10 Tongue Cancer Symptoms
Tongue cancer is a type of oral cancer. Cancer that is located in the anterior two thirds of the tongue is also known as oral tongue cancer which tends to be diagnosed early and is easily removed. Cancer that is located in the posterior one third of the tongue is categorized as hypopharyngeal tongue cancer.
Cancer at the posterior one third of the tongue is usually diagnosed at a more advanced stage where the cancer is larger and has a higher risk of spread. These different subtypes of tongue cancer may have different treatment protocols. Tongue cancer usually originates from the squamous cells. Squamous cells are flat, thin cells that cover the surface of the tongue.
Since tongue cancer is a type of oral cancer, the signs and symptoms of tongue cancer can be similar to symptoms of other types of oral cancer. Some of the treatments for tongue cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted drug therapy.

Symptom #1: Persistent Sore
A persistent sore on the tongue is one of the earliest symptoms of squamous cell cancer. The sore can be described to be pinkish red, persistent, and does not seem to heal over time. The sore is also often described to bleed easily if touched or bitten.
A persistent non-healing sore should be seen by a medical professional to rule out cancer especially if the affected individual is more than 50 years old.

Symptom #2: Persistent Tongue Pain
Tongue cancer that is located at the base of the tongue is usually asymptomatic. However, in more advanced cases, it can cause pain in the tongue and the surrounding tissue. This can result in changes in the tone of the voice.
Other associated symptoms often include difficulty swallowing, pain during swallowing, swelling of the tongue, and more. This can contribute to appetite loss that invariably results in weight loss.

Symptom #3: Lump
A lump or a swelling in the tongue can also be a symptom of tongue cancer. It can be a thickening of part of the tongue, nodule, or an anomaly felt in the tongue. The lump or swelling is usually painless and can be associated with a persistent sore that bleeds easily.
Lumps located on the side of the tongue are more likely to be cancerous especially if hard and painless. Patients who experience this issue should consult a medical professional especially if the lump has persisted longer than a week or two.

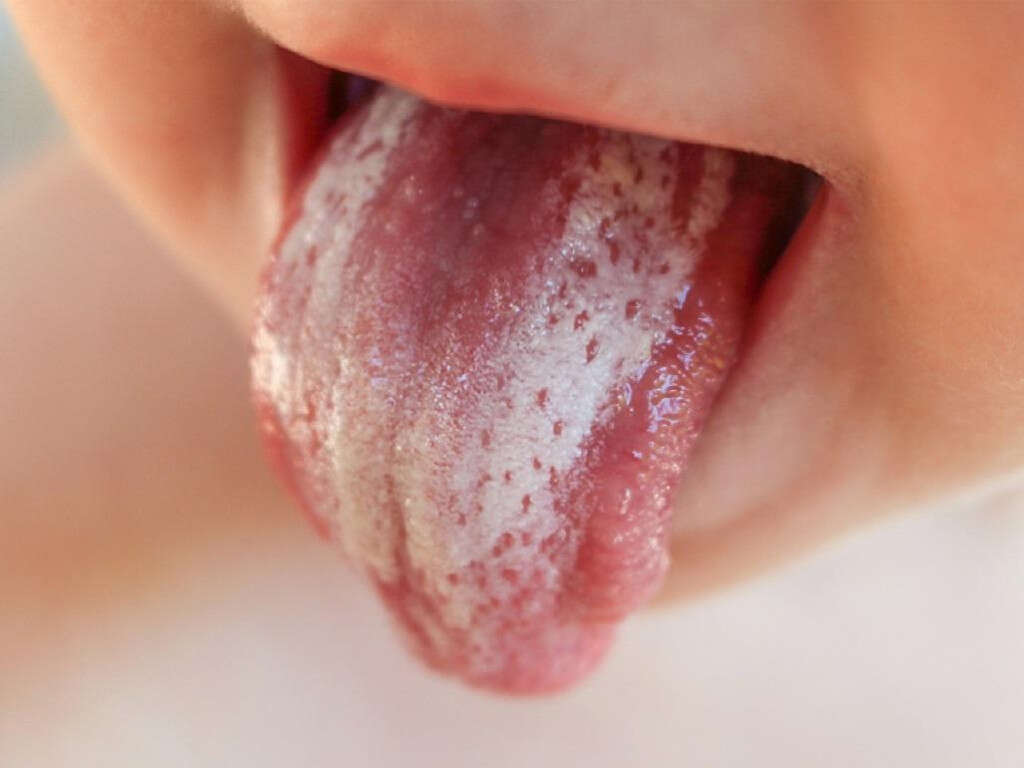
Symptom #4: White Patch on the Tongue
Red and white patches on the tongue can be a symptom of cancer. These patches usually have irregular margins and are located on the ventral or side of the tongue. It is important to note that red and white patches can also be due to a fungal infection known as thrush.
To differentiate these, patches caused by thrush usually rub off and are not related to cancer. Patients who experience this issue should seek professional medical opinion to rule out cancer or to administer early treatment if required.
Symptom #5: Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a term that refers to difficulty swallowing. Some patients with dysphagia are unaware that they are experiencing this issue. It is a sensation where there is difficult passage of solids to pass from the mouth to the stomach. This may be due to a lack of pharyngeal sensation or other inadequacies of the mechanisms involved in swallowing.
Patients with dysphagia have a higher risk of aspiration pneumonia. Patients who are undiagnosed with dysphagia often suffer from malnutrition, dehydration, and renal failure. Dysphagia is associate with inability to initiate a swallow, choking, coughing, frequent pneumonia, wet voice, nasal regurgitation, weight loss, and more.

