What Is Thrombophlebitis?
The human body contains up to 100,000 miles of blood vessels. They all fit inside the body because they are very small and are wrapped up inside the body. Veins are responsible for returning deoxygenated blood back to your heart from your various organs.
It’s easy to take veins for granted until something goes wrong with them. There are a variety of problems that can affect human veins. One such problem is thrombophlebitis. This condition is treatable by a medical professional and is often a short-term issue as long as treatment is sought.
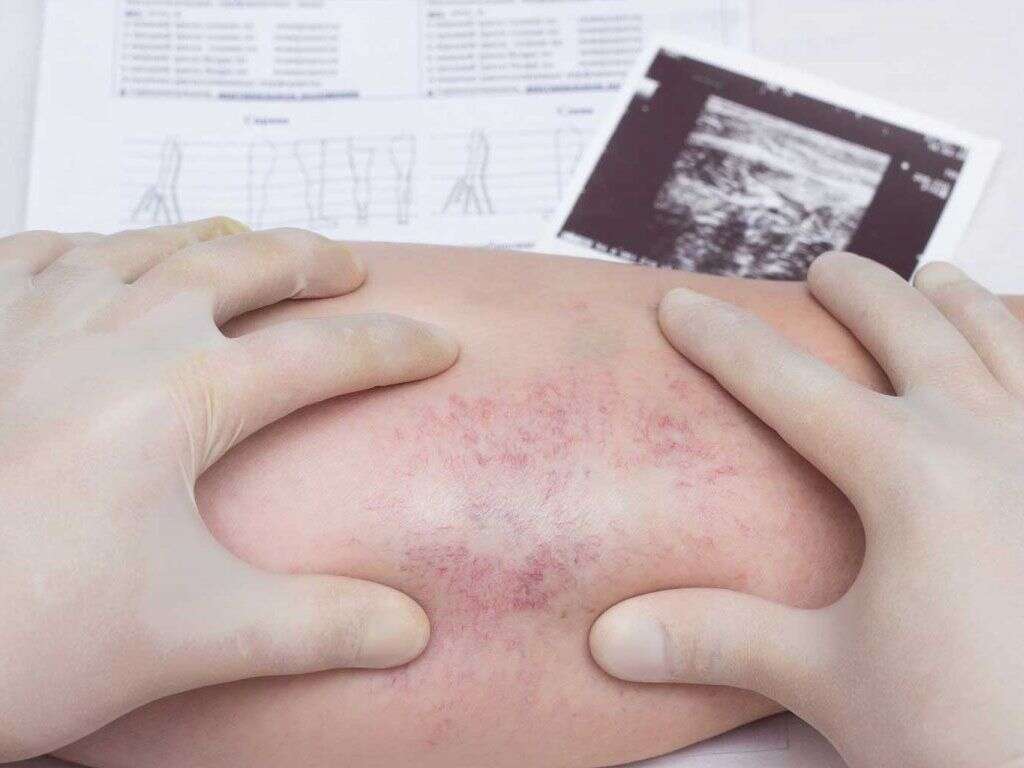
1. What Is Thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis is a condition that causes inflammation and pain in one or more veins. It occurs when a blood clot forms and blocks the affected vein. Though it often occurs just once, some people tend to get the condition multiple times and in multiple locations. When this happens, it is referred to as thrombophlebitis migrans, meaning it is a migratory form of the condition.
Thrombophlebitis usually affects surface-layer veins in areas associated with poor blood flow, especially the legs. However, it is also possible for the affected vein to be located within a muscle. This is referred to as deep vein thrombosis.
