What Is Cystic Fibrosis?
Mucus may be gross, but it is also very important. Mucus helps to line the surface of various parts of our bodies internally. This helps to protect delicate tissues against damage and also help to protect us against pathogens. Mucus is also important in aiding in various bodily functions.
Mucus is usually quite thin, but a condition known as cystic fibrosis can cause our mucus to become much thicker than usual. When this happens, the mucus can cause tubes and other passageways to become blocked, and this has the potential to cause serious problems. Although life expectancy in people with the condition is improving, patients are still likely to have their lives cut short.

1. Causes
Cycstic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in a gene. It is passed down from parents and the patient has to have one copy of the faulty gene from each of their parents. Somebody will not have cystic fibrosis if they only have a copy of the gene from one parent. They will, however, be a carrier of the gene.
The gene in question is known as the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. The gene is responsible for a protein that helps to regulate levels of salt in our cells. The patient ends up with a sticky mucus in the respiratory tract. The reproductive system and digestive systems are also affected.

2. Respiratory Symptoms
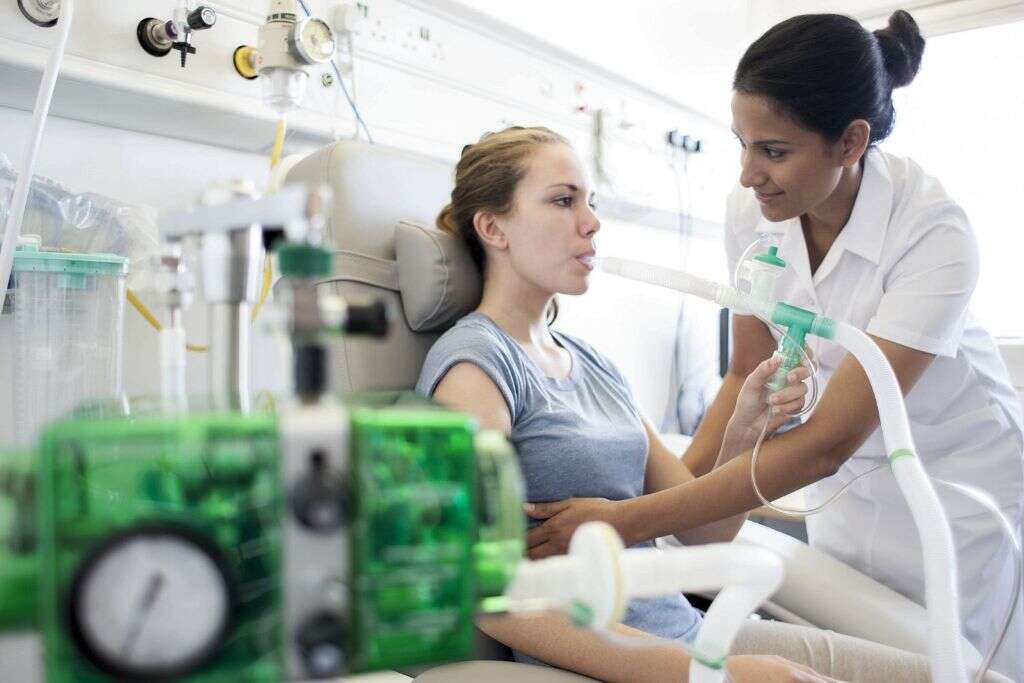
The severity of the symptoms will vary from case to case, and symptoms will typically affect the patient’s respiratory tract. The sticky mucus will line the airways to the lungs, making it harder for the patient to breathe. One of the symptoms is that the patient will regularly cough up thick sputum.
Lung infections will also be more frequent than usual, and the patient will also regularly develop sinusitis. The nasal passages can become inflamed and blocked, and the patient will often be wheezing as they try to breathe. Patients with cystic fibrosis tend to find exercising a lot more difficult than other people do.
3. Digestive Symptoms
As mentioned, cystic fibrosis can also affect the patient’s digestive system. The mucus can block tubes, preventing digestive enzymes from reaching the intestines where they are needed. This will mean the patient is not able to digest their food and absorb nutrients as well as they otherwise would be able to.
Because the patient is unable to get the nutrients they need, they will tend to be rather underweight. Another symptom is that the patient’s stools will be particularly malodorous, and they will have a greasy texture. Cystic fibrosis can also cause severe constipation, and this will sometimes lead to a rectal prolapse.
4. Respiratory Complications
In addition to the symptoms mentioned, cystic fibrosis can also cause severe complications of the respiratory system. These include pneumothorax which is a condition that causes a part of the lungs to collapse. Cystic fibrosis will also make lung infections more frequent than usual.
Acute exacerbations are another potential symptom, which means symptoms like coughing become more severe. The airways can become damaged, and this can lead to hemoptysis, which means the patient is coughing up blood. Cystic fibrosis can also lead to respiratory failure, which is a very serious condition indeed and is the most common reason for fatalities in people with cystic fibrosis.
5. Digestive Complications
Cystic fibrosis will sometimes cause the patient to develop diabetes because it can affect the functioning of the pancreas. The patient’s inability to absorb nutrients means that they will suffer from malnutrition, and this can result in further complications such as stunted growth in young patients.
Patients with cystic fibrosis will also sometimes go on to develop liver disease, which is also a condition that can cause severe problems for the patient. Intussusception can occur, which is when a part of the digestive system folds back into itself, and the digestive system can become blocked. Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome is another potential complication, and one that will require immediate medical assistance.
6. Reproductive Complications
Cystic fibrosis can also cause the tubes of the reproductive system to become blocked. In some cases, these tubes might even be missing altogether. This can make men infertile, and women are likely to be less fertile than they otherwise would be. Men with cystic fibrosis can often still often have children, however, thanks to surgical procedures and other fertility treatments.
Fertility treatments are also available for women who are having difficulty conceiving. Women with cystic fibrosis should be mindful that if they do get pregnant, the pregnancy is likely to make their symptoms worse. This means getting pregnant might be out of the question for people with more severe symptoms.