Symptom #6: Odynophagia
Odynophagia is a term referring to pain when swallowing. The pain is usually felt in the throat and mouth and can occur with or without dysphagia. Patients often describe the sensation as an ache, uncomfortable burning feeling, or a stabbing pain that radiates to the back of the throat.
Due to the pain and discomfort, many patients suffering from odynophagia also experience inevitable appetite and weight loss. Some causes of odynophagia include upper respiratory tract infections, ulcers, inflammation of the oral cavity, infection, immune disorders, and cancers.

Symptom #7: Loss of Appetite
The loss of appetite or anorexia occurs when the affected individual has a decreased sensation of wanting to eat. In infection, appetite loss is thought to be caused by the acute phase response that is triggered by pathogens such as the lipopolysaccharides of bacterial cell walls, viral glycoproteins and more.
Like cancer, infection triggers proinflammatory cytokines that can reduce appetite. Appetite loss is a common symptom that can be seen in cancer, chronic pain, pneumonia, anxiety, celiac disease, heart failure, dehydration, dementia, and many more.

Symptom #8: Weight Loss
Weight loss occurs when there is a total reduction of body mass due to the loss of muscle, fluid, connective tissue, adipose tissue, bone mineral deposits, or other compositions of the body. Unintentional weight loss can occur in states of disease due to poor appetite or higher metabolic demand.
Other mechanisms of weight loss include impaired absorption and excess nutrient loss. In patients with cancer, significant weight loss can be attributed to cachexia where there is muscle atrophy, fatigue, and weakness. It is a risk factor for death.

Symptom #9: Lymphadenopathy
Lymphadenopathy refers to disease of the lymph nodes where they can be different in consistency, size, or number. It is a common and nonspecific sign that can be seen in various infections, cancers, autoimmune diseases, and more.
Lymphadenopathy can be classified based on the location, size, extent, or malignancy. In tongue cancer, the lymph nodes that are most frequently involved are those located in the head and neck.

Symptom #10: Numbness of the Tongue
In more severe or advanced cases of tongue cancer, patients can experience numbness or difficulty moving the tongue. There may also be changes in taste as the nerves in the tongue that control movement and taste are involved.
Due to difficulty moving the tongue, there may also be changes in speech as movement of the tongue is required in articulation. Changes in taste can lead to poor appetite and weight loss.