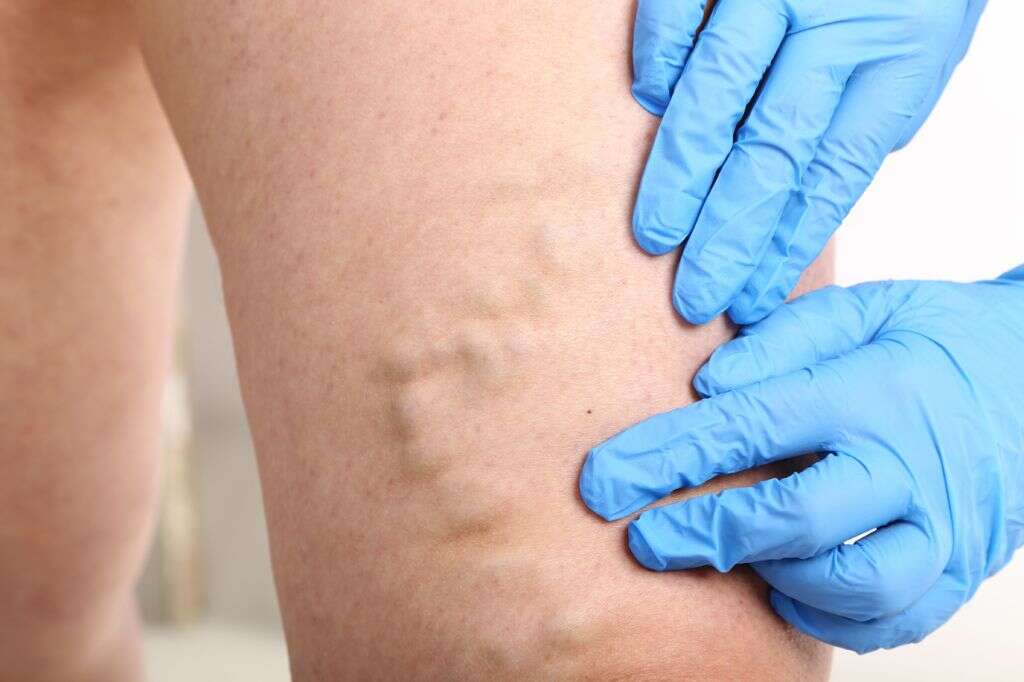
2. What Causes Thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis can be caused by a variety of factors. These include prolonged traveling and/or sitting, an increased tendency for blood clotting (an inherited blood-clotting disorder), and certain physiological states, such as pregnancy. Oral contraceptives, estrogen replacement therapy, and reduced speed of blood flow through the veins are also potential factors of the condition.
Specific disorders associated with the condition include pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and superficial thrombophlebitis (which affects