10 Cor Pulmonale Symptoms
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. Garrison, Daniel M., et al. 'Cor Pulmonale.' StatPearls /[Internet/], Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430739/
- 2. Tidy, Colin. 'Cor Pulmonale.' Patient, 30 Dec. 2016, patient.info/doctor/cor-pulmonale
- 3. 'Syncope (Fainting).' Johns Hopkins Medicine, Based in Baltimore, Maryland, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/syncope-fainting
- 4. Towers, M. K. 'Chronic Cor Pulmonale.' Postgraduate Medical Journel, vol. 42, 1966, pp. 506-512, pmj.bmj.com/content/postgradmedj/42/490/506.full.pdf
- 5. 'How Oxygen Affects the Extremities.' Lung Health Instititute, 28 Mar. 2016, lunginstitute.com/blog/oxygen-affects-extremities/
Cor pulmonale is a condition where the right side of the heart doesn't work as effectively or fails due to changes in its function or structure. This heart condition is caused by an issue in the respiratory system, which leads to high blood pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs.
Factors, such as cigarette smoking, air pollution and various lung diseases, can increase the risk of cor pulmonale. There are several treatment options, which commonly seek to address underlying lung conditions. Early cor pulmonale symptoms are typically nonspecific.1Garrison, Daniel M., et al. ‘Cor Pulmonale.’ StatPearls /[Internet/], Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2021, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430739/
Breathlessness
Breathlessness, known medically as dyspnea, is a common symptom of cor pulmonale. People commonly experience shortness of breath on exertion, such as when exercising, walking up stairs or carrying heavy items. Some people may feel breathless with minimal exertion.
Being short of breath may be among the first symptoms of cor pulmonale that a person notices. Breathlessness may increase over time, though an increase in the severity of feeling breathless isn't necessarily an indication that the primary lung condition is worsening. People generally find that they become less tolerant to exercise and activity.

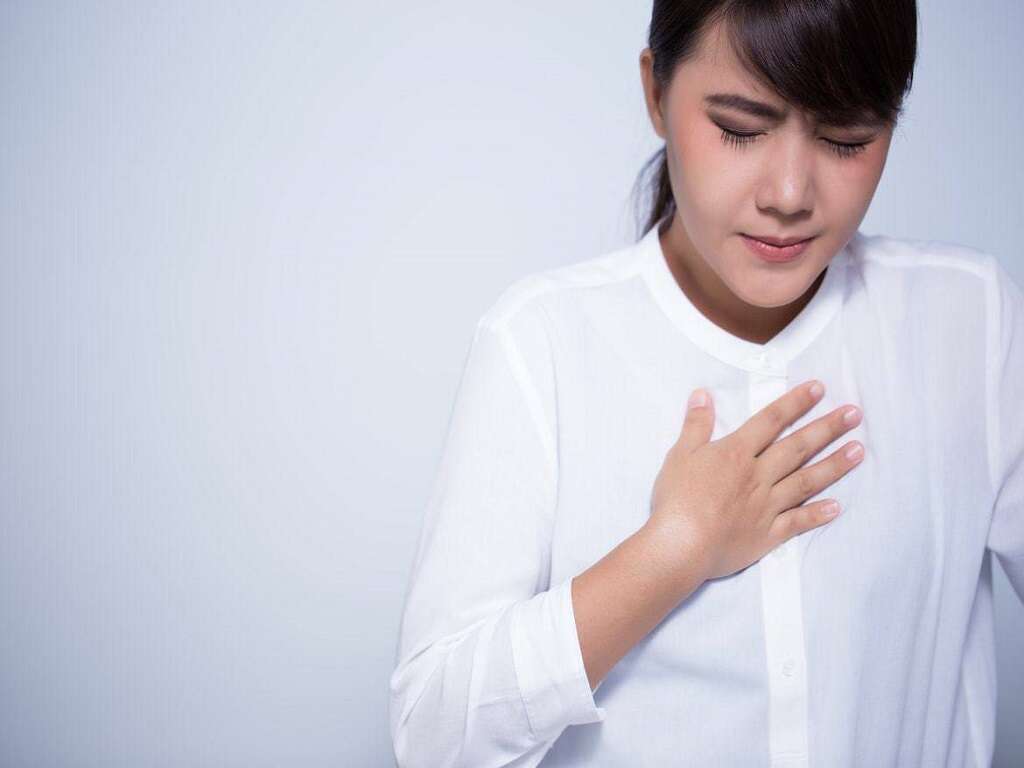
Chest Pain
Some people experience chest pain or discomfort as a symptom of cor pulmonale. While chest pain may be constant, individuals feel pain in their chest upon exertion. The chest may feel heavy or tight, and some people may experience sharp, shooting pains.
Chest pain caused by cor pulmonale doesn't typically respond to treatment using medicinal nitrates, medicine that relaxes veins and arteries. This could be because the pulmonary artery is stretched or the right heart chamber is deprived of oxygen.2Tidy, Colin. ‘Cor Pulmonale.’ Patient, 30 Dec. 2016, patient.info/doctor/cor-pulmonale

