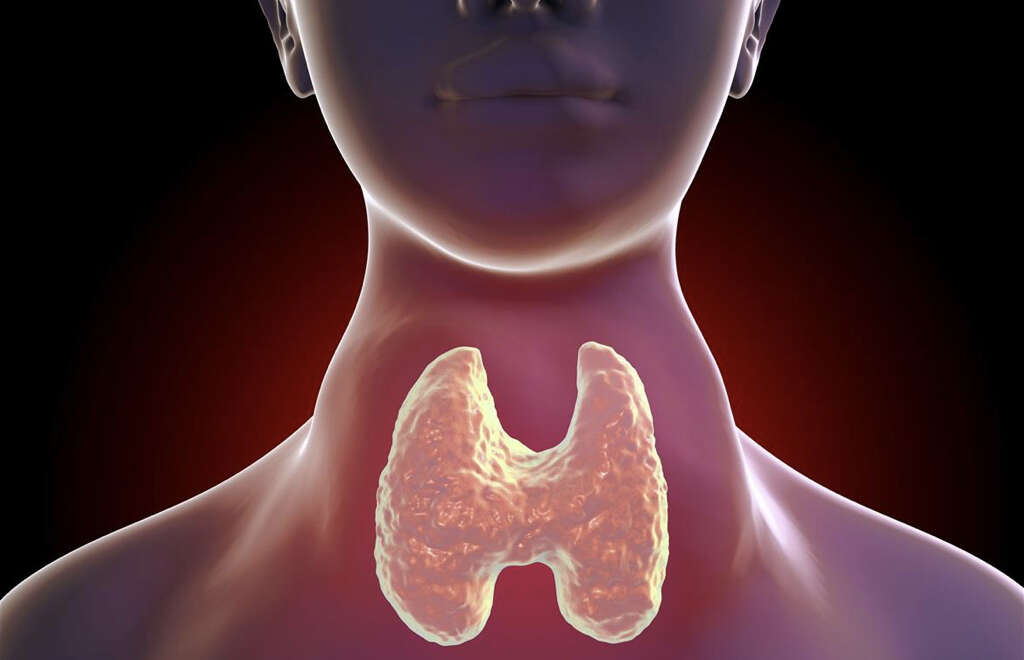
What Does the Thyroid Do?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front part of the neck. The gland consists of two lobes, each on either side of the front part of the neck. The thyroid gland is part of the endocrine system and produces thyroid hormones. When it works properly without deficiencies or other issues, it is not possible to feel the thyroid gland with your hand even if you apply pressure to your neck.
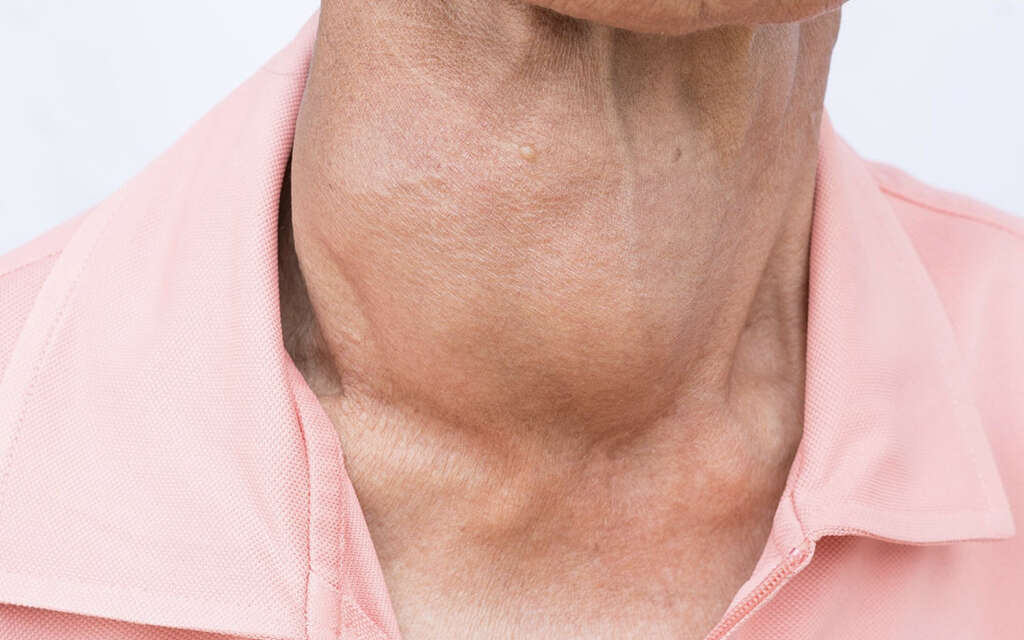
This, however, changes if the thyroid gland is exposed to disease; in which case, it enlarges, with the swelling showing in the neck. The condition whereby the thyroid gland is swollen is called a goiter. But what does the thyroid do and why is it an important part of the body?
