What Is Type A Flu?
People living in the past would not have had the same access to medical assistance that we do, and this made us a lot more vulnerable to diseases. Diseases that we more or less shrug of nowadays would have been far more threatening in the past, posing a very real threat to our lives.
One example of such a disease is the flu. It is a disease that has taken countless lives throughout history, and is still responsible for taking around 500,000 lives every year in the modern world. It also looks set to be with us for a lot longer still, although the good news is that it is less of a threat than it used to be.

1. What Is the Flu?
The flu is a disease that is caused by the influenza virus. It is a common virus and many people will fall ill with it at least once every year. It is a type of respiratory infection, meaning it affects the lungs and airways. It is thankfully not usually a serious condition, but it still has the potential to be dangerous.
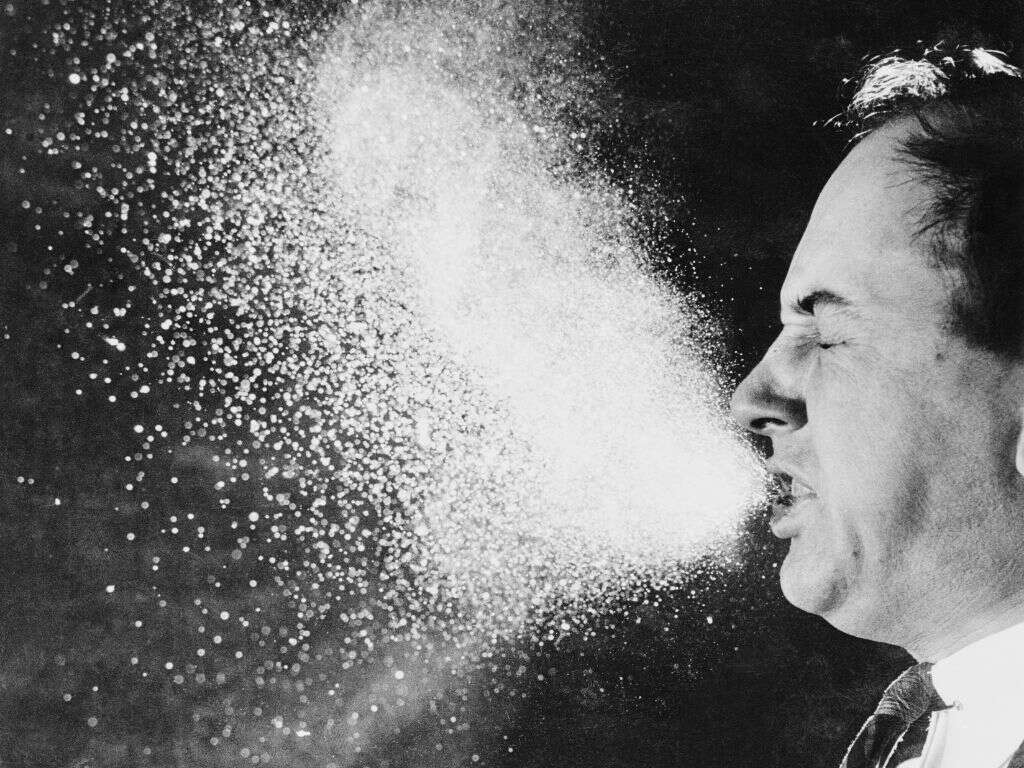
The flu is typically transmitted through infected droplets in the air, or by coming into contact with contaminated surfaces. The disease is very contagious, but its spread can be limited by taking certain precautions. While we usually think of the flu as a different disease, there are different varieties of it.

2. Type A Flu
Type A flu is the most common variety of the disease. It is very contagious and is often transmitted when somebody comes into contact with a contaminated surface. As well as being able to infect humans, type A flu is also able to infect other species, including pigs, bats, and birds.
Type A flu is constantly evolving which makes it harder to defeat, and it is also sometimes responsible for epidemics. Another key characteristic of the virus is that it will sometimes cross between different species. There is often the need to be vigilant to prevent a serious strain of the flu from being able to cause a serious pandemic.