superficial veins near the surface of the skin). Any injuries to the veins can also increase the chance of developing thrombophlebitis.

3. What Are Symptoms of Thrombophlebitis?
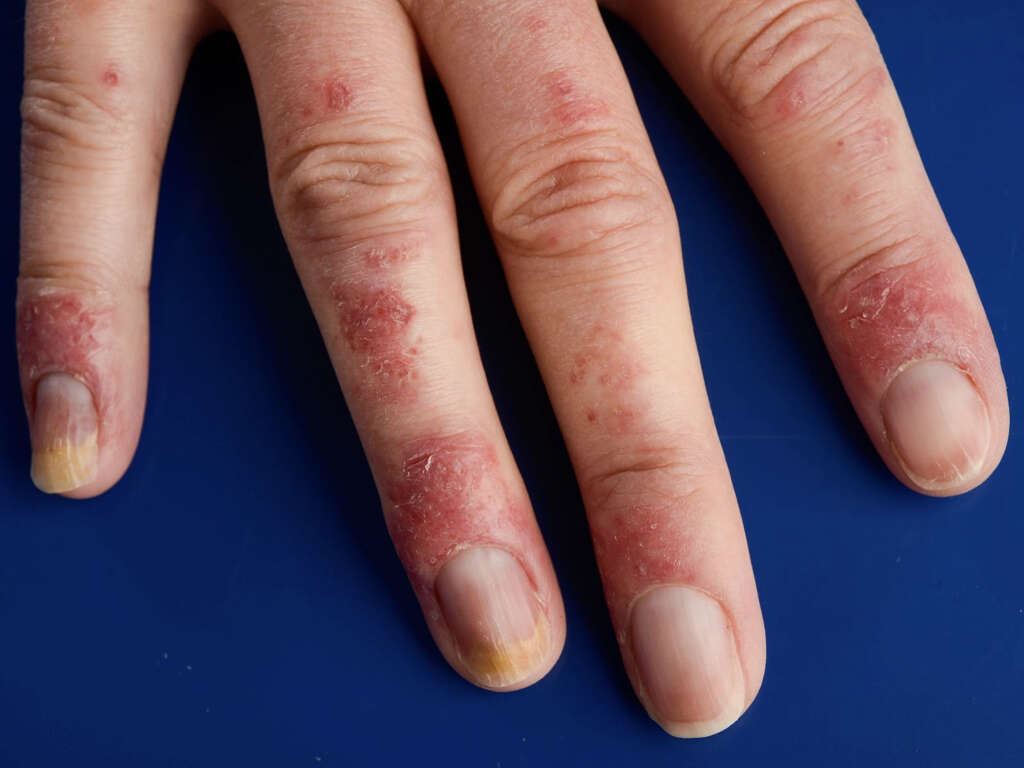
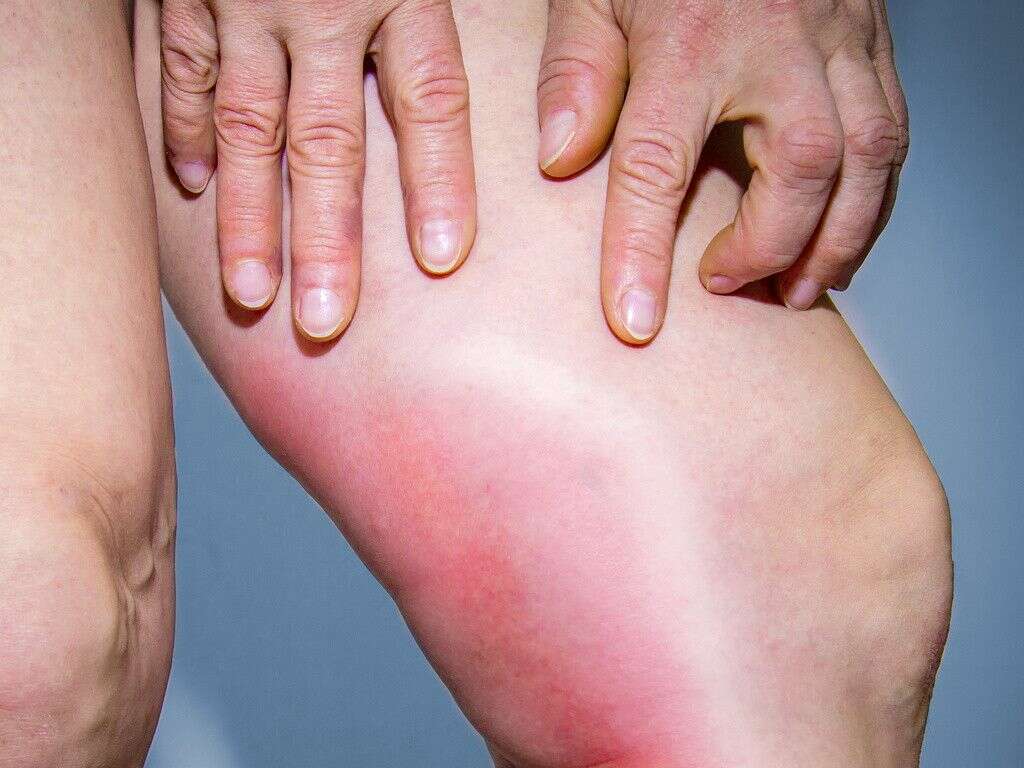
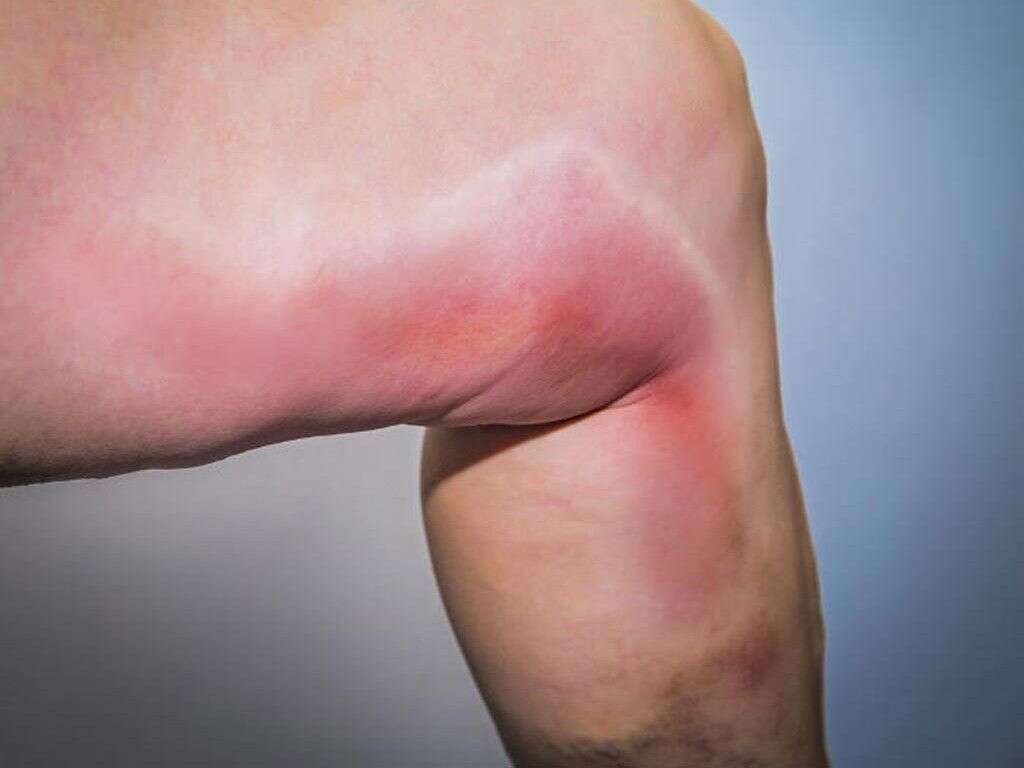
There are a variety of symptoms associated with thrombophlebitis. Some people with the condition may experience all of these symptoms, while others may experience only some. The most common symptoms associated with superficial thrombophlebitis include redness and swelling at the affected site, as well as warmth and pain in the affected area.
