What Is Hyperthyroidism?
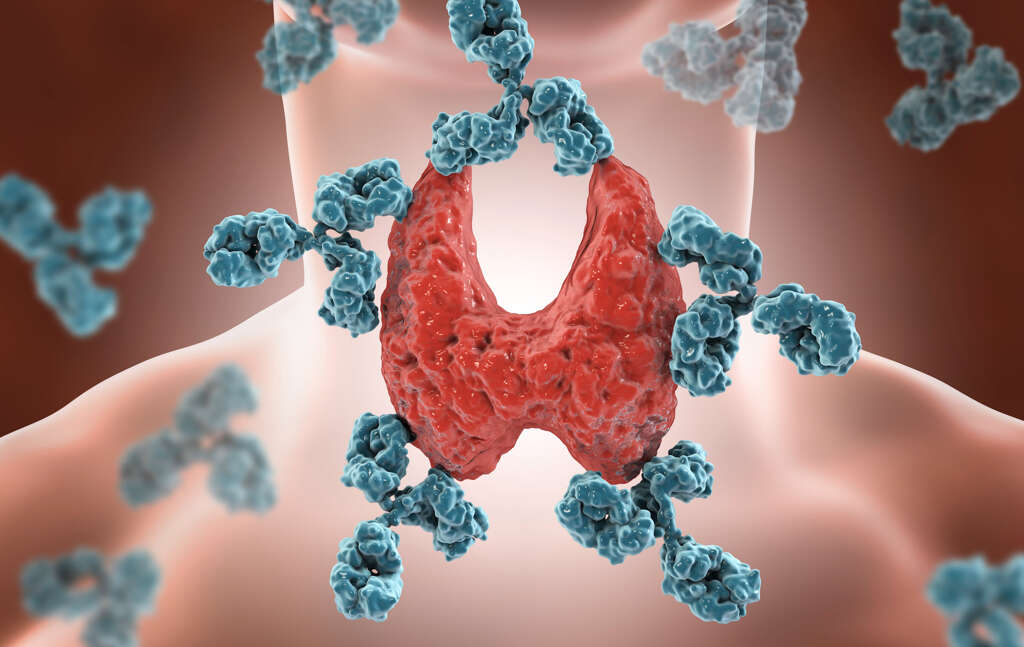
The thyroid gland is a butterfly shaped gland that is located in the neck. It is responsible for producing two hormones known as thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These hormones are responsible for helping to control a number of bodily functions, and they have a profound impact on our metabolism.
These hormones are very important for us, but it is possible for us to have too many of them in our blood stream. This is a condition known as hyperthyroidism, and it will need to be treated, and treatment is available. Here we look more closely at the condition, the symptoms it can cause, and how it can be treated.
1. Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition where the patient’s thyroid gland is producing the thyroxine hormone in larger quantities than it would usually be. This can have a profound effect on the patient, causing a number of unwelcome symptoms. The condition will have an impact on the patient’s metabolism in particular.
Hyperthyroidism is not necessarily a dangerous condition, but it can cause problems if it is left untreated. The good news, however, is that treatment is available, although the patient will likely need to take the medication for the rest of their life. There are numerous potential underlying causes of the condition.

2. Plummer’s Disease
Plummer’s disease is a condition that is also known as toxic adenoma, and toxic multinodular goiter. It happens when the patient has adenomas, which are a type of benign tumor, in their thyroid gland. It is possible for adenomas to become malignant, but this is not common, especially in the thyroid gland.
Although a tumor may be benign, it does not mean that they don’t cause any problem at all. They can grow large enough to affect the functioning of whichever organ they are found in. In Plummer’s disease, the presence of these tumors can cause the patient to produce more thyroxine than usual.
3. Graves’ Disease
Autoimmune diseases are medical conditions where the patient’s bodily tissues are being attacked by their immune system. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune condition that attacks the thyroid gland specifically. It results in the patient’s thyroid gland producing more thyroxine than usual, among other symptoms.
