What Is West Nile Virus?
Mosquitos are found in many parts of the world, and they are renowned for biting. Although mosquitos are very small, their bites can still be troublesome. Mosquito bites are notoriously itchy and infections can take place if the bites are scratched too much. There is also the risk of picking up diseases from these bites.
If a mosquito feeds on an animal that is infected with a virus, the mosquito can itself become infected. The mosquito can then transmit the virus to the next animal that it feeds from. There are numerous different viruses and other pathogens that can be transmitted in this way. One of these is the West Nile virus.

1. West Nile Virus
The West Nile virus can be found in many parts of the world and, relatively recently, was found in the United States. It is a member of the Flaviviridae family of viruses. Since its arrival in the United States, the virus can now be found in the vast majority of states. In the majority of cases, people will contract the virus by way of a mosquito bite.
The vast majority of cases of West Nile virus are mild, and many won’t even feel any symptoms at all. It will be serious in a small number of cases, however, so it should not be treated with complacency. People that are showing the more serious symptoms of the disease should be found medical attention as soon as possible.

2. Mosquito Bites
As mentioned, the West Nile virus is usually transmitted by a mosquito bite, and it can infect some other animals in addition to humans. It can be fatal in other animals, including in horses, and domestic and wild birds. The virus cannot be contracted through contact with infected animals or people.
People are obviously more likely to catch the disease when mosquitos are more active, and this means when the weather is warm. 14 different species of mosquito have been identified so far that can transmit the virus. There are other possible methods of the virus, although such cases are rare.

3. Alternative Transmission Methods
Although the vast majority of cases of West Nile fever will be transmitted by mosquito bites, it is possible to get the disease in other ways. One of these is by way of blood transfusions and organ transplants from infected people. The chances of this happening in developed countries are very low, however, because blood and tissues are heavily screened.
Another potential cause is exposure to the virus in a laboratory where safety precautions are not strict enough. There is also thought to be a chance that the virus can be passed from mother to child during breastfeeding. Cases of transmission of the virus not involving mosquito bites are rare, however.
4. Symptoms
As mentioned, the majority of people with the virus will show no symptom at all. When the patient does show symptoms, they will often be mistaken for the flu. The disease is known as West Nile fever, and a fever is one of the most typical symptoms of the disease. Many patients will also complain of a headache.
Other symptoms include fatigue, and aching joints and muscles. Nausea and vomiting will also be present in some cases, and some patients will also develop diarrhea. Some patients will also develop a rash. While these symptoms will usually only be mild, some patients will develop far more serious complications.

5. Complications
In a very low number of cases, West Nile virus can become very serious indeed. The virus can infect the membrane that protects the brain and spinal cord to cause a condition known as meningitis. It can also infect the brain itself, in a condition known as encephalitis. Both of these have the potential to be very dangerous.
Symptoms of these conditions typically include a high fever, a stiff neck, and a severe headache. Patients will also become confused more easily than usual. They can also experience weakness or paralysis of their muscles, and they may also develop tremors. A coma or stupor are other potential symptoms, and some patients will also have seizures. Death can occur in the more severe cases.

6. Lasting Effects
When we recover from an illness, we will usually stop showing any symptoms. This is not the case for some people that have had West Nile virus, however. Even in some cases where the patient only showed mild symptoms, the patient can continue to show symptoms for long afterwards.
Many people that had West Nile virus will complain of weakness, fatigue, headaches, joint pain, memory loss, and problems balancing for months or years after they recover from the virus. Some will even experience disabilities to varying degrees. Some of the symptoms will remain with the patient for the rest of their life.

7. Who’s at Risk?
Those most at risk of West Nile virus are those that live in areas where certain mosquitos are present, and during the warmer months. The majority of cases are mild, but certain group are at a risk of developing more severe symptoms. This includes older people. People that have certain medical conditions are also in a higher risk category.
This includes people with diabetes, high blood pressure, kidney disease, and cancer. People that have recently had an organ transplant are also at a higher risk of catching the disease. People who are in higher risk categories should do what they can to try and keep themselves from any disease, including West Nile virus.

8. Prevention
Preventing mosquito bites is the best way to avoid contracting West Nile virus. Mosquito larvae live in standing water, so ensuring that water is not left standing can be effective in preventing them. You should also try and ensure that mosquitos have as few ways to gain access to your home as possible.
When you are outside, try and wear long, loose clothing. This can help to protect you against other insect bites as well as mosquito bites. Also try and avoid being outside at dusk and dawn which is when mosquitos are at their most active. Using insect repellants can also help to prevent bites.

9. Diagnosis
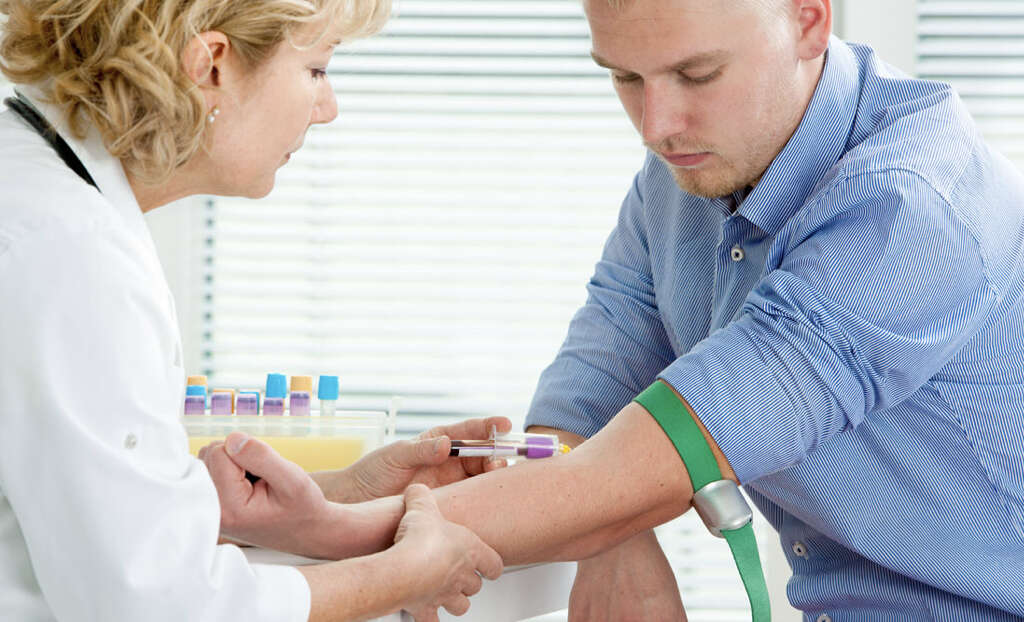
Your doctor is likely to perform a brief physical exam, but this is unlikely to be enough to reach a confirmed diagnosis. In order to diagnose West Nile fever, a blood sample will need to be taken so it can be examined to look for the antibodies that help fight the virus.
If the patient is suffering from severe symptoms, they will likely be tested for signs of encephalitis and meningitis. This can be achieved with help from an MRI scan that will help identify inflammation, while an EEG may also be used. A spinal tap may also be performed in order to help look for signs of meningitis.
10. Treatment
In the vast majority of cases, no treatment will be required. Indeed, in many cases the patient will not even be aware that they have the virus. For those that do need treatment – there is no treatment for West Nile virus. However, the patient can be prescribed medication that will help to soothe their symptoms.
Those that have more severe cases with complications like meningitis and encephalitis will often need supportive care. They may be placed on an intravenous drip and prescribed medication to help make them more comfortable. With no cure for the virus, there is little that can be done other than provide as much care as possible in the hope that the immune system will overcome the disease.