What Is Duodenitis?
Ensuring the good health of our digestive system is very important. It is essential to us because it helps ensure we can get all the nutrition we need from our food, and this will help to keep us healthy and well. Not only is it important for our physical health but also for our mental health.
Our digestive system is prone to developing problems, however. The linings of the various parts of the digestive system can become inflamed and this can lead to a number of conditions. One example of this happening is duodenitis, which is the inflammation of the walls of the duodenum.

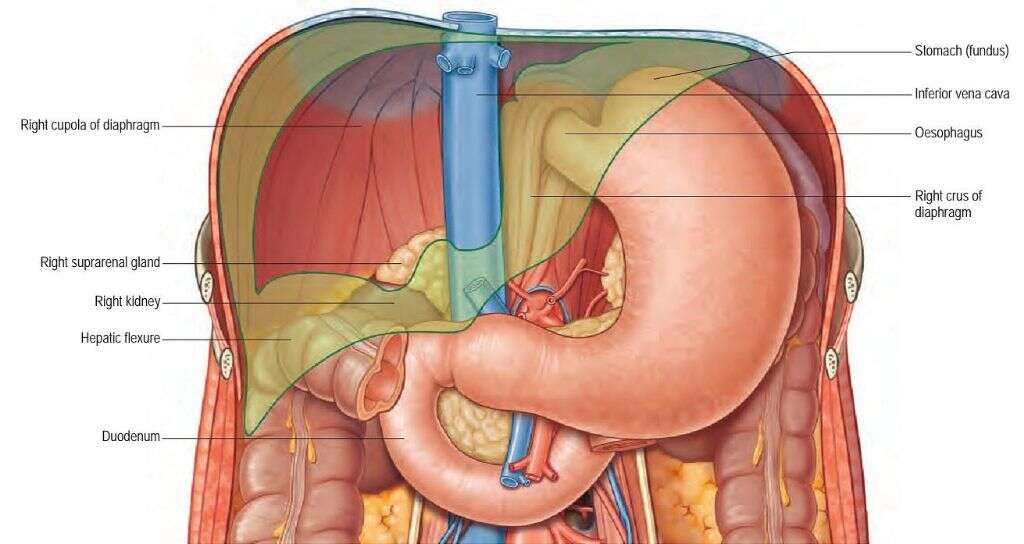
1. Duodenum
The duodenum is one of the key components of our digestive system. It is the first part of the small intestine and also the smallest part. Partially digested food from the stomach will pass into the duodenum where the next step of digestion will begin. It is at this point that the absorption of nutrients begins.
It is in the duodenum that bile and other digestive juices are added to the mix. Contraction of the walls of the duodenum will help to move the chyme mixture along the organ before it will eventually move on to the rest of the small intestine.
2. Duodenitis
Duodenitis is the medical term given for the inflammation of the duodenum. It is very similar to gastritis, which is the inflammation of the stomach lining. The symptoms, treatments, and causes of both duodenitis and gastritis are so similar that the two conditions can easily be confused with each other.
Duodenitis can affect people of all ages, and it can also occur in men and women. Both of these diseases can thankfully be cured, and it is unlikely that any long-term problems will remain. There is both a chronic version and an acute version of both gastritis and duodenitis.

3. Helicobacter Pylori
Helicobacter pylori is a commonly found bacteria that is thought to have infected up to half of all people in the united states. That figure may be as high as 80 % in many developing countries. It is thought to be spread through infected water and food. Thankfully, the bacterium will cause no ill effects in the vast majority of cases.
In some instances, however, the bacteria can proliferate beyond usual numbers and this can cause problems. Too many of the bacteria will cause the lining of the duodenum to become inflamed in some cases, thus resulting in duodenitis. Helicobacter pylori is also thought to be a common cause of stomach ulcers.
4. Other Causes
While helicobacter pylori is perhaps the most common cause of duodenitis, it is not the only cause. There are numerous other potential underlying causes, some of which are unlikely to do the patient any harm. Some examples include bile reflux, and celiac disease.
Some viral infections in people with a weakened immune system can also be a cause, and some autoimmune conditions can result in duodenitis. An injury to the area can also result in the condition, as can major surgery or shock. Smoking cigarettes, and ingesting caustic substances, are also potential causes. Duodenitis can also be caused by chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.

5. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease is thought to be caused by a variety of autoimmune disorders. The actual cause is unclear, however, and genetics or certain environmental factors may also contribute to the condition. Inflammatory bowel disease means the patient is suffering from chronic inflammation of the tissues in their digestive system.
Examples of inflammatory bowel disease include Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. People with the condition are also more likely to develop then duodenitis than people who don’t have it. Inflammatory bowel disease cannot be cured, but treatments are available that can at least help to reduce the severity of the symptoms.