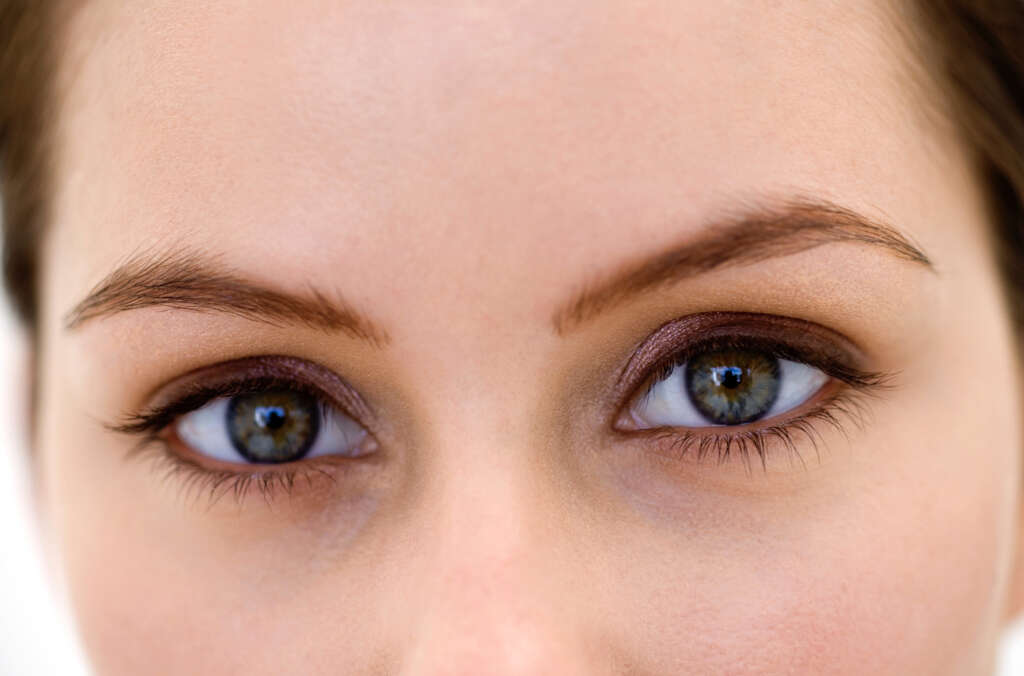
In addition to causing the symptoms of hypothyroidism, Graves’ disease can also cause Graves’ ophthalmopathy. This is a condition where the patient’s eyes are affected, and this can mean dry eyes, excessive tearing, discomfort, vision problems, and protruding eyeballs. It is most likely to affect smokers, and the eye problems will usually clear up with no treatment.
4. Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is the name given to the inflammation of the thyroid gland. This can happen for a number of reasons, including autoimmune conditions, and it is also sometimes caused by pregnancy. It is not always understood what the underlying cause of the condition is.
Thyroiditis is often painless, but it will cause some pain for the patient in some cases. The thyroid gland will store excess thyroxine for storage for when it is needed. The swelling that comes with thyroiditis can caused the stored hormone to be forced out of the gland and into the blood stream. This will, in turn, result in hyperthyroidism.
5. Tachycardia
Hyperthyroidism will cause a number of unwelcome symptoms for the patient, one of which is tachycardia. This is the name for a condition where the patient’s heart is beating faster than it should be. The patient may also feel palpitations, which is a sensation caused by the pounding of their heart.
Hyperthyroidism can also cause the patient to develop tremors, which will usually happen in their hands and fingers. The patient can also begin to sweat excessively and for no apparent reason; even when they are not hot. Hyperthyroidism will also often cause the patient to become anxious and nervous, and they can also become easily irritable.

6. Weight Loss
Hyperthyroidism can also cause the patient to lose weight regardless of how much they are eating. Indeed, hyperthyroidism can also increase the patient’s appetite and they can still lose weight. It should also be noted that losing weight too quickly can be very bad for your health.