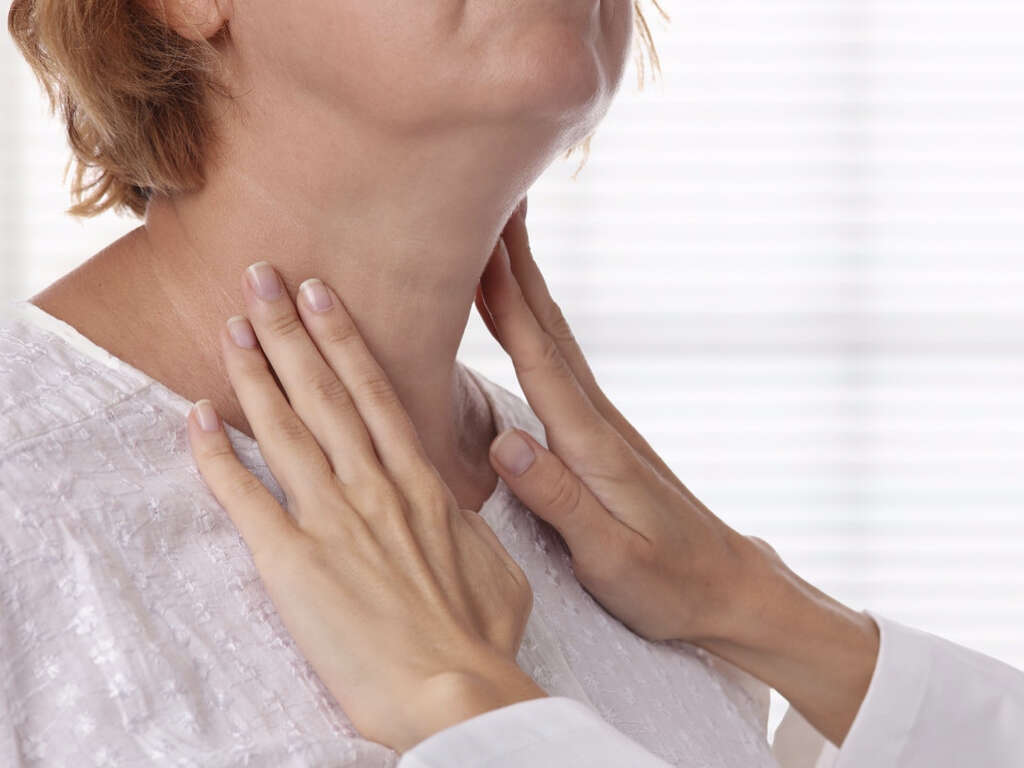

1. Produces Thyroid Hormones
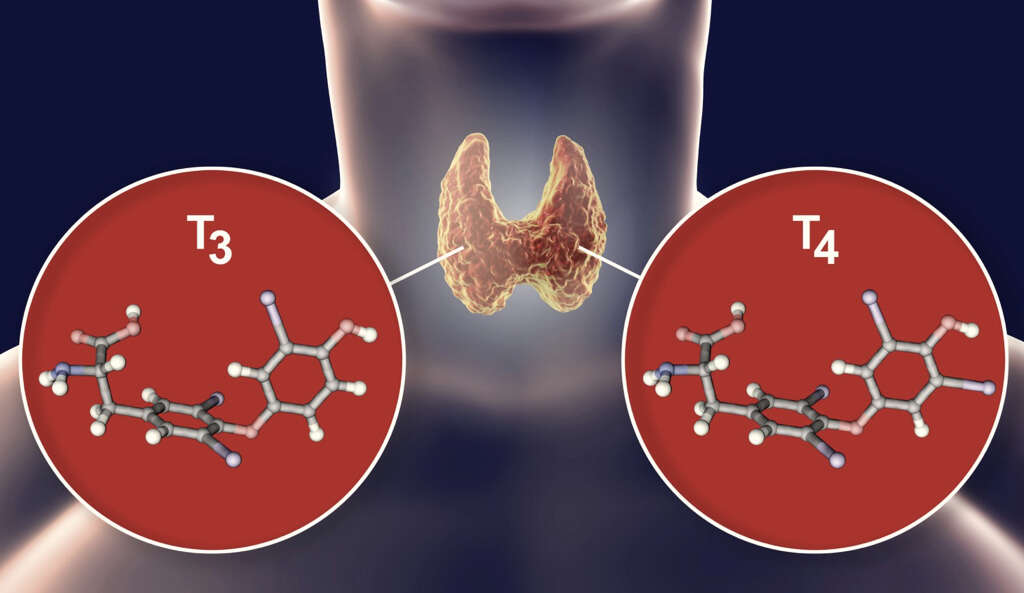
The main function of the thyroid gland is the production of thyroid hormones. These include T3, T4, and calcitonin.
