What is Chlamydia?
Sex is one of the most natural and most enjoyable experiences we can take part in. It also has a practical purpose, of course, because it is necessary if we are to reproduce. Despite all the positives, we still need to act responsibly when enjoying sex. This is partly because of the risk of unwanted pregnancies, while there is also the chance of spreading disease.
One disease that is sometimes spread from sexual intercourse is chlamydia. It is a very common disease and it is thankfully not too serious. Chlamydia is fairly easy to treat, although people should get treatment to help prevent the chances of it becoming more serious.

1. Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an infection that is caused by the chlamydia trachomatis bacterium. It is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases and is most common in sexually active young adults and teenagers. It is estimated that around 4 to 8 million new cases happen every single year in the United States alone.
Chlamydia is not usually a serious condition and it can be treated with antibiotics. It should be treated, however, because it can cause some potentially serious complications if it is not. People should also take what precautions they can to help protect them from catching the disease.

2. Transmission
As mentioned, chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease. This basically means that the disease is transmitted through sexual contact with another person that is already infected. It is also a very infectious disease, which means the chances of transmission are high if sexual contact takes place.
The disease can be transmitted through direct contract with semen and female lubricant. It can also be caught through simple contact with another person’s genitals even if penetrative sex does not take place. It can also be passed on to a baby by a pregnant mother, and it can also be transmitted through sharing sex toys and similar.

3. No Symptoms
Most people that have chlamydia will not be aware that they have it. While this is obviously beneficial in one sense, it is also a drawback in another. The drawback being that the infected person is more likely to transmit the disease to other people. This is because the patient is not aware, and their sexual partners won’t recognize any symptoms.
That there are no symptoms also means that it is a good idea to get regular check-ups. Check-ups are fairly straight forward and can be requested by a sexual health clinic, or from your local doctor. Young, sexually active people are especially encouraged to get checked regularly.

4. Discharge
When symptoms do arise, the patient is likely to experience an unusual discharge. It is a relatively common symptom of the condition, especially in women. The discharge typically has a milky white appearance but it is not the same for everybody. Many will not notice the discharge until they see it in their underwear.
Discharge is less common in men, but it does occur in some cases. It is likely to be more noticeable in men because the penis, unlike a vagina, usually has no discharge except for urine and semen. The discharge can also come from the anus in some cases.

5. Pain When Urinating
Urinating is usually a very quick and simple affair. We simply need to get ourselves in an appropriate position, relax, and let mother nature do the rest of the work for us. This is a good thing because we need to urinate several times a day. Unfortunately, even relieving ourselves is not always so easy in some cases.
Both men and women can find that urinating becomes quite painful when they have chlamydia. Men can also find that ejaculation becomes painful. Pain like this is not normal and should encourage the patient to speak with a medical professional if they have not done so already.

6. Abdomen Pain
Chlamydia can sometimes also cause some patients to develop a pain in the abdomen area. The pain is sometimes described as being a dull ache, while other people describe it is sharp and as though they have a cramp. It is usually experienced in the lower part of the abdomen.
Some women will also experience bleeding after sex, even when they are not menstruating. Men might also sometimes experience a bloody discharge from their penis. Bleeding from the genitals is not normal, except for in menstruating women, and it is something that should be checked out as soon as you are able.

7. Swollen Testicles
In men, chlamydia will sometimes cause a man’s testicles to become very swollen, while they can also become quite painful. There are numerous potential reasons for this and it is something that should be checked out as soon as possible. In addition to chlamydia, these symptoms can also be caused by testicular cancer.
Testicular cancer is, fortunately, a condition that is relatively easy to treat. That is, however, provided it is caught early on in its development. It is recommended that men perform regular check-ups on themselves, and that they see a medical professional the moment they notice something is wrong.

8. Complications
While chlamydia does not usually cause any symptoms, that does not mean to say it is not without its potential complications. In some cases, for example, it can cause reactive arthritis. This is a variety of arthritis that is caused by an infection elsewhere in the patient’s body.
Other problems include inflamed testicles, while pelvic inflammatory disease is also a potential complication of chlamydia. The disease will also cause the patient to become infertile in a small number of cases. The good news is that chlamydia is treatable, and that these complications can be avoided if treatment is found soon enough.