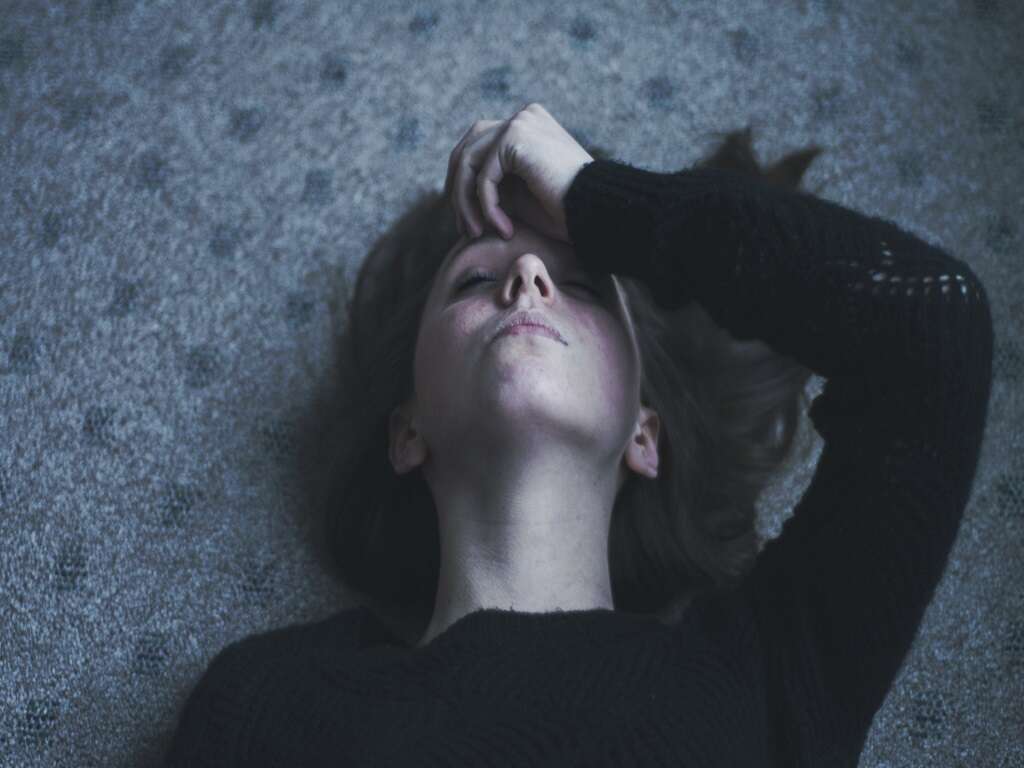
Fainting
People with cor pulmonale may faint. Fainting, medically known as syncope, is a sudden and short period of unconsciousness. It happens when there is a temporary decrease in the amount of oxygenated blood reaching the brain.3‘Syncope (Fainting).’ Johns Hopkins Medicine, Based in Baltimore, Maryland, www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/syncope-fainting
If fainting occurs as a result of cor pulmonale, it typically occurs upon exertion. For example, an individual may pass out when exercising. Immediately before fainting, an individual may feel lightheaded or nauseous or experience blurred vision or slurred speech. Generally, people recover consciousness soon after fainting.