The patient’s muscles can also feel very weak and the patient can also feel fatigued all of the time. Hyperthyroidism can also cause patients to feel fatigued no matter how much rest they might be getting. This can be made even worse by another symptom that can be caused by hyperthyroidism, which is difficulty sleeping.

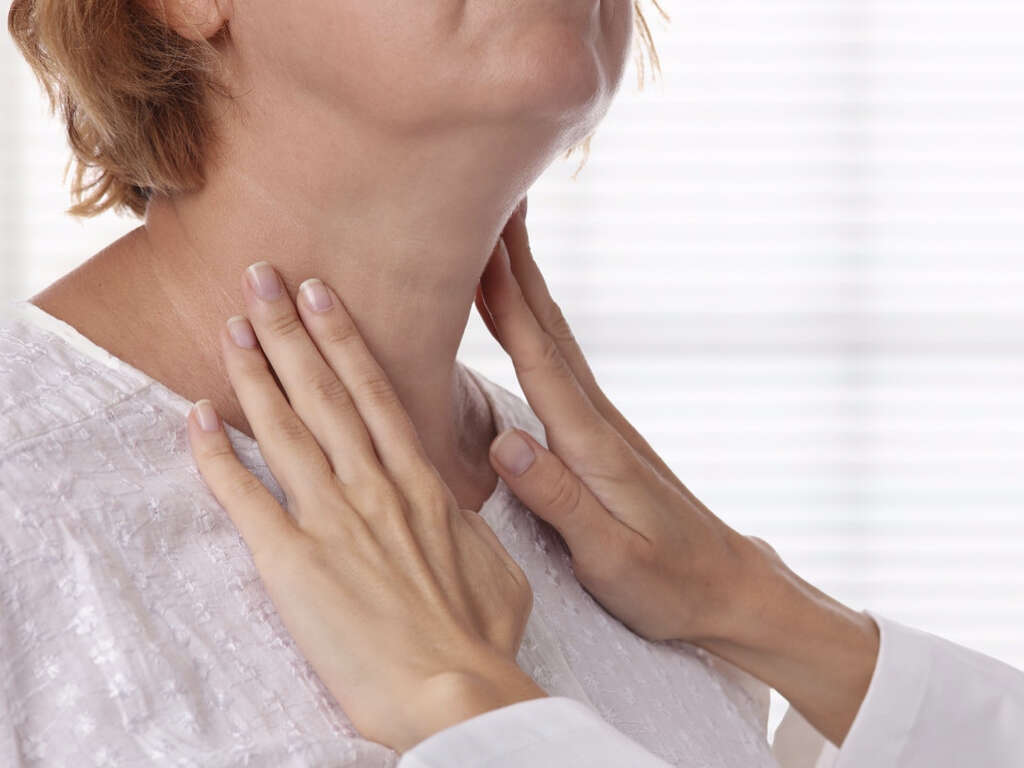
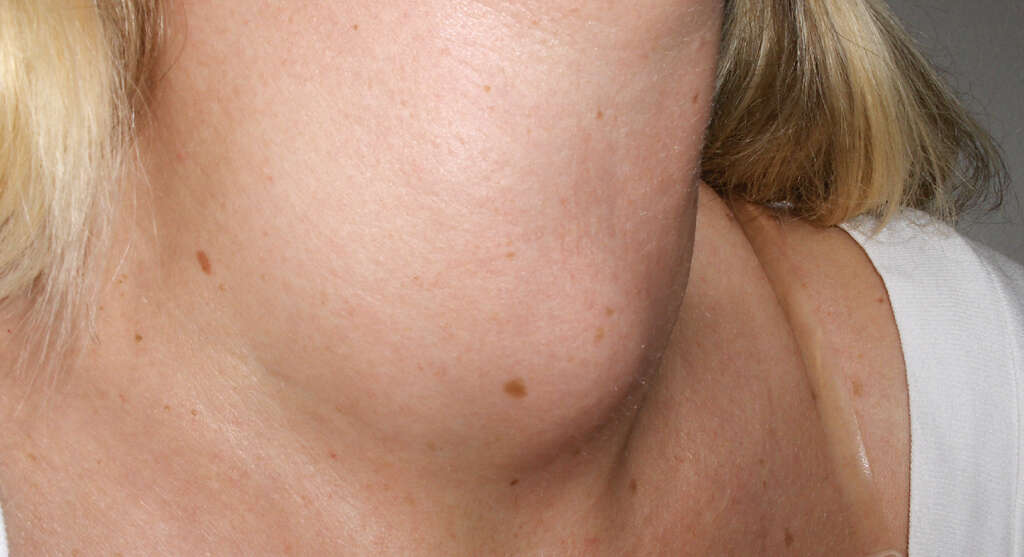
7. Goiter
A goiter is the name given to a thyroid gland that has become enlarged, which causes the base of the neck to become swollen. The symptom is often very clearly visible and it can be quite striking. The patient’s hair can also become brittle and finer, and their skin may become thinner than it usually would be.