9. Prevention
Although chlamydia is very contagious under the wrong circumstances, people can still take precautions to help keep themselves safe. People that are most at risk are those that are sexually active with different partners. This is especially the case for people that don’t also take other precautions.
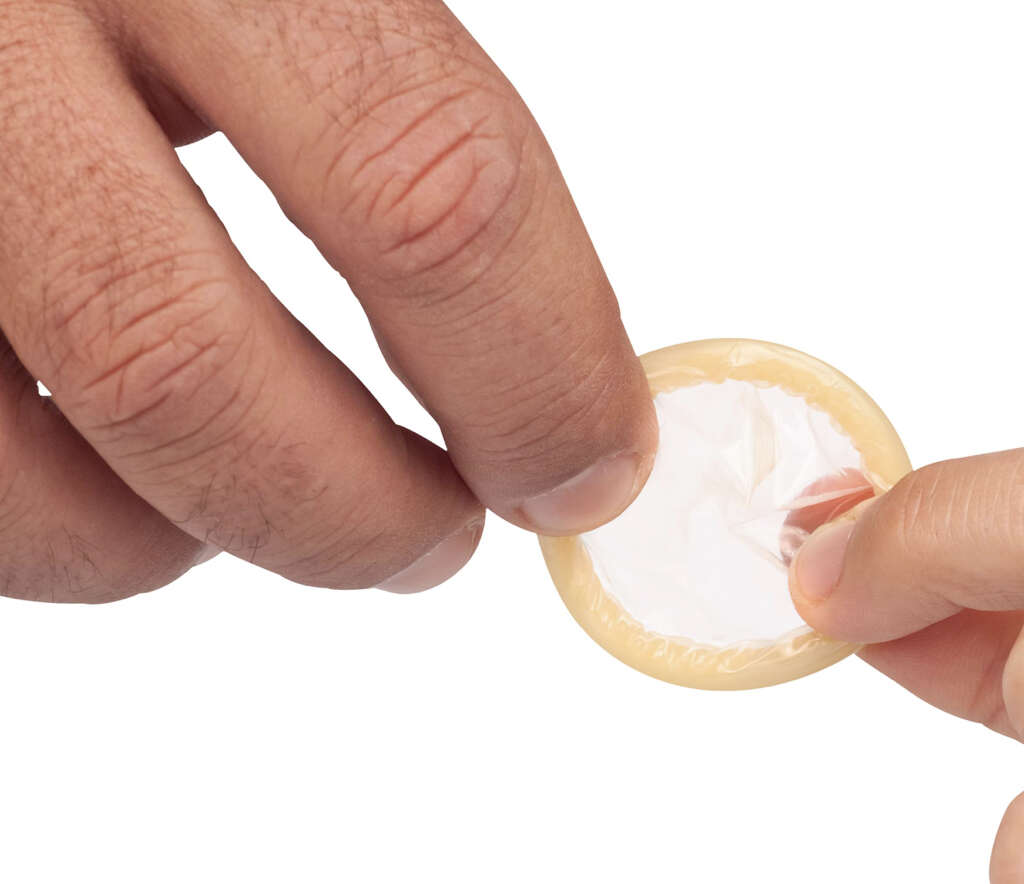
Using a condom can help both partners to be safer from the disease. However, the exchange of bodily fluids is not necessary for an infection to happen. While it cannot be transmitted by kissing, it can be transmitted through oral sex. People should also avoid sharing any sex toys to help prevent an infection.
10. Treatment
As a bacterial infection, chlamydia is treated with antibiotics. Some people will be prescribed tablets to take over the course of a week. Others may be given tablets that are all to be taken on the same day. Patients should not have sex for a week regardless of which method of treatment they receive.
If you have chlamydia then your partner should also be tested, and treated if necessary. In addition, you should also try and contact any sexual partner you have had recently. It is advisable to be tested again around 3 months or so after treatment has been completed.