What Is Body Dysmorphia?
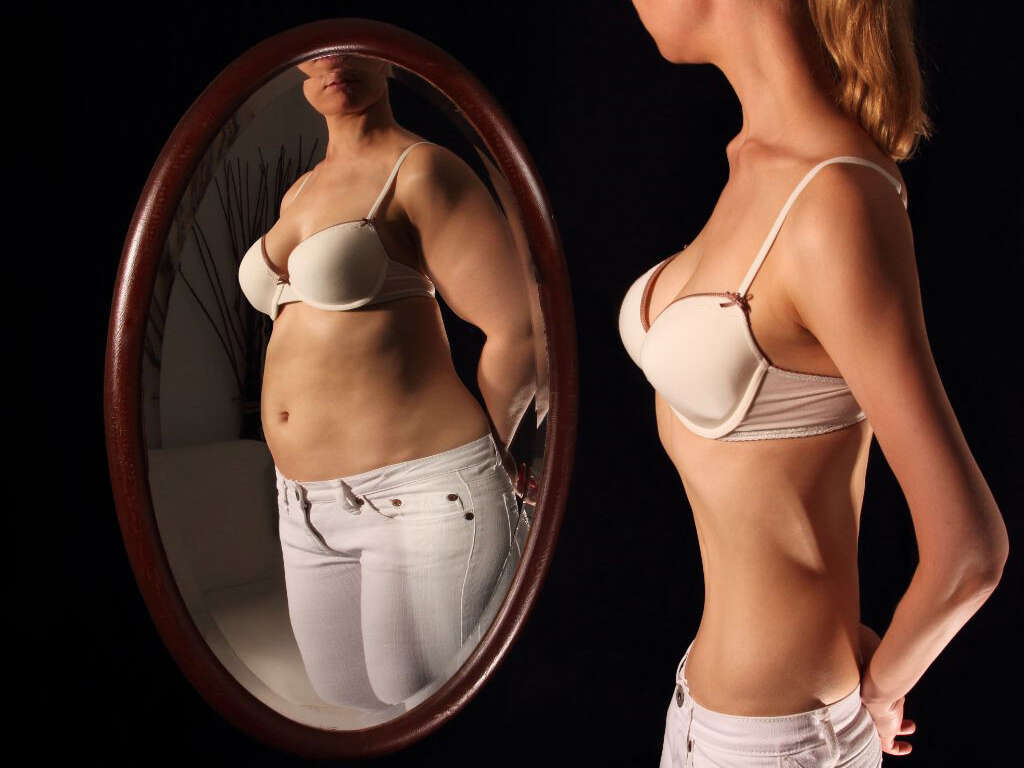
If asked, most people could list a few things they would change about their appearance if they could. Maybe there is a gap between their teeth, or they think of themselves as too thin or too fat. They may even cringe slightly when they look in the mirror or change the way they dress to mask these perceived flaws.
People who experience body dysmorphia, however, are consumed by the things they believe are wrong with their bodies. They can become obsessed, trying to think of ways to change their bodies to look the way they think they should look. They may even engage in risky behaviors to bring about those changes. Here are some things to know about body dysmorphia.

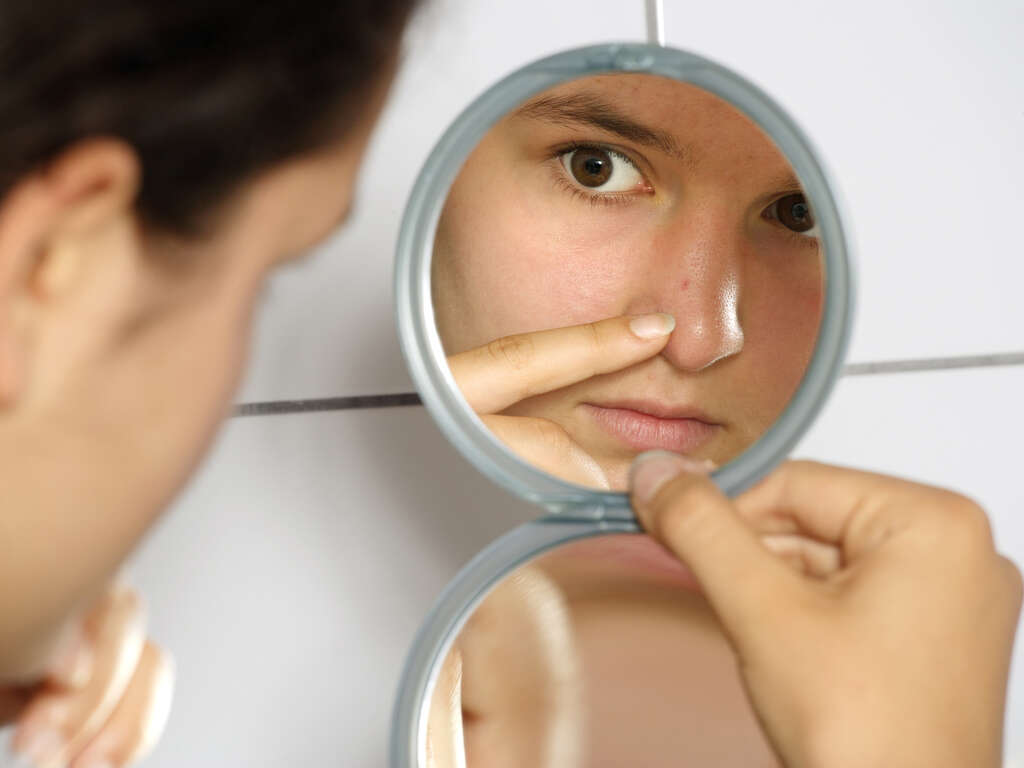
1. What Are the General Signs of Body Dysmorphia?
People with body dysmorphia engage in extreme behaviors to either overcome or avoid the problem. They may check mirrors constantly, picking at skin flaws or trying out poses that hide the part of their body that they despise. Others avoid mirrors altogether, trying to forget that the problem area even exists.
Body dysmorphia can be difficult to diagnose because of the intense shame associated with the maligned body part. Those who suffer from this problem are often reluctant to discuss it, even with a trusted therapist. Because they may also feel that their assessment is correct, they are likely to be resistant to any suggestion that there’s something wrong with their judgment that needs to be addressed.

