What Is Blue Waffle?
Sex is one of the most natural things that we can do, and most people will enjoy a sexually active life. Not only can sex help us to start families, but it is also a very enjoyable experience, meaning many of us want to enjoy sex frequently. While it is OK to enjoy sex, it should also be enjoyed with some level of responsibility.
One of the biggest problems involving sex is that the close physical contact makes it easier for diseases to be transmitted. One disease that has been seen a lot on the internet is blue waffle, but what is this disease?

1. Blue Waffle
Blue waffle is the name given to a certain type of vaginal infection. It gets its name from the slang use of the word waffle to mean vagina. It is known as ‘blue’ waffle particularly because the infection causes the exterior of the vagina to turn blue. Other symptoms of the condition include lacerations, and sores.
There is some very good news about this very unpleasant sounding disease, however - it is fake. It appears as though the claims were little more than click-bait, meaning it was a way of enticing people to click on a link to read more. While blue waffle is a fake disease, however, there are other sexually transmitted diseases that can cause some very unwelcome symptoms indeed.

2. Human papillomavirus (HPV)
Of all the sexually transmitted diseases that people can catch, the human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common. There is believed to be over 200 varieties of the virus, and 40 of them are spread by sexual intercourse. The disease is spread by skin to skin contact with another infected person.
Such is the prevalence of this disease that the majority of sexually active people are likely to catch it at some point. Thankfully, however, the symptoms are only very mild, and most people will experience no symptoms at all. Such infections will occasionally cause warts on the genitals, but the symptoms will usually clear up without treatment
3. Genital Herpes
Genital herpes is another type of disease the spread from person to person through sexual contact, and there are two types of the herpes virus that can result in the condition. Of all the people that catch the disease, the symptoms will be mild, or non-existent, in around 90% of cases.
When symptoms do show, they will typically include itchiness and pain in the genital area. The patient can also develop flu-like symptoms, and the patient’s lymph nodes can become inflamed. Bumps, blisters, and ulcers are other typical symptoms of the disease. There is no cure for the condition but the virus will usually remain dormant. It can reactivate at any time, however.

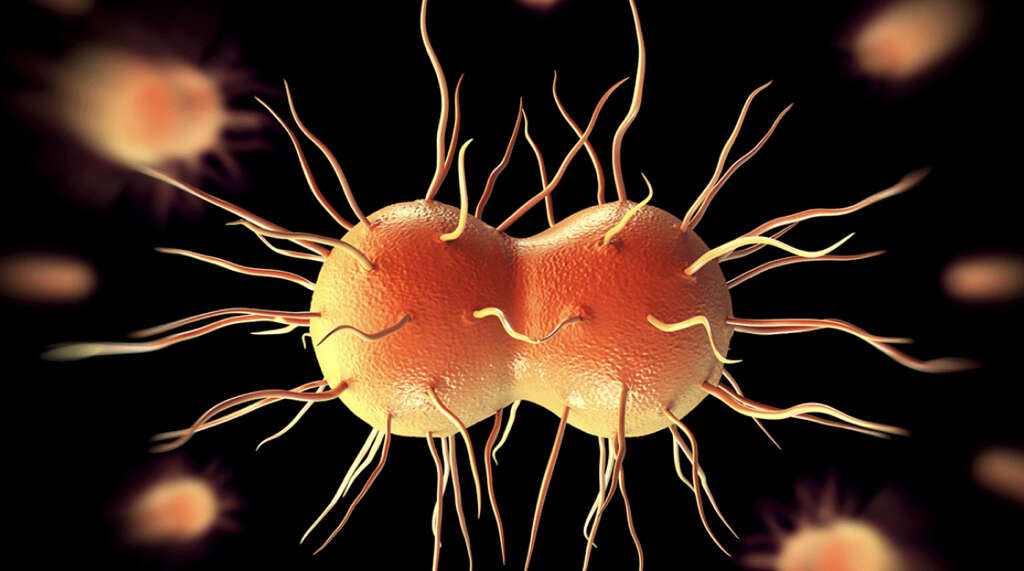
4. Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a type of bacterial infection that is caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacterium. Skin to skin contact with an infected person is often all it takes for somebody to become infected. In many cases, infected people will experience no symptoms, but symptoms can be unpleasant when they do arise.
When they show, typical symptoms include pain when urinating, and sex may also be painful. Men can experience swollen testicles, and women may experience bleeding in between their periods. A pain in the lower part of the abdomen is another possibility, while patients will also typically experience a discharge coming from their genitals. It is also possible for the rectum to become infected.
5. Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
This is a disease that will only affect women, and it is the most common genital disease in women below the age of 44. It can be caused by a number of bacteria, including gardnerella vaginalis, but it is not considered to be a sexually transmitted disease.
The vagina naturally has bacteria living inside it. These are usually harmless, and even helpful in some cases. However, an imbalance in the bacteria in the vagina can cause problems. It is not clear why such an imbalance happens, but there are some activities that might encourage it. This includes douching, and promiscuity.