Deep vein thrombosis, which is related to but is not the same as thrombophlebitis, usually presents similar symptoms, including pain and swelling in the affected area. It’s generally easier to recognize superficial thrombophlebitis because this condition affects veins closer to the surface of the skin.
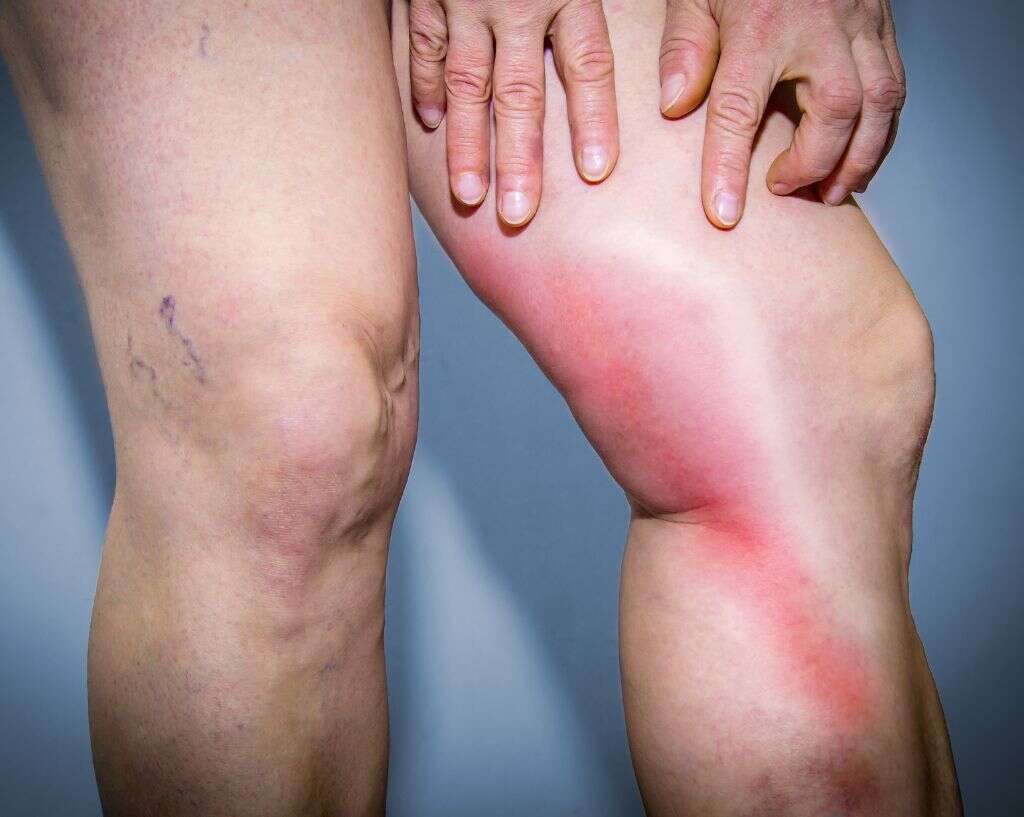
4. What Are Possible Complications of Thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis has the potential to cause serious and even life-threatening complications. One of the most serious possible complications is a pulmonary embolism, which can result in death. An embolism occurs when a deep vein thrombosis becomes dislodged and travels to the lungs through the heart.
Other potential complications of thrombophlebitis include serious damage to the veins of the legs, which can lead to post-phlebitic syndrome. This condition can cause chronic swelling and pain in the leg. Depending on severity, it can be disabling.
