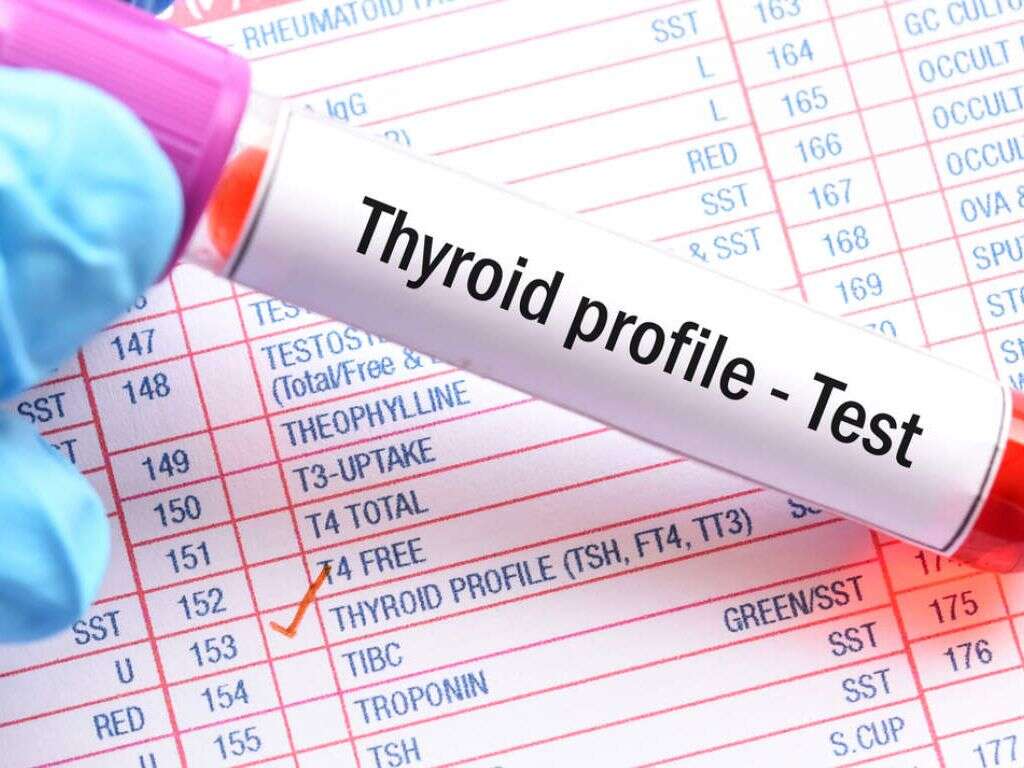
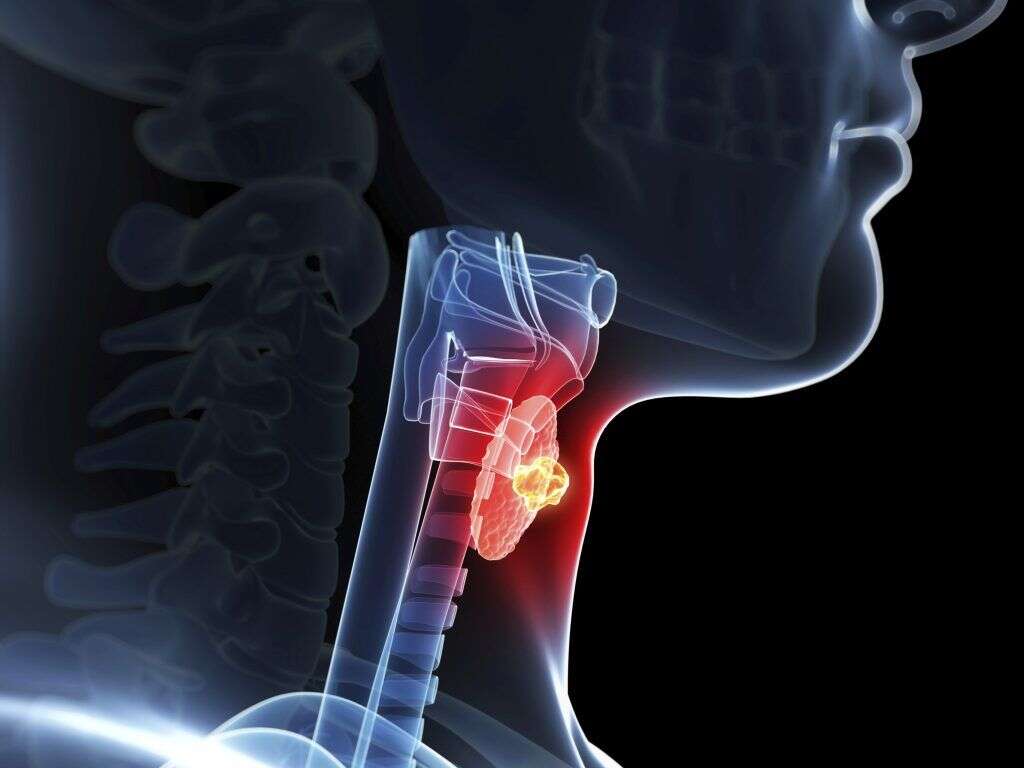
What Is Hypothyroidism?
Hormones are a type of chemical that helps to ensure the proper functioning of numerous bodily functions. They help us to digest our food, they help us to react to the environment around us, they help give us energy, and they also have a profound impact on how we are feeling.
Most of the hormones we use are manufactured in glands in our body, and one of these glands is the thyroid gland. If something was to go wrong with this gland then it would not be able to produce sufficient volumes of a particular type of hormone. This is a condition known as hypothyroidism, and it can have a significant impact on our well-being.
1. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. It is a type of autoimmune disease, which means that the patient’s immune system is attacking their body instead of protecting it. There is little known about the condition, and immune disorders in general are not at all well understood.
It is thought that the condition might be caused by something in the patient’s environment, and genetics could also be a factor in some cases. The condition cannot be cured, but it can at least be treated. Regardless, the condition affects the ability of the thyroid gland to make hormones that our body needs.

