What Is Trigger Finger?
Trigger finger, sometimes called trigger thumb or stenosing tenosynovitis, is a condition in which tendons responsible for bending a finger do not work as they should. When this happens, it becomes difficult to bend the finger. Although trigger finger can affect any finger, in most cases, it occurs in the thumb or the ring finger.
Trigger finger causes a locking sensation, stiffness, or pain in the affected finger. The condition occurs as a result of inflammation or thickening of the tendon. Women, people with arthritis, diabetics, and those whose work or other regular activities are straining to the hands are at a higher risk of getting trigger finger. The condition worsens in the morning.
1. Symptoms of Trigger Finger
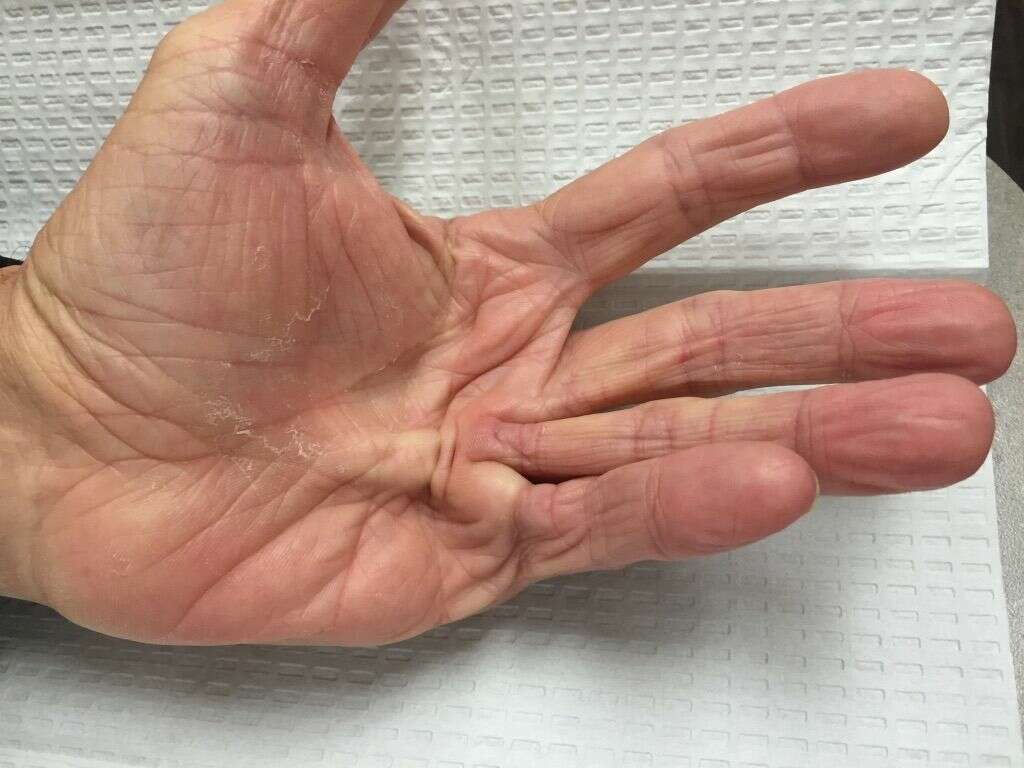
Symptoms of trigger finger usually start after a period of heavy use of the hand, especially in activities whereby the fingers are used extensively. The initial symptoms may include a lump at the base of the finger on the palm side. This can make the base of the finger sensitive to pressure. This may be followed by other symptoms including reduced finger movement, pain, a popping sound when you try to stretch the finger, and a locking sensation.
These symptoms tend to worsen after a period of inactivity such as when you wake up in the morning. This may cause the finger to remain bent similar to a finger pulling a trigger.

2. Causes of Trigger Finger
There is no clear cause of trigger finger. However, the condition develops when the tendons that help pull the finger inward toward the palm do not work as they should. This happens as a result of trauma arising from repetitive exertion of the fingers and thumbs, as happens during activities like gripping, pruning, and gardening.
Trigger finger can also occur as a result of inflammation due to some medical conditions.
3. Inflammation
Whether inflammation results from over-exertion of the fingers, injury, or a medical condition, when it affects a tendon in a finger or thumb, it makes it difficult for the tendon to slide through the sheath enveloping it.
When this happens, the affected tendon may end up catching within the sheath such that it cannot move the finger inward. This leads to the condition of trigger finger.
4. Trigger Finger and Chronic Diseases
Some chronic conditions are also associated with the development of trigger finger. These include inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, and gout.
A person with any of these conditions can suffer from inflammation in different parts of the body. When the inflammation affects tendons in the fingers, it can lead to trigger finger.

