Thyroiditis Symptoms, Causes and More
 Article Sources
Article Sources
- 1. NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/thyroiditis/.
- 2. 'Thyroiditis.' American Thyroid Association, www.thyroid.org/thyroiditis/.
- 3. 'Thyroiditis: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.' Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15455-thyroiditis.
- 4. 'Thyroid Disease.' Womenshealth.gov, 1 Apr. 2019, www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/thyroid-disease.
- 5. 'Hashimoto's Disease.' Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 11 Feb. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hashimotos-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20351855.
- 6. Staff, Familydoctor.org Editorial. 'Thyroiditis - Symptoms and Treatment.' Familydoctor.org, 15 Oct. 2019, familydoctor.org/condition/thyroiditis/.
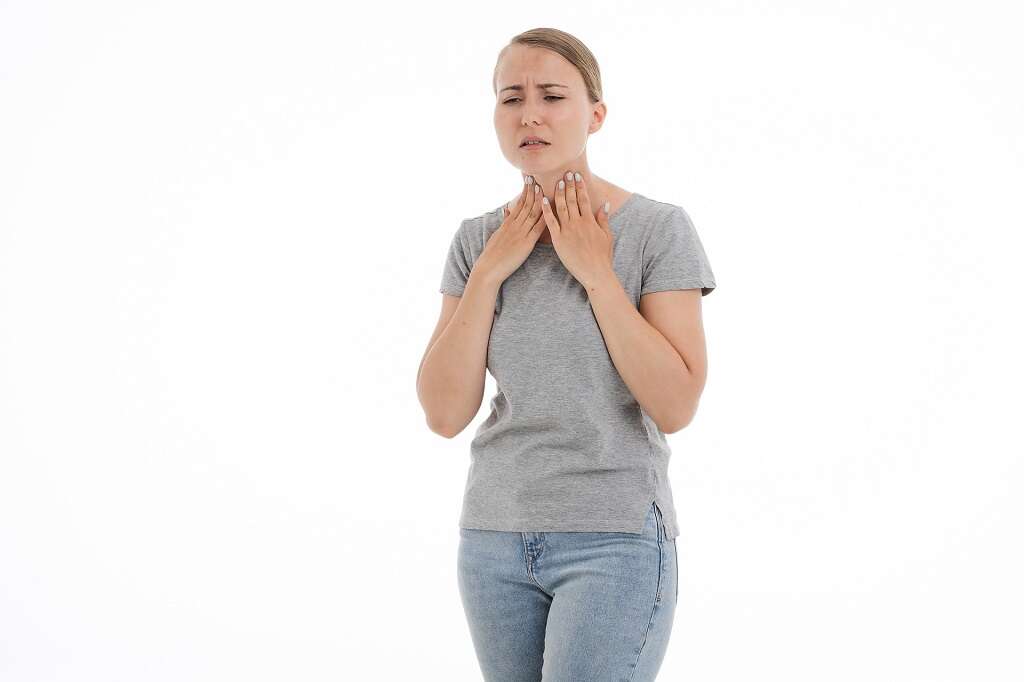
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck below the Adam's apple. As part of the body's endocrine system, it produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolic rate, controlling heart, muscle and digestive function, brain development and bone maintenance.1NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/thyroiditis/. Most people are unaware of their thyroid gland unless it swells or becomes painful.
Thyroiditis is another name for the swelling or inflammation of the thyroid gland. This condition can lead to over-(hyperthyroidism) or under-production(hypothyroidism) of thyroid hormones, causing a range of symptoms.2‘Thyroiditis.’ American Thyroid Association, www.thyroid.org/thyroiditis/.
1. Thyroiditis Symptoms
Thyroiditis may cause the thyroid gland to become enlarged and/or painful. Hyperthyroidism occurs if too much of the thyroid hormone is present in the body. The person may feel irritable, anxious, worried and nervous, and they may have trouble sleeping. They may lose weight, have increased appetite and experience profuse sweating. Their heart rate may be fast, and they may experience fatigue.
When too little thyroid hormone is present, hypothyroidism occurs. Symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, constipation and dry skin. A person with hypothyroidism may find physical exercise challenging, and they may have trouble focusing and concentrating.3‘Thyroiditis: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15455-thyroiditis.

2. Thyroiditis Causes
In some cases, thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease, where the body produces antibodies that attack the thyroid, resulting in inflammation. The reason this occurs is unknown, although autoimmune diseases often run in families.2‘Thyroiditis.’ American Thyroid Association, www.thyroid.org/thyroiditis/. Women are five times more prone to developing thyroid disease than men.4‘Thyroid Disease.’ Womenshealth.gov, 1 Apr. 2019, www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/thyroid-disease.
A viral or bacterial infection may cause the thyroid gland to become inflamed. Thyroiditis may also develop when the thyroid is damaged by radiation and medications such as interferon, lithium and amiodarone.2‘Thyroiditis.’ American Thyroid Association, www.thyroid.org/thyroiditis/.

3. Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
The most common cause of thyroiditis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, is an autoimmune disease that primarily attacks middle-aged women, but it can occur in people of any age and sex. Hashimoto's thyroiditis progresses slowly, damaging the thyroid and lowering the levels of thyroid hormone in the blood.
Left untreated, this condition can lead to heart problems, mental health issues, goiters and birth defects. People with Hashimoto's thyroiditis can take synthetic thyroid replacement hormone pills daily to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels and reduce symptoms.5‘Hashimoto’s Disease.’ Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 11 Feb. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/hashimotos-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20351855.

4. Subacute and Acute Thyroiditis
Subacute thyroiditis, also called deQuervain's thyroiditis is thought to be caused by a virus, such as the mumps or flu. This condition causes thyroid pain along with symptoms of hyperthyroidism, which are later replaced by hypothyroid symptoms. All symptoms normally resolve within a few months.
Acute thyroiditis develops as a result of a bacterial infection. This type of infection is painful, associated with a fever, and progresses rapidly. It can affect children and adults, but it is more common among children. Treating the underlying infection normally alleviates the thyroiditis symptoms.6Staff, Familydoctor.org Editorial. ‘Thyroiditis - Symptoms and Treatment.’ Familydoctor.org, 15 Oct. 2019, familydoctor.org/condition/thyroiditis/.

5. Silent Thyroiditis
Silent thyroiditis, or painless thyroiditis, is another autoimmune form of thyroiditis. It's the second-most-common form of thyroiditis, and it frequently affects women.3‘Thyroiditis: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15455-thyroiditis.
A person with this type of thyroiditis experiences hyperthyroid symptoms for one to three months followed by hypothyroid symptoms that last nine to 12 months. In most cases, normal thyroid function returns within 12 to 18 months from the onset of symptoms. Hypothyroidism may be permanent in 20 percent of cases and can be treated with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement medication.2‘Thyroiditis.’ American Thyroid Association, www.thyroid.org/thyroiditis/.

6. Postpartum Thyroiditis
Postpartum thyroiditis impacts women who have given birth within the previous months. A form of autoimmune thyroiditis, its symptoms and progression are similar to silent thyroiditis. Most women first experience hyperthyroid symptoms, followed later by hypothyroid symptoms. However, not every woman with postpartum thyroiditis will go through both these phases.
In most women, thyroid function returns to normal within 12 months of the birth, although low thyroid hormone levels can sometimes be permanent. Treatment with daily synthetic thyroid hormone replacement pills may be necessary.6Staff, Familydoctor.org Editorial. ‘Thyroiditis - Symptoms and Treatment.’ Familydoctor.org, 15 Oct. 2019, familydoctor.org/condition/thyroiditis/.

7. Radiation-Induced Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis may develop in people who receive radiation therapy to treat head and neck cancers. It may also affect those whose hyperthyroidism is treated with radioactive iodine. This condition can develop years after treatments have been completed.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism may result from these treatments. Hyperthyroid symptoms usually subside, but hypothyroid symptoms are sometimes permanent, requiring thyroid hormone replacement treatment to maintain adequate levels of thyroid hormone levels in the body.2‘Thyroiditis.’ American Thyroid Association, www.thyroid.org/thyroiditis/.,6Staff, Familydoctor.org Editorial. ‘Thyroiditis - Symptoms and Treatment.’ Familydoctor.org, 15 Oct. 2019, familydoctor.org/condition/thyroiditis/.
8. Drug-Induced Thyroiditis
Certain medications may cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism in some people. These medications include amiodarone, interferons, lithium, and cytokines. This type of thyroiditis may cause pain in the thyroid region, which can be mitigated with over-the-counter pain medications or prescription steroids.
Symptoms are usually short lived and may get better after you stop taking the medicine. Only a small percentage of people who take these medications experience drug-induced thyroiditis.1NHS Choices, NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/thyroiditis/.,3‘Thyroiditis: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15455-thyroiditis.