2. Thyroid Surgery
Hypothyroidism is also sometimes caused by surgery to the thyroid gland. Another potential cause is radiation treatment that is often used to help treat certain cancers. Radiation treatment can cause hypothyroidism if the thyroid gland is exposed to the radiation. Certain medications can also cause hypothyroidism, including some that are used to treat psychiatric patients.
Hypothyroidism is also sometimes caused by treatment of hyperthyroidism. In attempting to bring the production of certain hormones down to normal levels, the treatment can sometimes be too effective. This can result in the patient developing hypothyroidism permanently, so it is important to not overdo it.
3. Iodine Deficiency
The thyroid gland needs iodine in order to produce certain hormones. Therefore, the thyroid gland will not be able to produce the hormones it needs if there is not enough of the mineral. This is rare in developed countries where iodine is often added to food to ensure people get enough of it.
Another potential cause is a pituitary disorder. This is a condition with the pituitary gland, which is responsible for releasing a hormone that helps to stimulate the thyroid gland. In some cases, a person will be born with a faulty thyroid gland or even no thyroid gland at all.

4. Symptoms In Adults
The symptoms of hypothyroidism tend to start off mild and develop gradually. To begin with, patients might begin to feel a little more tired than usual, and they might also gain a little weight. The symptoms will become more noticeable as the condition develops, however.
Other symptoms include constipation and an increased sensitivity to the cold. Aches and pains can occur in the muscles, as can pain and stiffness in the joints. The patient’s heart rate can begin to slow down, and their blood cholesterol levels will rise. They can also develop a goiter, their hair can grow thinner, and their voice can become hoarser.

5. Symptoms in Children
When children and adolescents have hypothyroidism, they will tend to show the same symptoms that adults do. However, they can also show additional symptoms, which largely revolve around their development. One example of this is that hypothyroidism in children can cause them to not grow as tall as they otherwise would do.
Hypothyroidism in children and adolescents will also sometimes cause puberty to come later than it otherwise would. In some cases, it will also cause the patient’s permanent teeth to come through late. What’s more is that the condition will also sometimes cause that patient’s mental development to be stunted.

6. Hypothyroidism In Infants
Unfortunately, the condition can also affect the very young, including newborns. Newborns will often not show symptoms to begin with, and the condition will often not be diagnosed for a while. Many countries have through screening in newborns as standard, however. Which symptoms do show, they will usually include jaundice, which is caused by a poorly functioning liver.
The patient’s tongue can also grow larger than usual, and the patient may find it difficult to breathe. They may also develop constipation, and an umbilical hernia is another possibility. The patient can also sleep more than usual, while they can also cry with a sound that is hoarser than usual.

7. Complications
In addition to the symptoms already mentioned, hypothyroidism can also result in a number of symptoms that have the potential to be rather serious. For example, high levels of ‘bad’ cholesterol can lead to heart failure and other similar problems. Also, pregnant women that have hypothyroidism are more likely to experience severe complications with their pregnancy.
Peripheral neuropathy, which is damage to the peripheral nerves, is another potential complication. Myxedema, which is an extreme form of hypothyroidism, can also occur if hypothyroidism is left untreated. Hypothyroidism can also result in depression, which can also pose a very real threat to the patient’s life.
8. Who’s At Risk?
Hypothyroidism can develop in anybody, but certain types of people are more at risk than others are. For example, it is more likely to occur in the over 60s, and women are also more prone to the condition. People are also at a higher risk if there is a history of the condition in their family.
People that have had thyroid surgery are also more likely to develop hypothyroidism. Those that have certain autoimmune conditions are also in a higher risk category. Radiation treatment will also increase the chances of hypothyroidism developing. Women who have recently been pregnant are also more prone to developing the condition.

9. Diagnosis
Your doctor will need to ask you about your symptoms and medical history. If hypothyroidism is suspected, then tests can be requested to help confirm the condition. Blood samples will typically be requested so they can be sent away for examination. This will usually involve looking for levels of certain hormones.
Experts are likely to look for levels of TSH, or thyroid stimulating hormone, in particular. Not only can this metric help diagnose hypothyroidism, but it can also help diagnose subclinical hypothyroidism. It should be noted that certain medications can skew the results, so you should let your doctor know which medications you are taking before testing.

10. Treatment
Treatment for hypothyroidism typically involves the use of a synthetic hormone that helps to replace the natural hormone. It is an oral medication that helps to restore hormone levels in the body, and the treatment will be fairly quick acting. The patient will likely need to continue to take this medication for the remainder of their lives.
It is important that the patient is given the right dose, and the dosage will likely be adjusted a few times as doctors monitor how the patient reacts to the medication. The patient will also need to avoid certain foods that may hinder their ability to absorb the synthetic hormone.