6. Symptoms
Some people with duodenitis will not display any symptoms whatsoever. When symptoms do arise, however, they can be very uncomfortable. One of the most common symptoms of the condition is a pain in the abdomen area. The pain will often also be felt in the back, and patients will also sometimes experience cramping and/or a burning sensation.
Indigestion is another common symptom, while many patients will also feel nauseous. Nausea will result in vomiting in many cases. Sometimes the patient’s vomit will resemble coffee grounds and their stools can be very dark. Both of these are a symptom of internal bleeding and should be treated as a medical emergency.

7. Who’s at Risk
Those most likely to develop duodenitis are those that have a H. pylori infection. As mentioned, however, the bacterium is very common but few people with the infection will develop problems. There are also other factors that can increase the likelihood that somebody will develop duodenitis.
Other factors include people that have inflammatory conditions like Crohn’s disease. People that drink a lot of alcohol are also at a higher risk, as are people who smoke. Severe illnesses and prolonged stress are also contributory factors. People that take certain medications are also at a higher risk, as are people that have undergone certain cancer treatments.

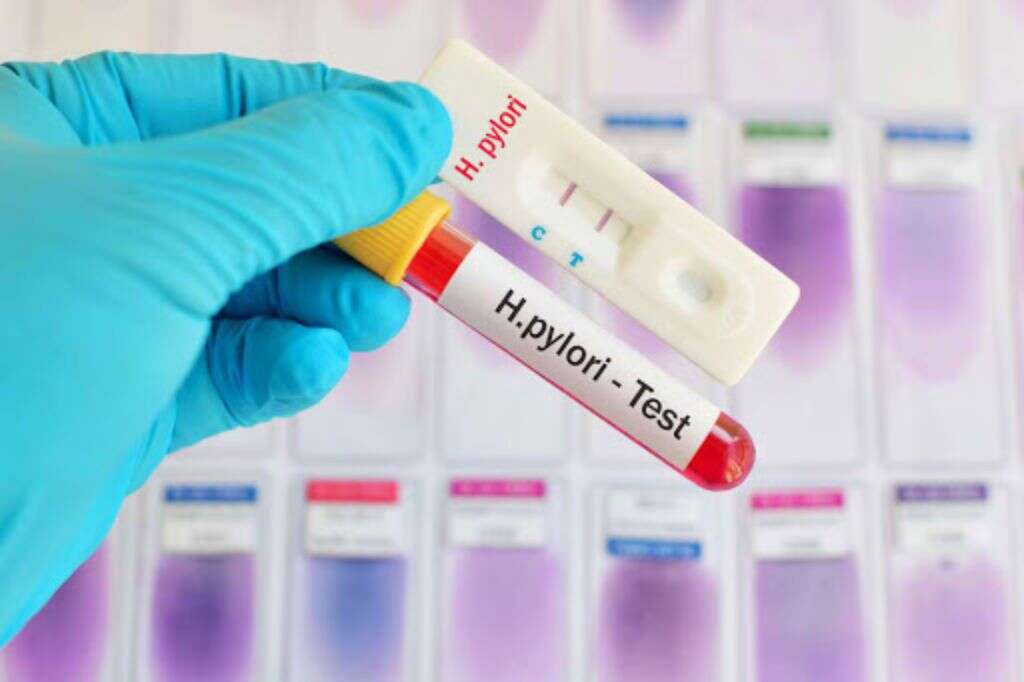
8. Diagnosis?
Because H. pylori is the most common cause of duodenitis, doctors will first look for signs of the bacterium when looking for a diagnosis. One test will likely be a breath test that will check the levels of carbon dioxide in your breath. If there is more of the gas present than usual, it is an indicator that H. Pylori is present.
Other methods of detecting the bacterium include stool tests, and blood tests. Some doctors might opt to perform an endoscopy to look for signs of inflammation, and a biopsy may be carried out in some cases. Knowing the exact cause of the condition is important if the right treatment is to be administered.
9. Medicinal Treatment
Antibiotics are the most common form of treatment where H. pylori infections are concerned. The patient will usually need to take the medication for at least two weeks, and more than one type of drug is likely to be used in order to ensure that all of the H. pylori bacteria have been killed.
The patient will also often be prescribed medication like proton pump inhibitors that will help to reduce the acidity in the patient’s small intestines. Antacids can also be prescribed to help provide some temporary relief to the patient’s symptoms. For a lot of people with duodenitis, considerable changes in lifestyle may be deemed necessary.

10. Lifestyle Changes Treatment
Some patients will need to stop the use of certain medications, particularly NSAIDS and aspirin, because they can contribute to inflammation of the duodenum. It is also recommended to stop smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol as much as possible. If the patient is not willing to quit completely then they should consider at least limiting their usage.
In some cases, lifestyle changes will need to be made to address the underlying cause of the condition. This can mean avoiding gluten for patients that have celiac disease, along with any other foods that can cause the irritation of the lining of the duodenitis.