What Is Thyroid Disease?
All day, every day, our bodies are performing countless different functions. We tend not to notice, but these functions include things like the digestion of our food, processing food for energy, the beating of our heart, and so much more. These functions need to be all working well in order for our good health to be maintained.
Helping with the functioning of these functions are chemicals that are produced by our bodies. These chemicals are known as hormones and they are manufactured in our glands from nutrients in our food. There are numerous different glands in the body the produce different hormones, and one of these glands is known as the thyroid gland.

1. The Thyroid Gland
The thyroid is a small gland that is found in the neck. We don’t usually know it is there, but it performs some very important functions for us. This is mainly the production and secretion of hormones that are important for the day to day functioning of our bodies.
Some people will develop problems with their thyroid gland, and this can impact the levels of hormones in our body. It has the potential to make us quite ill and the more severe cases can even be dangerous to us. When the thyroid is affected in this way, it is generally known as thyroid disease.

2. Thyroid Disease?
Thyroid disease is an umbrella term for medical conditions that affect the production and release of hormones from the thyroid gland. As these hormones play an important role in the running of our body, they can have a real impact on how our body functions. Thyroid disease can also be broken down into another two sub-categories.
These categories are hypothyroidism, and hyperthyroidism. The former means that the thyroid gland is producing too few hormones, while the latter means that too many hormones are being released into the body. Each type has different potential causes, and will also result in different symptoms.
3. Hypothyroidism Causes
As mentioned, hypothyroidism means that the thyroid gland is not producing enough hormones. One potential cause of this is thyroiditis, which is an inflammation of the gland. Another potential cause is that the patient has insufficient levels of iodine in their diet, although this is fairly easy to remedy.
Hashimoto’s disease is a condition where the patient’s thyroid gland is being attacked by their immune system, which can affect hormone production. There is also postpartum thyroiditis, which happens in some women after they have given birth. Another potential cause is that some people are born with a thyroid gland that is not functioning properly.
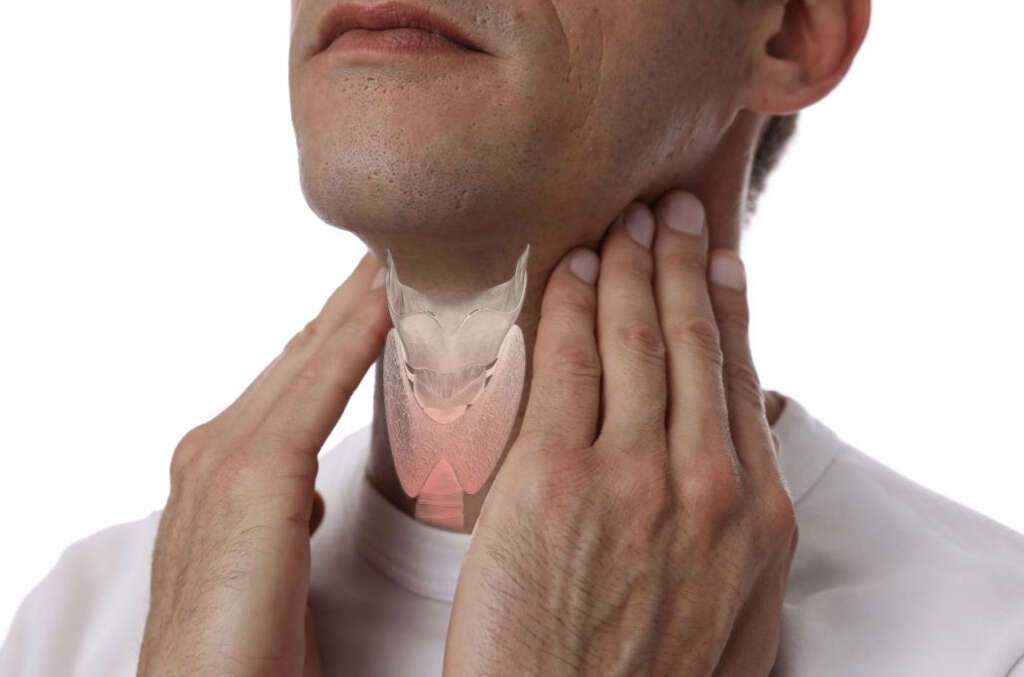
4. Hypothyroidism Symptoms
Symptoms of hypothyroidism typically include the patient feeling fatigued through much of the day. This will be regardless of their diet, and how much rest they get. Another fairly common symptom of the condition is weight gain as the patient’s metabolism slows down.
The patient can also become less tolerant to the cold and reluctant to leave the home in cold climates. The patient can also develop a hoarser voice, and their hair can become coarser and dryer than usual. Women can find that their periods are heavier and more frequent than usual. Hypothyroidism will also cause some patients to become forgetful.
5. Hyperthyroidism Causes
Hyperthyroidism means that the thyroid gland is producing too many hormones. This is sometimes caused by thyroiditis, which is also sometimes the cause of hypothyroidism. Thyroiditis tends to cause hyperthyroidism by causing the gland to release hormones that were being stored in the gland.
Another potential cause is that there is too much iodine in the patient’s body, and this is often the result of using certain medication. Some people will develop nodules on their thyroid gland which can affect hormone production. There is also Grave’s disease, which is a type of autoimmune condition and is the most common underlying cause of hyperthyroidism.

6. Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
Patients who have hyperthyroidism will typically be more irritable and nervous than usual, and they can also have difficulties getting to sleep. Another fairly common symptom is a goiter which is a visibly swollen thyroid gland that causes the bottom of the neck to bulge outwards.
The patient can also start to lose weight, and losing weight too rapidly can be bad for your health. Hyperthyroidism can also cause the patient to become more sensitive to heat than usual, while it can also cause tremors and weakness in muscles. Eye problems can also develop, while women can also experience irregular periods.

7. Who’s At Risk
Anybody can develop thyroid disease, and it is a relatively common condition. However, there are certain people who are more prone to the disease than others. One category is sex, and women are at a considerably higher risk of developing the disease than men are. The disease is also more likely to develop in people as they get older.
Having previously received treatment for cancer or another thyroid condition will also increase the chances of developing thyroid disease. Certain medication will also increase the risk, as will certain medical conditions, including type 1 diabetes. People for whom there is a history of the condition in their family are also more prone.
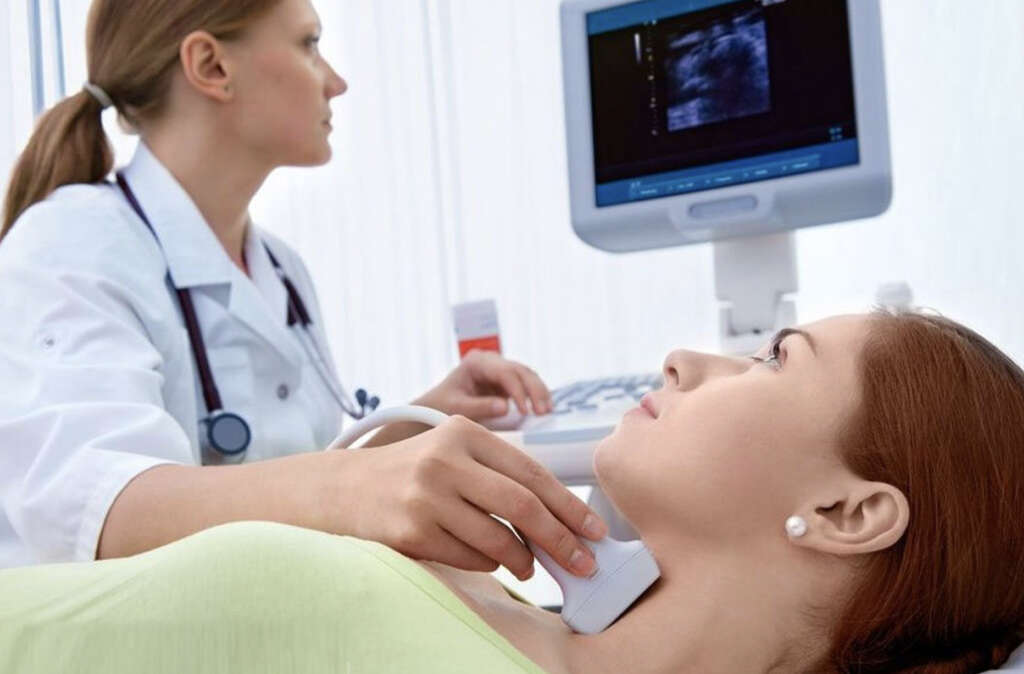
8. Diagnosis
The symptoms of thyroid disease tend to be similar to many other conditions, making it harder to diagnose. To help narrow down the possibilities, the doctor will likely need to ask you about your symptoms, and about your medical history. They will also likely need to perform a brief physical exam.
Tests will need to be performed to confirm the diagnosis, and this will often involve imaging tests. Ultrasound is often the preferred option, and the patient may be asked to ingest a specialized dye that will help structures to show more clearly. Blood tests will also likely be performed to help check hormonal levels in the patient’s blood.

9. Medication
Thyroid disease is often treated with the help of medication. Depending on the exact nature of the condition this can mean medication that helps to increase the levels of hormones in the body. Adversely, treatment for thyroid disease will sometimes mean decreasing the hormone levels.
Other potential treatments include beta blockers. Although these won’t help to restore natural hormone balances, they can help to manage the patient’s symptoms. Radioactive iodine will also be prescribed in some cases, and this will help to reduce how many hormones the thyroid gland is producing. In some cases, the patient will need to continue taking medication for the rest of their life.
10. Surgery
If medication alone is not effective then surgery may be considered necessary, and there are different surgery options available. Which option is selected will depend on a number of factors, including the extent to which the thyroid is swollen, if at all.
The procedures may involve removing just a part of the gland, or removing it altogether. Surgery can involve minimally invasive procedures that reduce the chances of complications, but open surgery will be required in some cases. In many cases, the patient will need to continue to take medication to help manage the levels of hormones in their body after surgery.