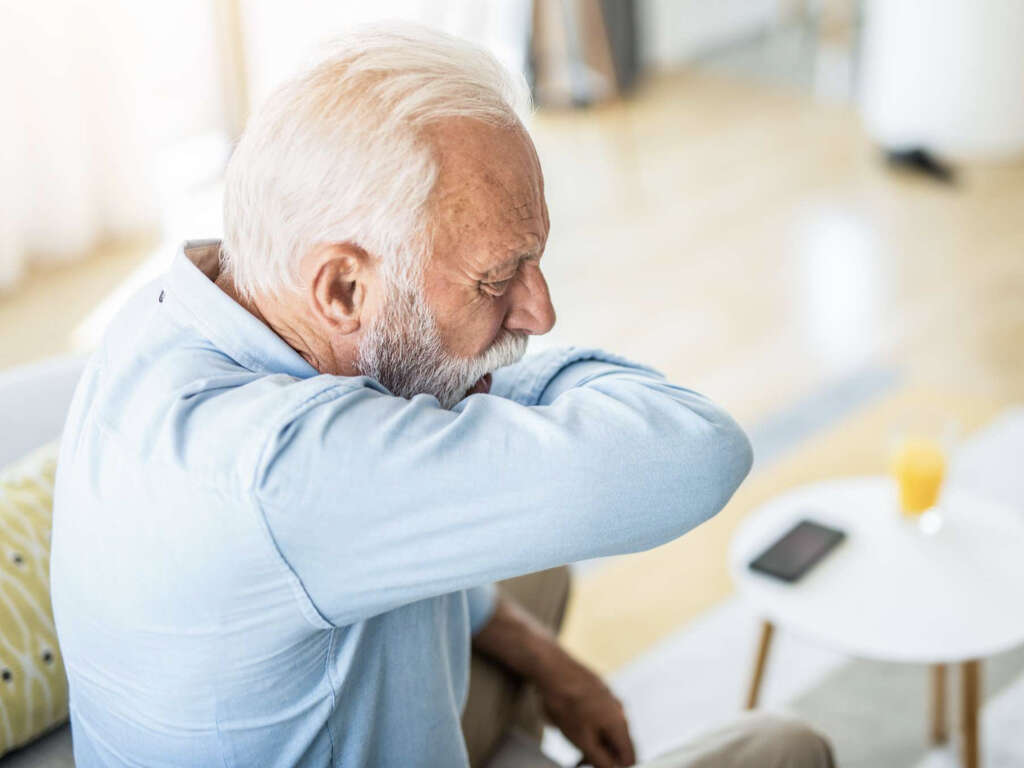
Cough
An excessive cough, particularly when the cough is dry and there is no phlegm or sputum, may be a cor pulmonale symptom. People may, however, also experience productive coughs, which can be accompanied by wheezing sounds when breathing. Some research suggests that coughing may be worse in cold weather.
Coughing caused by cor pulmonale typically worsens over time, and medicinal cough remedies may offer little relief. Occasionally, people may faint due to intense fits of coughing.4Towers, M. K. ‘Chronic Cor Pulmonale.’ Postgraduate Medical Journel, vol. 42, 1966, pp. 506-512, pmj.bmj.com/content/postgradmedj/42/490/506.full.pdf

Fatigue
People with cor pulmonale can experience fatigue, which can be physical or mental. Fatigue is commonly caused by the reduced amount of oxygen-carrying blood being pumped around the body. As a result, less oxygen reaches the brain.
Fatigue can make it difficult for individuals to perform their regular daily activities. People may feel overwhelmingly tired, have aching muscles and be unable to concentrate. Fatigue can lead to distress and frustration.

Swollen Ankles
When people have cor pulmonale, they may experience swelling of the ankles, known as edema of the ankles. Swelling can also affect the legs and feet. Skin may feel tight and tender.
When the heart cannot efficiently pump blood around the body, blood traveling in the veins towards the heart moves slower. This can cause fluid to leak into tissue surrounding the veins. Because of gravity, this fluid typically gathers in lower body parts.5‘How Oxygen Affects the Extremities.’ Lung Health Instititute, 28 Mar. 2016, lunginstitute.com/blog/oxygen-affects-extremities/

Swollen Abdomen
Cor pulmonale can lead to abdominal swelling, or abdominal edema. As with swollen ankles, this is due to fluid leaking into areas around the veins. Fluids can gather in abdominal spaces, known medically as ascites. It can be painful or uncomfortable.
When swelling of the abdomen occurs as a cor pulmonale symptom, it may accompany swelling of the legs, feet or ankles. Abdominal swelling is typically a later symptom of cor pulmonale.

Blue Skin
Skin may appear to have a bluish tinge in people with cor pulmonale. The medical term for such discoloration of the skin is cyanosis. It usually affects the fingers and toes or the lips and mouth.
The skin looks blue because of the color of blood. While healthy, oxygen-filled blood is red, blood is blue when it does not contain enough oxygen. Lack of oxygen in the blood occurs with cor pulmonale because the heart is unable to pump blood around the body efficiently.

Vocal Changes
Cor pulmonale may cause vocal changes. An individual might sound hoarse. The voice may be softer, quieter or at a lower pitch, and it can sound strained or raspy.
Hoarseness can arise as a cor pulmonale symptom if the pulmonary artery is stretched. When wider, this artery can put pressure on a nerve called the recurrent laryngeal nerve. This nerve is responsible for sending signals between the brain and the muscles of the larynx, or voice box.

Palpitations
Palpitations can be a symptom of cor pulmonale. This symptom may begin with exertion, gradually worsening so that people feel as though their heart is beating abnormally, even when at rest.
Palpitations can feel like the heart is beating harder than normal, sometimes referred to as pounding, or beating faster than normal, sometimes called racing. Palpitations can also make a person feel as though their heart is fluttering or missing beats.