Another potential symptom of hyperthyroidism is that the patient becomes more sensitive to heat. They can also experience changes in their bowel movements, which usually means making trips to the bathroom more frequently than usual. Women with hyperthyroidism may also experience changes in their menstrual patterns.
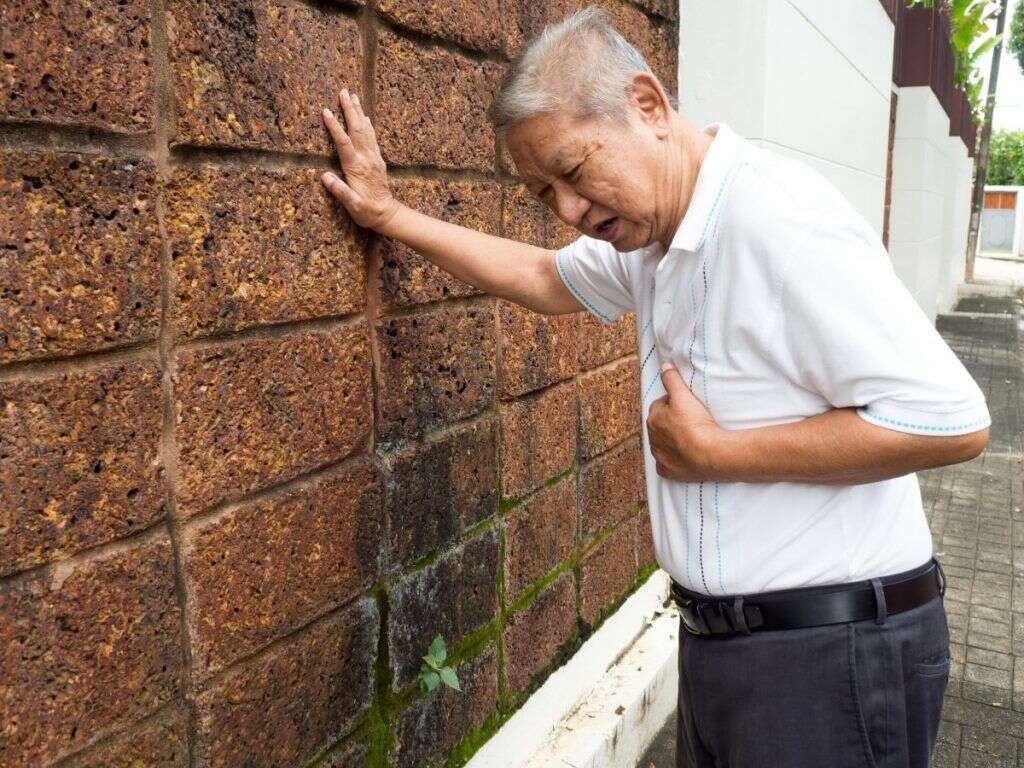
8. Complications
In addition to the symptoms mentioned, hyperthyroidism can also cause complications for the patient. For example, it can cause the patient to develop brittle bones, and this can make them more prone to breaking. When the condition is caused by Graves’ disease, the patient might also lose their vision.