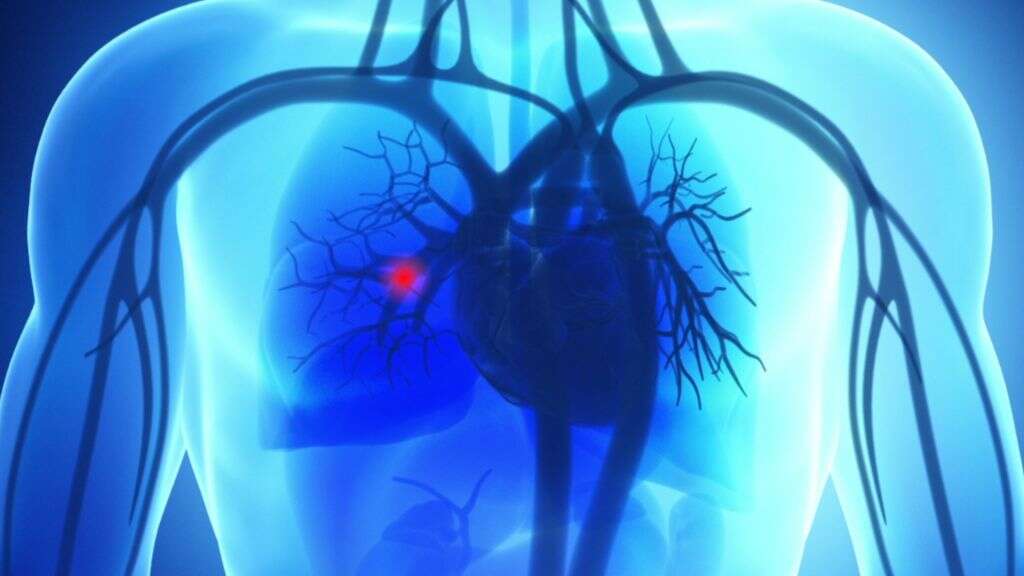
5. Who Is at Risk of Thrombophlebitis?
Your risk of thrombophlebitis increases if you take hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills (both of which can cause your blood to clot more easily), are pregnant or have recently given birth, or are older than 60. Other risk factors include having cancer or a history of cancer, having a pacemaker, a history of blood-clotting disorders, and having a stroke.
Some risk factors for thrombophlebitis are directly related to lifestyle, such as being overweight or obese, smoking, and staying inactive for prolonged periods of time. This can include sitting for long periods of time, such as when traveling by plane or car. If you have other risk factors, talk to your doctor about prevention strategies before going on a road trip, taking a long flight, or being put on bed rest.

6. Are There Ways To Avoid Thrombophlebitis?
You may be able to avoid thrombophlebitis by taking a few preventative measures. Allow time for frequent breaks while on road trips so you can stretch your legs and get your blood flowing properly. If you’re on an airplane, you may wish to take regular trips to the bathroom so you aren’t sitting the entire time.
Other ways to prevent vein inflammation include drinking plenty of water and other fluids (non-alcoholic) to avoid becoming dehydrated. You should also try to take walks regularly if you work at an office job that requires you to sit for hours at a time.

7. When Should I See a Doctor for Thrombophlebitis?
It’s not always easy to determine when it’s time to see your doctor for leg pain. However, if you have a vein that’s visibly swollen, tender, and red, you should immediately call your doctor to make an appointment as soon as possible.
A trip to your local emergency room may be warranted if the swelling and pain in your vein is severe, or if you are also experiencing chest pain, shortness of breath, coughing up blood, or other symptoms that may indicate the blood clot is traveling or has traveled to your lungs. Call 911 if you are unable to get to the emergency room while experiencing these symptoms.

8. How Is Thrombophlebitis Diagnosed?
To diagnose thrombophlebitis, you need to visit your doctor. He or she can use a variety of tests and techniques to officially diagnose the condition. If the underlying cause is not easily identifiable by the appearance of the affected area, you may need to have your blood pressure, temperature, and pulse checked.
Additional tests to diagnose thrombophlebitis can include an extremity arteriography, doppler ultrasound, and blood clotting tests.

9. How Is Thrombophlebitis Treated?
For superficial thrombophlebitis, your doctor may recommend that you do a few things at home, including elevating the affected leg, applying a heat pad to the sensitive area, and using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that you can get over the counter. The condition frequently improves on its own when such measures are taken.
However, if you do need further treatment, your doctor may give you a prescription for medication that can relieve your pain and swelling. He or she may also recommend that you wear compression stockings to help improve blood flow to your legs. In cases of severe thrombophlebitis, blood thinners or an IV may be prescribed.

10. What Is the Outcome for Thrombophlebitis?
Typically, the prognosis for thrombophlebitis is good, as long as the condition is superficial. In fact, if you follow your doctor’s orders and take care of the affected area without diving back into sports or heavy physical activities, you could fully recover in as little as one to two weeks.
If an infection develops, recovery will likely take longer. Additionally, if you have deep vein thrombosis, you should expect your recovery time to be lengthier than otherwise.