5. Complications of Trigger Finger
If trigger finger remains untreated for an extended period of time, the affected finger or thumb may become permanently deformed. This can make the finger a chronic source of pain and stiffness. In this state, it may become difficult to use the affected finger and by extension, the hand to carry out otherwise easy work activities.
In other words, an untreated trigger finger can lead to some degree of disability. Considering the fairly effective treatment with positive outcomes and minimal risk of complications, a patient with trigger finger should not suffer with these complications. It is advisable that patients seek treatment to overcome trigger finger.

6. Disease Process
For a finger to bend, a tendon slides through a sheath that provides a lubricated surrounding to allow for this movement. The tendon sheath is attached to the bones in the finger such that it also provides a pulley system for the tendon as it aids the finger to bend inward.
If, however, inflammation or swelling occurs, the easy movement of the tendons will be affected. This means that the tendon can no longer slide easily through the sheath. By extension, the finger can no longer bend as easily. Depending on the amount of inflammation or swelling, pain, popping, or locking may develop. This condition is called trigger finger.

7. Diet and Lifestyle to Ease Trigger Finger
Trigger finger mainly occurs due to inflammation. It follows that consuming foods with anti-inflammatory properties may help lower inflammation and therefore reduce occurrence of trigger finger. Common anti-inflammatory foods include broccoli and other leafy green vegetables, seaweed, asparagus, blueberries, cranberries, oranges, watermelon, grapes, turmeric, black pepper, cinnamon, apples, chamomile tea, cloves, rosemary cumin, sage, mint, and thyme. These foods contain anti-inflammatory compounds that soothe and prevent inflammation. At the same time, avoid or reduce intake of foods with inflammatory properties like fatty fast foods, sugar, alcohol, dairy, meat, and poultry.
Additionally, regular exercises involving the fingers can help in recovery and prevention of trigger finger. The exercises are aimed at improving the range of motion and strengthening the fingers and the tendons, thereby supporting recovery and reducing the risk of trigger finger. The exercises include stretching, abduction, grasping and massaging the fingers and the hands. It is worth noting that regular use of diet and exercise is necessary to achieve the desired results.

8. Diagnosis
By examining the hand and the affected finger, and taking a patient’s medical history, a doctor can reach the diagnosis of trigger finger. The first thing your doctor will notice is probably the trigger bend in the affected finger. But whether this is present or not, the doctor will look for additional signs like tenderness, swelling, or thickening of the tendon sheath on the palm side of the affected finger or thumb.
Other pointers the doctor will look for include stiffness or a popping sound when you bend the finger. No X-ray or other imaging routine is necessary to arrive at a diagnosis of trigger finger.

9. Treatment
The objective of treating trigger finger is to stop the catching and the inflammation that causes it. Treatment that can achieve this allows for the easy movement of the tendon and, therefore, the finger. The first line of treatment is probably to avoid the repetitive activity responsible for the condition.
Other treatment methods include applying splints and using anti-inflammatory medications. Physical therapy that includes specific exercises may also be used in the treatment of trigger finger. However, if these treatment methods don’t work, the doctor may suggest that you undergo surgery. The surgical procedure is carried out to relieve the catching or locking and allow for the tendon to slide freely so that it can move the finger without pain.
10. Long-Term Outlook
Trigger finger has a generally positive long-term outlook. Avoiding activities that are likely to trigger the condition can help to prevent it. Regular exercises of the fingers and hands, in addition to taking an anti-inflammatory diet, can also help in recovering from trigger finger, as well as prevent recurrence.
Anti-inflammatory medication can also provide relief from trigger finger. If, however, the condition persists, surgical intervention may be necessary. The good thing is that treatment is generally successful. And while a significant percentage of patients who take anti-inflammatory medication or steroid injections get repeat symptoms, this is unlikely for those who undergo surgical treatment for trigger finger.