3. Type B Flu
There are some distinct differences between type B flu and type A flu. Perhaps the main difference is that type B flu is not found in other animals; only humans can be infected by it. Type B flu is also not going to be responsible for any pandemics. When it does infect somebody, the symptoms are also likely to be milder than with the type A virus.
Although type B flu tends to be mild and is unlikely to cause any real harm, it can be serious for some people. With that in mind, it is always best to not take the disease too lightly and to keep an eye on vulnerable patients.
4. Type C Flu
Type C flu is the rarest of varieties in people. It is also sometimes found in other animals, particularly pigs. In addition to being the rarest, it is also the mildest. In many cases, the patient will show no symptoms and, when symptoms do appear, they will often be mistaken for the common cold.
Although type C flu is the mildest variety, it will have the potential to be serious in a small percentage of cases. The virus will not be responsible for pandemics, but it can be responsible for localised outbreaks. Again, vulnerable people with the flu should be monitored for signs of complications.

5. Complications
The vast majority of patients with type A flu will make a full recovery within 2 weeks, often considerably less. However, the virus does have the potential to cause some potentially life-threatening complications. One of these is pneumonia, which is a dangerous condition that can make it very difficult for the patient to breathe.
Severe flu infections can also go on to cause conditions like encephalitis, meningitis, and kidney failure. The virus will also sometimes go on to cause sepsis. This is a very dangerous condition that is caused by an extreme response from the immune system to the infection.

6. What Is the Bird Flu?
As mentioned, type A flu can infect other animals as well as humans, and this includes birds. Perhaps one of the most well-known of these is bird flu, which started making headlines in 2003 due to a surge of cases being reported. This lead to wide spread reforms in poultry rearing practices.
The outbreak resulted in high numbers of poultry being destroyed. This, in turn, had a severe financial impact on many people who relied upon poultry for their income. Systems remain in place to help prevent a serious outbreak of bird flu, especially considering some people have also been infected by the disease.

7. Who’s At Risk?
Anybody can fall ill with the flu, even people with the strongest of immune systems. However, some people are more prone to the disease than others are. This includes people who are over the age of 65, while particularly young people are also in a higher risk category.
People with a weakened immune disease are also in a higher risk category, as are people with certain other medical conditions. Not only are certain people more likely to fall ill, but these people are also more likely to develop serious complications. Anybody that is in a higher risk category should be monitored, and a doctor should be called as soon as serious symptoms emerge.

8. Prevention
There is a vaccine for the flu, and vulnerable people are recommended to get vaccinated. The flu is known for evolving rapidly, however, meaning that a booster jab may be required once every 1 or 2 years. In addition to vaccines, there are other steps we can take to help prevent the spread of the disease.
One of these steps is to regularly wash your hands with warm, soapy water. The soap is important because it helps to break down the thin fatty layer that otherwise helps to protect the virus and hold it together. It is also advised to cover your nose and mouth when coughing or sneezing.
9. Diagnosis
In most cases, your symptoms alone will be able to let your doctor known what the problem is, and this will often be deemed sufficient. In some cases, however, it may be necessary to perform tests in order to confirm what is causing the patient’s symptoms.
A test for diagnosing the condition will involve your doctor taking a swab of fluid from your nose or throat. This swab can then be sent to a lab for testing, and the results will come through fairly quickly. In cases where a serious condition is suspected, the results can come back in 30 minutes if the facilities are available.
10. Treatment
In the majority of cases, the patient is simply asked to take on plenty of fluids and get as much rest as they can. The immune system will usually be strong enough to defeat the virus without help from medication. In the more serious cases, anti-viral medication may be used to help at least slow down the virus.
Some people will need to be treated for serious complications if they arise, and this will sometimes mean putting the patient on oxygen. It may also be necessary to put the patient on a ventilator to help ensure their body gets the oxygen it needs.