All these thyroid hormones are composed of two main substances, namely iodine and tyrosine. T3 contains 3 iodine atoms while T4 contains 4 iodine atoms. These hormones have different roles in the body as discussed elsewhere in this article.
2. Produces Calcium Regulating Hormone
Calcitonin is one of the hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Calcitonin is required for the regulation of the level of calcium in blood. The hormone is produced depending on the need for it in the body.
When the calcium level increases, the thyroid gland is triggered to start producing calcitonin. Calcitonin reduces calcium level in blood by inhibiting the release of calcium from bones. It does this by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts, which are responsible for breaking down bones to release calcium. Calcitonin returns the calcium into the bones and decreases its level in blood.
3. How the Thyroid Gland Produces Thyroid Hormones
The process of production of thyroid hormones involves production of thyroglobulin, which combines with iodine to form thyroid hormones. Thyroglobulin is a protein that interacts with iodine to transform into thyroid hormones.
Iodine gets to the thyroid gland from the digestive system where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Once in the thyroid gland, iodine and other raw materials go through various processes until the formation of the various thyroid hormones.
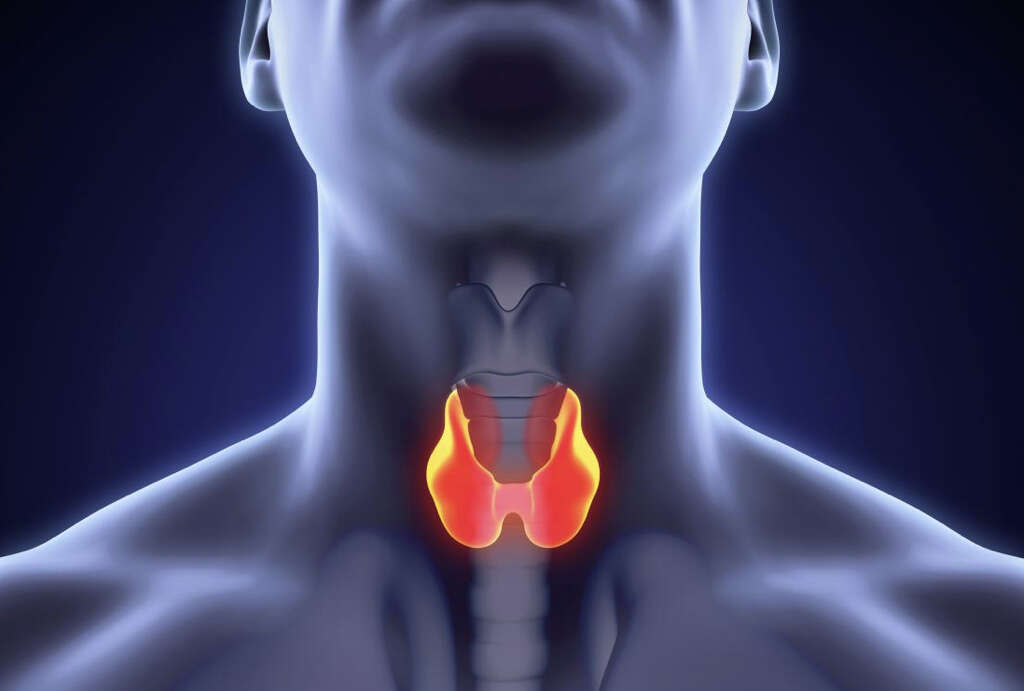
4. Metabolic Functions of Thyroid Hormones
The most important role of thyroid hormones is the metabolic function that impacts all cells in the body. The process of metabolism avails nutrients for use in the production of energy and other associated processes necessary for life.
In its metabolic function, the thyroid gland, through the hormones it produces, influences appetite, how the gastrointestinal tract absorbs different nutrients, movement of the bowels, and production of hormones, among other processes.
5. Cardiac Functions of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones have an effect on the working of the heart. The hormones influence heartbeats including the rate of heartbeats.
At the same time, thyroid hormones also influence breathing rate, and the amount of oxygen getting into the bloodstream. With the proper amounts of thyroid hormones, the heartbeat and oxygen intake help to provide the body with the adequate energy levels needed.