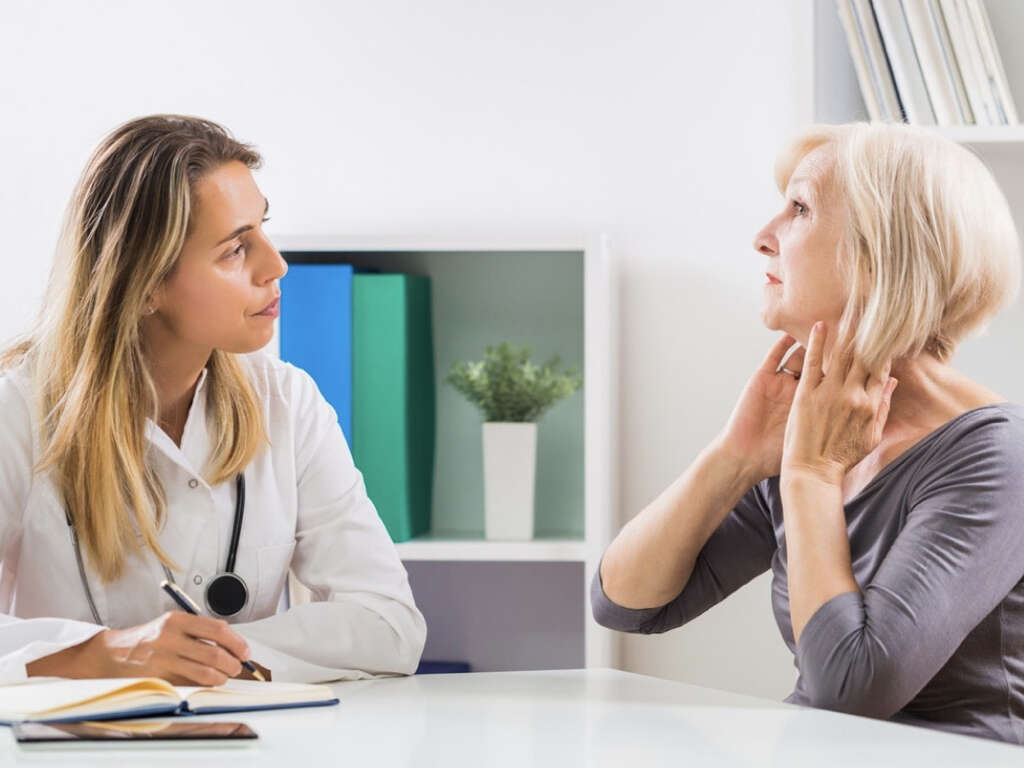
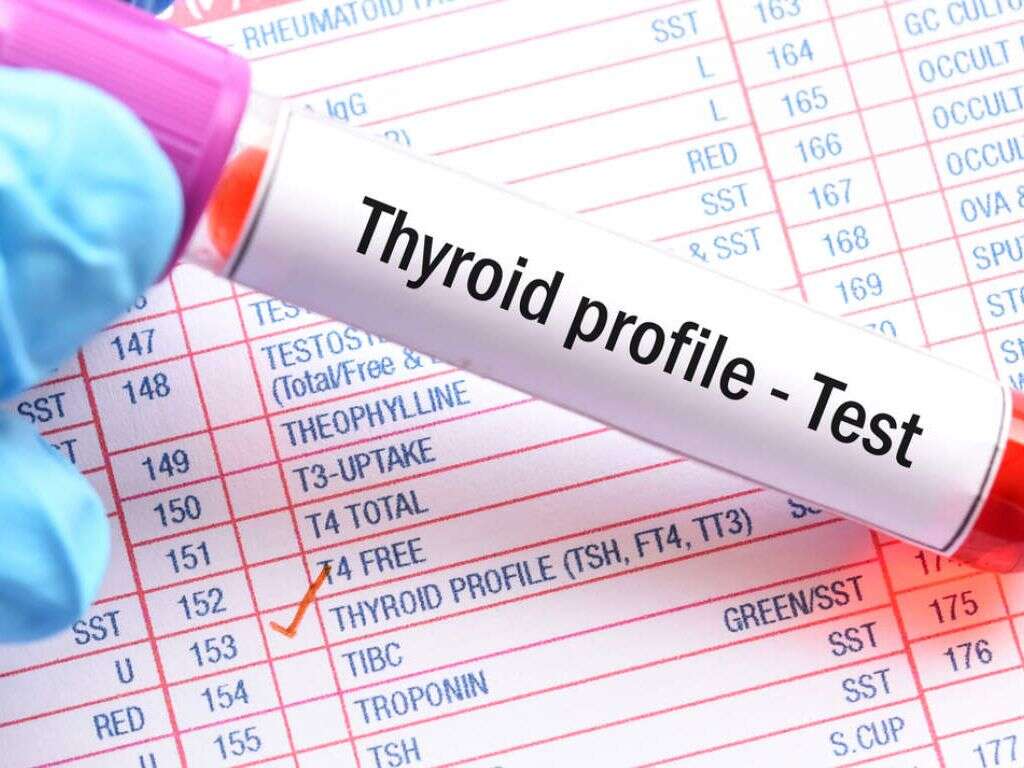
9. Diagnosing Thyroiditis
Health care providers diagnose thyroiditis through several blood tests. Thyroid function tests measure the level of thyroid hormones in the blood. Other blood tests detect the presence of inflammation and measure the number of thyroid antibodies in the blood.
An ultrasound of the thyroid may also be helpful in identifying nodules, the density of the gland and changes in blood flow. Radioactive iodine uptake indicates the amount of iodine the thyroid absorbs.3‘Thyroiditis: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15455-thyroiditis.

10. Treating Thyroiditis
In some cases, thyroiditis resolves with no treatment or by treating the underlying infection. Over-the-counter pain medications can help alleviate temporary discomfort when the thyroid gland is painful. For those experiencing profuse sweating, palpitations, anxiety, and tremors, beta blockers are helpful.
Thyroid replacement therapy is necessary for those with hypothyroidism. In some cases, this therapy is only needed temporarily. People with Hashimoto's thyroiditis often must continue this therapy throughout their lives.3‘Thyroiditis: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment.’ Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15455-thyroiditis.