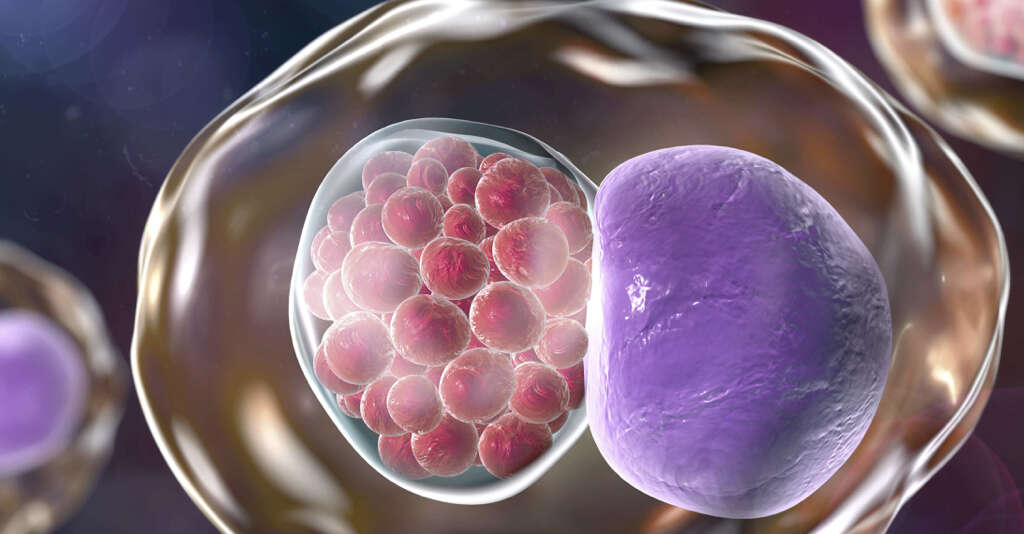
6. Chlamydia
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease that is caused by the chlamydia trachomatis bacterium. Many people who are infected will experience no symptoms and, when symptoms do show, it will be several weeks after the infection took place. When symptoms do show, they will typically include a discharge from the genitals.
Other symptoms of the disease include a burning sensation when urinating. In men, the disease can also cause the testicles to become swollen. Chlamydia can also infect the rectum, and this can result in symptoms that include pain in the rectum, rectal bleeding, and a discharge from the rectum.
7. HIV
HIV, or human immunodeficiency virus, is perhaps the most dangerous of all sexually transmitted diseases. Once infected, the patient can go on to develop AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). The disease goes on to suppress the patient’s immune system, making it harder for them to defend themselves against disease.
There is no cure for HIV/AIDS yet, but treatment for the condition is increasingly effective. When the disease first arrived, people with it could expect to live for another 20 years or so. With advancements in medicine, even people that are diagnosed at 20 years old can go on to live to 70 years old.

8. Prevention
The only sure way to avoid catching sexually transmitted diseases is to abstain from sex completely. Even then, some STD’s can still be passed in some other ways. Regardless, it is not really practical for most people to abstain completely. At least limiting how many sexual partners you have can help keep you safer, however.
Another way of helping to keep you safe is to use condoms. These will help to prevent the sharing of bodily fluids, as well as reducing contact with mucous membranes. Even when using condoms, however, some STDs can still be transmitted by skin to skin contact. You should also help prevent the spread of diseases by abstaining from sex if you are infected.

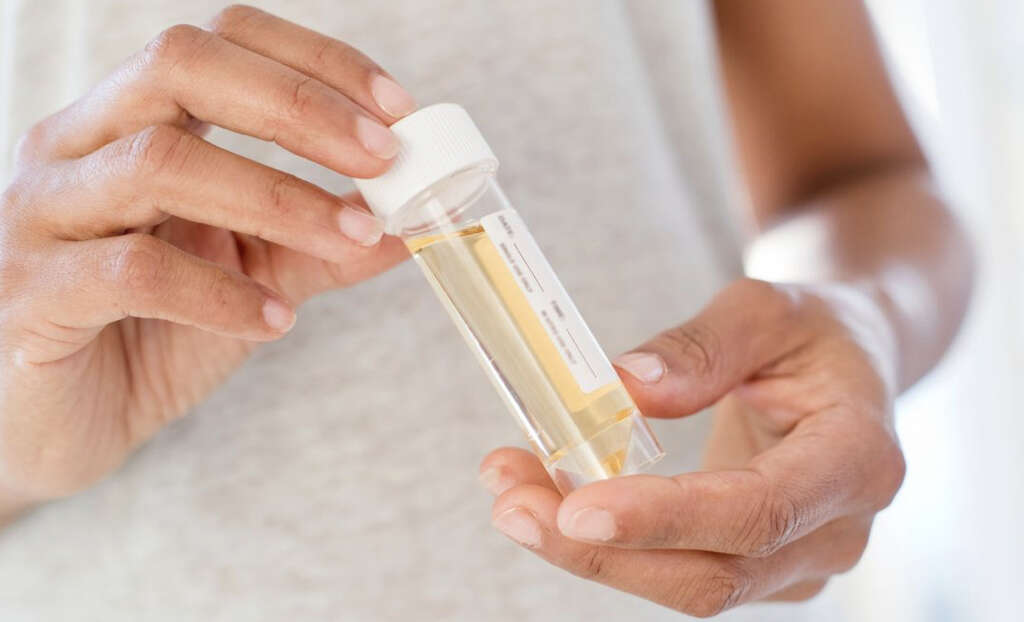
9. Diagnosis
Diagnosing the condition will vary according to which disease you have caught. Your doctor will likely want to ask you questions about your symptoms, and also about your lifestyle choices. A test will often be required to determine what treatment should be used.
Tests will typically involve taking a blood test or urine test so they can be sent away for analysis. A swab from the genitals may also be required in some cases. Depending on the nature of the disease and how severe it is, further tests may be required to see if the disease is causing complications.
10. Treatment
Some sexually transmitted diseases cannot be cured. In which case, the patient will need to manage their symptoms. Treatment is often available to treat the symptoms, however, and most people with an incurable sexually transmitted disease will live a relatively normal life.
In some cases, a sexually transmitted disease can be cured by antibiotics or by antiviral medications. The treatment is usually straight forward and a single injection is often all that is needed in many cases. It is also important that any sexual partners that might have been exposed to the disease also get a check-up and treatment if necessary.