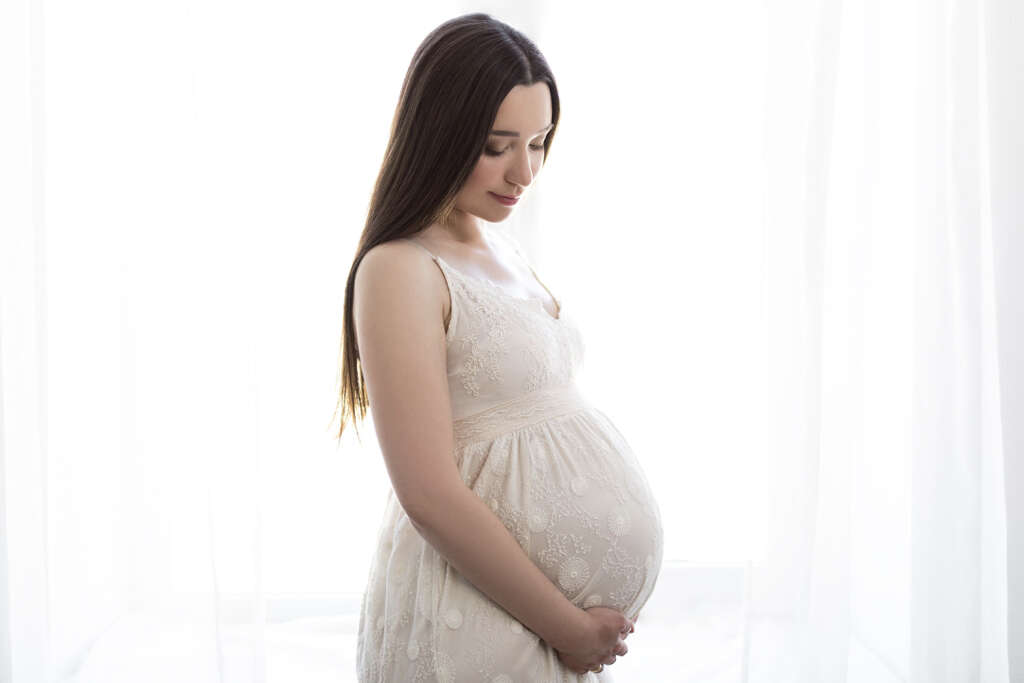
6. Developmental Functions of Thyroid Hormones
Thyroid hormones are essential for normal growth and development of the body. During pregnancy, the developing brain requires thyroid hormones for proper development.
And after delivery, thyroid hormones continue their role in the growth of the brain and the rest of the nervous system. In older children and teenagers, thyroid hormones increase the rate of growth into maturity.

7. Sexual Maturity
In addition to general growth and development, thyroid hormones are important for healthy maturity of the sex organs and the reproductive system.
Thyroid hormones are also important for normal sex life including sexual performance, libido, and normal menstruation. In this respect, changes in thyroid hormone levels can impact sex life.

8. Hyperthyroidism and Other Thyroid Problems
There are two main problems that can affect the thyroid gland: hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism. Hyperthyroidism refers to excessive activity of the thyroid gland.
The condition occurs when the thyroid gland becomes overactive, thus producing excessive amounts of hormones. Hyperthyroidism is rare in infants and young children, and usually develops during teenage years or later in life.
9. Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which thyroid gland activity slows down significantly. This leads to low levels of thyroid hormones. Hypothyroidism is usually an autoimmune condition, whereby the body’s immune system attacks own organs or tissues.
Other causes of hypothyroidism include decreased intake of iodine and the use of certain thyroid-inhibiting drugs. If a woman has hypothyroidism during pregnancy, there is a high risk of giving birth to a baby with developmental problems such as learning difficulties, physical growth problems, and delayed brain maturation. Hypothyroidism during adulthood can cause metabolic disorders due to a slowing down of the basal metabolic rate. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, cold intolerance, slow heartbeat, suppressed appetite, poor memory, mental illnesses such as depression, muscle problems, and infertility.

10. Thyrotoxicosis
Thyrotoxicosis is a condition in which there is a high level of thyroid hormones in blood. This can be caused by factors such as hyperthyroidism, infection and inflammation of the thyroid gland, and benign tumors in the gland.
Thyrotoxicosis is characterized by unbearable body heat, significant loss of weight, increased appetite, irregular bowel movements, irregularities in menstruation, increased heart rate, tachycardia, palpitations or irregular heartbeats, weakness, chronic fatigue, significant loss of hair, and a staring appearance due to a retraction of the eyelids.