Hyperthyroidism can also cause problems with the patient’s heart. This, in turn, can lead to congestive heart failure and the patient is also more likely to have a stroke. The more severe cases can result in a thyrotoxic crisis, which means the patient’s symptoms have become severe to the point that the patient’s life is in danger.

9. Who’s At Risk
Pretty much anybody can develop hyperthyroidism. Certain groups of people are more likely to develop the condition than others are, however. For example, women are more likely to develop hyperthyroidism than men are. People are also more likely to develop the condition if there is a history of it in their family.
People that have a history of some other diseases in their family are also in a higher risk category. These diseases include pernicious anemia, and type 1 diabetes. Primary adrenal insufficiency is another potential risk factor. This is a condition where the gland that produced cortisol, another type of hormone, is damaged.

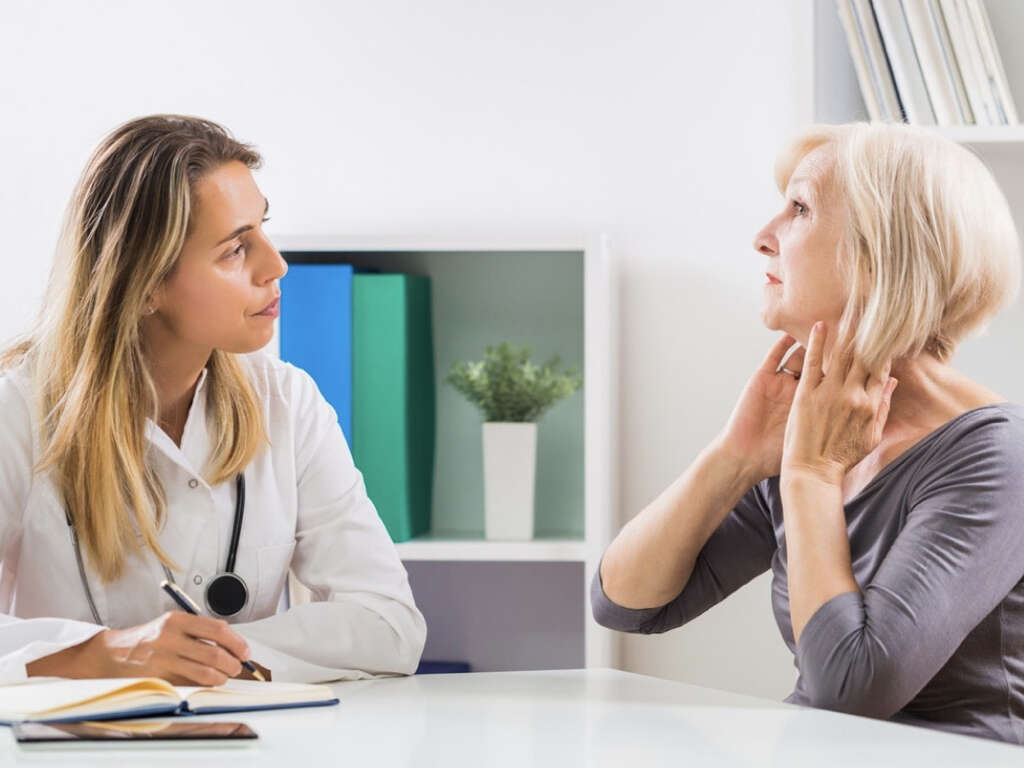
10. Treatment
The treatment for hyperthyroidism will depend largely on the underlying cause of the condition, the severity of the symptoms, and the patient’s overall health. In many cases, treatment will involve using radioactive iodine which will reduce any swelling in the gland.
Other medications are available that will help reduce the volume of hormones being produced by the thyroid gland. In some cases, medication like beta-blockers may be used to help treat the patient’s symptoms. If the condition is severe enough then surgery may be performed to remove most of the patient’s thyroid gland. Surgery may also be considered necessary in some cases to treat Graves’ ophthalmopathy.