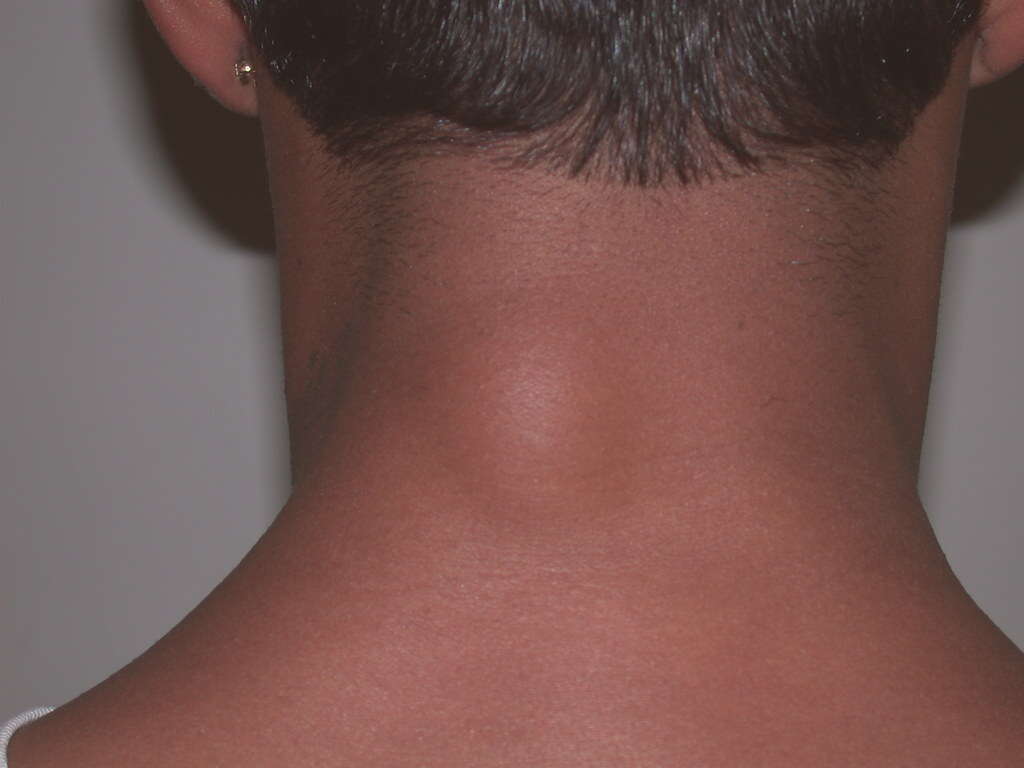
Moves When Prodded
Lipomas are not attached to muscle or skin, which makes their removal uncomplicated. Depending on the size, it may only require day surgery. Because it is not directly attached to either the skin or muscle tissue, the lipoma moves beneath the skin when prodded.
This movement of the lipoma when prodded causes no pain. If there is pain, it may be a sign of a more serious condition that needs medical investigation.

Slow Growth
Lipomas develop slowly and may be initiated by an injury, though the cause is not known. Genetics plays a role as lipomas can be hereditary. Children may have several lipomas at similar locations on the body as the parent.
Normally ranging in size from a pea to a couple of inches, they can remain unchanged in size for years. In rare instances, a lipoma may grow rapidly and present with additional complications, such as ulceration.3Kosztyuova, T., & Shim, T. N. (2017). ‘Rapidly enlarging lipoma.’ BMJ Case Reports, 2017, bcr2017221272. www.doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-221272

Sudden Discovery
The sudden discovery of a lump under the skin can be cause for alarm. Lipoma is a non-cancerous growth of fatty tissue between the skin and the muscle layers below. It can present as a spongy capsule that is painless to touch and moves when prodded.
It will normally remain constant in size for many years, and if it doesn't cause any discomfort or unsightliness, it doesn't need to be removed. If, however, the growth is painful, the affected individual should consider seeking medical attention.
Sometimes Painful
Lipoma is a broad categorization of tumors of fatty tissue. There are more than eight types of lipoma, mainly categorized by their location in the body and their relation to other diseases. Conditions that cause lipoma are Gardner's syndrome and Madelung's disease.
Those who have undiagnosed lumps appearing on their body may want to have them checked by a health professional. It's usually not a dangerous condition, but if it's tender, it may need further investigation.

Easy Bruising
A lipoma shares similarities with liposarcoma, which is a rare form of cancer that begins in the fat cells. Liposarcoma is a deep-seated tumor that typically grows on the thigh, groin or back of the abdomen. It is also painless and grows slowly, although sometimes liposarcoma can grow fast and ulcerate on the surface.
An indicator of liposarcoma is easy bruising and ulcerations, although this applies to other conditions. The treatment involves surgery followed by radiotherapy, while chemotherapy may be an option for some.

Digestive Problems
A lipoma could form in the intestinal tract and may cause digestive problems. The vast majority present no symptoms, but larger ones can cause blockages or be mistaken for malignant tumors.
Signs of lipoma in the gut can include watery diarrhea, constipation, bloody stools and discomfort. In most cases, however, the region will be soft to the touch. There may also be complications affecting other organs, such as the liver, spleen and gallbladder.4Agrawal, Amit, and K J Singh. Symptomatic Intestinal Lipomas: Our Experience. Medical Journal, Armed Forces India, Elsevier, Oct. 2011, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4920661/.

Fatigue
Dercum's disease is a rare condition characterized by the growth of multiple painful lipomas and fatigue. These lipomas may occur anywhere on the body and can cause severe pain. Other symptoms may include weakness and memory disturbances. This disease is chronic and tends to be progressive.
A diagnosis of Dercum's disease can be made after a thorough physical exam, identifying the characteristic features, and ruling out other conditions. The condition is classified as rare.5Dercum’s Disease. NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders), 26 Mar. 2020, rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/dercums-disease/

Migraine Headaches
Because benign fatty tumors can form anywhere fat cells are present, some can form in the brain. These brain lipomas are sometimes associated with head trauma. The brain lipomas are usually small and harmless, but they can cause complications if they grow larger and exert pressure on the nerves, resulting in migraines.
The removal of the lipoma from the brain can provide total relief of migraine symptoms, as the nerves are decompressed.6Singh, Mansher et al. ‘Causal Relation between Nerve Compression and Migraine Symptoms and the Therapeutic Role of Surgical Decompression.’ Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. Global open vol. 3,5 e395. 5 Jun. 2015, doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000000345