7. Other Complications
Cystic fibrosis can also result in some other potentially serious complications. One of these is dehydration due to the imbalance of salt in their bodily fluids. Symptoms of dehydration include fatigue, weakness, an increased heart rate, and low blood pressure. The condition can also result in electrolyte imbalances and this can have an effect on the central nervous system.
Osteoporosis, which causes the bones to become weaker, is another potential complication. This can cause pain and arthritis, and it means the patient’s bones can break more easily than usual. The patient can also develop mental health conditions, including anxiety and depression.

8. Who’s At Risk
As mentioned, cystic fibrosis is an inherited condition and it cannot be acquired later in life. It is also more common in people that have a Northern European hereditary. If you do have cystic fibrosis, or if there is a history of the condition in the family, speaking with a genetic counselor can help you assess the risk of your children having it.
Bearing in mind that a person must have two copies of the faulty gene, there is no risk if only one parent carries it. This can easily be verified with a blood test that can help look for the faulty gene. If you have already conceived, then tests can be conducted on the developing fetus to see if they have the condition.
9. Diagnosis
In order to help diagnose the condition, your doctor is likely to want to ask about your symptoms and perform a physical exam. Using a stethoscope, they will be able to look for signs of breathing problems. If cystic fibrosis is suspected, then tests will need to be requested in order to confirm the diagnosis.
A blood sample may be taken to help look for signs of cystic fibrosis. This includes looking for a certain chemical that is manufactured by the pancreas. This test is not always able to give an accurate diagnosis so further tests may be required. This can include genetic testing to help look for the faulty genes.

10. Treatment
As things stand, cystic fibrosis cannot be cured and the patient will have the condition for life. However, the patient can have their symptoms treated to make them feel more comfortable, and to help prevent serious complication arising. Some of the most important treatments include preventing too much mucus from accumulating in the lungs.
It will also be necessary to help prevent the lungs from becoming infected. Blockages of the digestive system will also need to be prevented, and it will be important to ensure the patient gets all the nutrition they need. Treatment will also likely be needed for complications when they do arise. Despite treatment, the average expected lifespan of people with cystic fibrosis is below 40 years old.