2. What Are the Most Common Body Parts Associated with Body Dysmorphia?
Body dysmorphia can manifest as a preoccupation with one particular body part, or it may encompass several areas of the body. Perceptions of skin defects are common, particularly in regard to aging. Wrinkles, discoloration and acne can all be problems that people become obsessed with resolving.
No gender is more prone to body dysmorphia than others. Internalized, idealized standards for the gender with which people identify can lead to dysmorphia, though. A focus on hair thickness, muscle tone, body shape and genitalia can easily become fixation if these body parts don’t match the image of how the person thinks they should look.

3. What Is the Difference Between Dissatisfaction and Dysmorphia?
It’s unusual to meet someone who is completely at peace with how his or her body looks. Many people can think of at least one way they’d like to improve their appearance. They may even take action, such as changing their diet or exercise regimen, to address problem areas.
The intensity of the attention they give to a perceived flaw is what marks the difference between mere dissatisfaction and dysmorphia. An inordinate investment of time, money or emotion in fixing the issue crosses the boundary between awareness and disorder.

4. What Is the Relationship Between Body Dysmorphia and Eating Disorders?
Eating disorders and body dysmorphia share some common symptoms. Both are characterized by intense dissatisfaction with body image. People who experience eating disorders also exhibit the same obsessive need to change or control the way their bodies look.
Although it is likely present, body dysmorphia is often not diagnosed in people with eating disorders. Certain goals, such as getting necessary nutrition, are prioritized more heavily in the treatment of anorexia or bulimia.

5. What Are Some Risk Factors That Can Lead to Body Dysmorphia?
People with body dysmorphia want to achieve a perceived standard of physical correctness. Many of these standards are received from outside sources. Societal beauty norms, as well as teasing or bullying from others, send messages about how they fall short in measuring up to these standards.
Body dysmorphia is common in the transgender community. For many trans persons, the way their body looks does not line up with the gender with which they identify. They may seek hormonal therapy or surgical options to address this issue.

6. What Are the Social Symptoms of Body Dysmorphia?
Any social situation where others can observe the body issues that plague people with dysmorphia can seem problematic. As the problem intensifies, they may start to avoid optional social situations altogether, too ashamed of how they look to risk the scrutiny of others.
People with body dysmorphia have difficulty accepting praise. While they may seek reassurance, they have a hard time believing that the positive things their friends and family members say about them are true. Compliments are in conflict with everything they believe about their appearance.

7. How Can Body Dysmorphia Affect a Person’s Job?
As with other social situations, showing up for work can be a challenge for those with body dysmorphia. Unless they have a way to disengage from others frequently, their obsession may render them less productive. Many people with this disorder miss work on a regular basis.
Rigid dress codes can exacerbate dysmorphia. These rules take away part of the control that the sufferer believes is necessary to cope with the problem. For the dysmorphic individual, the dress code then becomes the distraction it was designed to resolve.

8. What Are the Psychological Effects of Body Dysmorphia?
Anxiety is almost always present when someone experiences body dysmorphia. This can manifest as a general anxiety disorder or social anxiety. It is often characterized by panic attacks, particularly in situations in which the person feels unable to hide the perceived flaw from others.
The self-isolation often seen in depression or agoraphobia tends to mirror that of body dysmorphia. It is not uncommon to see co-occurrence between these disorders.

9. Is There a Link Between Body Dysmorphia and Suicide?
People with body dysmorphia may go to great lengths to change their appearance and get rid of the perceived problem. They may seek surgery or other aggressive treatments. Some even engage in self-harm, attempting to actually cut away the offending issue.
When nothing else works, suicide may start to seem like a viable option. For many, body dysmorphia consumes their thoughts and overwhelms their lives. Their doctors must always be on the lookout for the progression to suicidal ideation when their patients grow hopeless about possible solutions.
10. What Are the Treatment Options?
As with any psychological disorder, effective treatment starts with an accurate diagnosis. People who are diagnosed with body dysmorphia can benefit from cognitive behavioral therapy, wherein they learn to identify negative thoughts and feelings so that they can begin to act in ways to change them. Certain medications used to treat anxiety and depression may also be helpful when a chemical imbalance is present.
Daily life is the test of whether or not treatment will be effective. People with body dysmorphia must commit to putting the things they learn from their doctors into practice. In some cases, brief hospitalization can help them learn these practices in a controlled environment.











